|
Essential Thrombocythemia
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a rare chronic blood cancer (myeloproliferative neoplasm) characterised by the thrombocythemia, overproduction of platelets (thrombocytes) by megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. It may, albeit rarely, develop into acute myeloid leukemia or myelofibrosis. It is a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm (blood cancers) wherein the body makes too many White blood cell, white or red blood cells, or platelets). Signs and symptoms Most people with essential thrombocythemia are asymptomatic, without symptoms at the time of diagnosis, which is usually made after noting an elevated platelet level on a routine complete blood count (CBC). The most common symptoms are bleeding (due to dysfunctional platelets), thrombosis, blood clots (e.g., deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism), fatigue, headache, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, visual disturbances, dizziness, Syncope (medicine), fainting, and numbness in the extremities; the most common signs are leukocytos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocythemia
Thrombocythemia is a condition of high platelet (thrombocyte) count in the blood. Normal count is in the range of 150x109 to 450x109 platelets per liter of blood, but investigation is typically only considered if the upper limit exceeds 750x109/L. When the cause is unknown, the term thrombocythemia is used, as either primary thrombocythemia or essential thrombocythemia. The condition arises from a fault in the bone marrow cells leading to over-production of platelets but the cause of the fault is unknown, and this type is not common. When the cause is known such as another disorder or disease, the term thrombocytosis is preferred, as either secondary or reactive thrombocytosis. Reactive thrombocytosis is the most common type and though it can often have no symptoms it can sometimes predispose to thrombosis. In contrast, thrombocytopenia refers to abnormally low blood platelet numbers in the blood. Signs and symptoms High platelet counts do not necessarily signal any clinical pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenomegaly
Splenomegaly is an enlargement of the spleen. The spleen usually lies in the left upper quadrant (LUQ) of the human abdomen. Splenomegaly is one of the four cardinal signs of ''hypersplenism'' which include: some reduction in number of circulating blood cells affecting granulocytes, erythrocytes or platelets in any combination; a compensatory proliferative response in the bone marrow; and the potential for correction of these abnormalities by splenectomy. Splenomegaly is usually associated with increased workload (such as in hemolytic anemias), which suggests that it is a response to hyperfunction. It is therefore not surprising that splenomegaly is associated with any disease process that involves abnormal red blood cells being destroyed in the spleen. Other common causes include congestion due to portal hypertension and infiltration by leukemias and lymphomas. Thus, the finding of an enlarged spleen, along with caput medusae, is an important sign of portal hypertension. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Count
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm that are derived from the megakaryocytes of the bone marrow or lung, which then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site of interrupted endothelium. They gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ER Retention
ER retention refers to proteins that are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, after folding; these are known as ER resident proteins. Protein localization to the ER often depends on certain sequences of amino acids located at the N terminus or C terminus. These sequences are known as signal peptides, molecular signatures, or sorting signals. The classical ER retention signal is the C-terminal KDEL sequence for lumen bound proteins and KKXX (signal sequence is located in cytoplasm) for transmembrane localization. These signals allow for retrieval from the Golgi apparatus by ER retention receptors, effectively maintaining the protein in the ER. Other mechanisms for ER retention are being studied but are not as well characterized as signal retention. ER retention receptors proteins * KDELR1 * KDELR2 * KDELR3 See also * KKXX (amino acid sequence) * KDEL (amino acid sequence) * Signal peptide *Protein targeting :''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
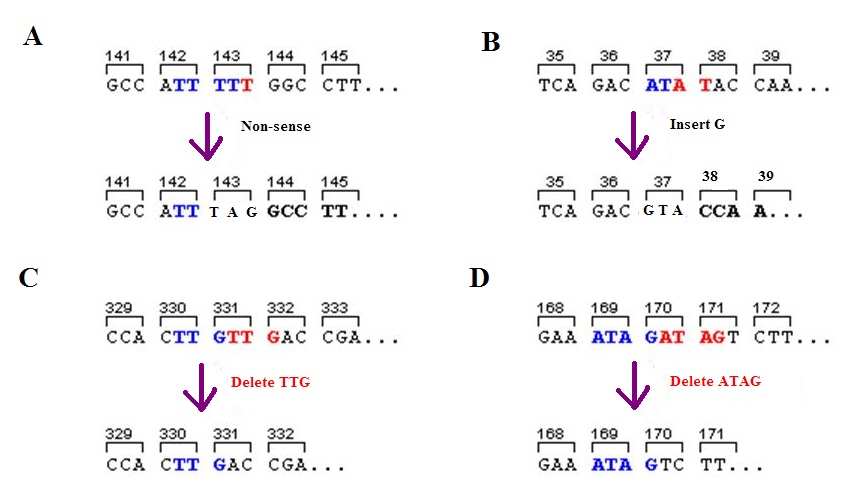
Frameshift Mutation
A frameshift mutation (also called a framing error or a reading frame shift) is a genetic mutation caused by indels ( insertions or deletions) of a number of nucleotides in a DNA sequence that is not divisible by three. Due to the triplet nature of gene expression by codons, the insertion or deletion can change the reading frame (the grouping of the codons), resulting in a completely different translation from the original. The earlier in the sequence the deletion or insertion occurs, the more altered the protein. A frameshift mutation is not the same as a single-nucleotide polymorphism in which a nucleotide is replaced, rather than inserted or deleted. A frameshift mutation will in general cause the reading of the codons after the mutation to code for different amino acids. The frameshift mutation will also alter the first stop codon ("UAA", "UGA" or "UAG") encountered in the sequence. The polypeptide being created could be abnormally short or abnormally long, and will most l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloproliferative Disease
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are a group of rare blood cancers in which excess red blood cells, white blood cells or platelets are produced in the bone marrow. ''Myelo'' refers to the bone marrow, ''proliferative'' describes the rapid growth of blood cells and ''neoplasm'' describes that growth as abnormal and uncontrolled. The overproduction of blood cells is often associated with a somatic mutation, for example in the JAK2, CALR, TET2, and MPL gene markers. In rare cases, some MPNs such as primary myelofibrosis may accelerate and turn into acute myeloid leukemia. Classification MPNs are classified as blood cancers by most institutions and organizations. In MPNs, the neoplasm (abnormal growth) starts out as benign and can later become malignant. As of 2016, the World Health Organization lists the following subcategories of MPNs: * Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) * Chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) * Polycythemia vera (PV) * Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) ** PM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombopoietin Receptor
The thrombopoietin receptor also known as the myeloproliferative leukemia protein or CD110 (Cluster of Differentiation 110) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MPL (myeloproliferative leukemia virus) oncogene. Discovery In 1990 an oncogene, v-mpl, was identified from the murine myeloproliferative leukemia virus that was capable of immortalizing bone marrow hematopoietic cells from different lineages. In 1992 the human homologue, named, c-mpl, was cloned. Sequence data revealed that c-mpl encoded a protein that was homologous with members of the hematopoietic receptor superfamily. Presence of anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotides of c-mpl inhibited megakaryocyte colony formation. Function The ligand for c-mpl, thrombopoietin, was cloned in 1994. Thrombopoietin was shown to be the major regulator of megakaryocytopoiesis and platelet formation. The protein encoded by the c-mpl gene, CD110, is a 635 amino acid transmembrane domain, with two extracellular cytokine recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Kinase 2
Janus kinase 2 (commonly called JAK2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a member of the Janus kinase family and has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family (e.g. interferon receptors), the GM-CSF receptor family ( IL-3R, IL-5R and GM-CSF-R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g., IL-6R), and the single chain receptors (e.g. Epo-R, Tpo-R, GH-R, PRL-R). The distinguishing feature between janus kinase 2 and other JAK kinases is the lack of Src homology binding domains ( SH2/ SH3) and the presence of up to seven JAK homology domains (JH1-JH7). Nonetheless the terminal JH domains retain a high level of homology to tyrosine kinase domains. An interesting note is that only one of these carboxy-terminal JH domains retains full kinase function (JH1) while the other (JH2), previously thought to have no kinase functionality and accordingly termed a pseudokinase domain, has since been found to be catalytically active, albeit at only 10% that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calreticulin
Calreticulin also known as calregulin, CRP55, CaBP3, calsequestrin-like protein, and endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60 (ERp60) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CALR'' gene. Calreticulin is a multifunctional soluble protein that binds Ca2+ ions (a second messenger in signal transduction), rendering it inactive. The Ca2+ is bound with low affinity, but high capacity, and can be released on a signal (see inositol trisphosphate). Calreticulin is located in storage compartments associated with the endoplasmic reticulum and is considered an ER resident protein. The term "Mobilferrin" is considered to be the same as calreticulin by some sources. Function Calreticulin binds to misfolded proteins and prevents them from being exported from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. A similar quality-control molecular chaperone, calnexin, performs the same service for soluble proteins as does calreticulin, however it is a membrane-bound protein. Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janus Kinase
Janus kinase (JAK) is a family of intracellular, non-receptor tyrosine kinases that transduce cytokine-mediated signals via the JAK-STAT pathway. They were initially named "just another kinase" 1 and 2 (since they were just two of many discoveries in a PCR-based screen of kinases), but were ultimately published as "Janus kinase". The name is taken from the two-faced Roman god of beginnings, endings and duality, Janus, because the JAKs possess two near-identical phosphate-transferring domains. One domain exhibits the kinase activity, while the other negatively regulates the kinase activity of the first. Family The four JAK family members are: * Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) * Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) * Janus kinase 3 (JAK3) * Tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) Transgenic mice that do not express JAK1 have defective responses to some cytokines, such as interferon-gamma. JAK1 and JAK2 are involved in type II interferon (interferon-gamma) signalling, whereas JAK1 and TYK2 are involved in type I int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. This transesterification produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAK2
Janus kinase 2 (commonly called JAK2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a member of the Janus kinase family and has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family (e.g. interferon receptors), the GM-CSF receptor family (IL-3R, IL-5R and GM-CSF-R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g., IL-6R), and the single chain receptors (e.g. Epo-R, Tpo-R, GH-R, PRL-R). The distinguishing feature between janus kinase 2 and other JAK kinases is the lack of Src homology binding domains ( SH2/ SH3) and the presence of up to seven JAK homology domains (JH1-JH7). Nonetheless the terminal JH domains retain a high level of homology to tyrosine kinase domains. An interesting note is that only one of these carboxy-terminal JH domains retains full kinase function (JH1) while the other (JH2), previously thought to have no kinase functionality and accordingly termed a pseudokinase domain, has since been found to be catalytically active, albeit at only 10% that of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)