|
Ernest, Margrave Of Austria
Ernest (german: Ernst, 1027 – 10 June 1075), known as Ernest the Brave (''Ernst der Tapfere''), was the Margrave of Austria from 1055 to his death in 1075. He was a member of the House of Babenberg.Lingelbach 1913, p. 90. Biography He was born to Margrave Adalbert of Austria and his wife Frozza Orseolo, daughter of Doge Otto Orseolo of Venice. He increased the territory of his margraviate by amalgamating the Bohemian and Hungarian frontier marches up to the Thaya, March and Leitha rivers in what is today Lower Austria. In his time, the colonisation of the remote '' Waldviertel'' region was begun by his ministeriales, the Kuenring knights. Ernest received his epithet due to his fighting against King Béla I of Hungary and his son Géza I on behalf of their rival Solomon according to the chronicler Lambert of Hersfeld. In the commencing Investiture Controversy, he sided with King Henry IV of Germany and battled against the Saxons, dying at the Battle of Langensalza. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Langensalza (1075)
The First Battle of Langensalza was fought on 9 June 1075 between forces of King Henry IV of Germany and several rebellious Saxon noblemen on the River Unstrut near Langensalza in Thuringia. The battle was a complete success for Henry, resulting in the subjugation of the Saxons shortly before the Investiture Controversy commenced. In Germany the battle is known as the ''Schlacht bei Homburg an der Unstrut'', after a nearby ''Kaiserpfalz'' and monastery. Background The Salian king Henry IV had inherited the quarrels with the Saxons from his father Emperor Henry III, whose long and costly sojournments at the Imperial Palace of Goslar had annoyed the local nobles. From the start of his reign in 1065, 15-year-old Henry IV suffered numerous setbacks enforcing his Imperial authority in Saxony after the regency of his mother Agnes of Poitou. Attempts to restore the rights over the Harz forests were not received well by the Saxon freedmen, and efforts to extend the crownlands in general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
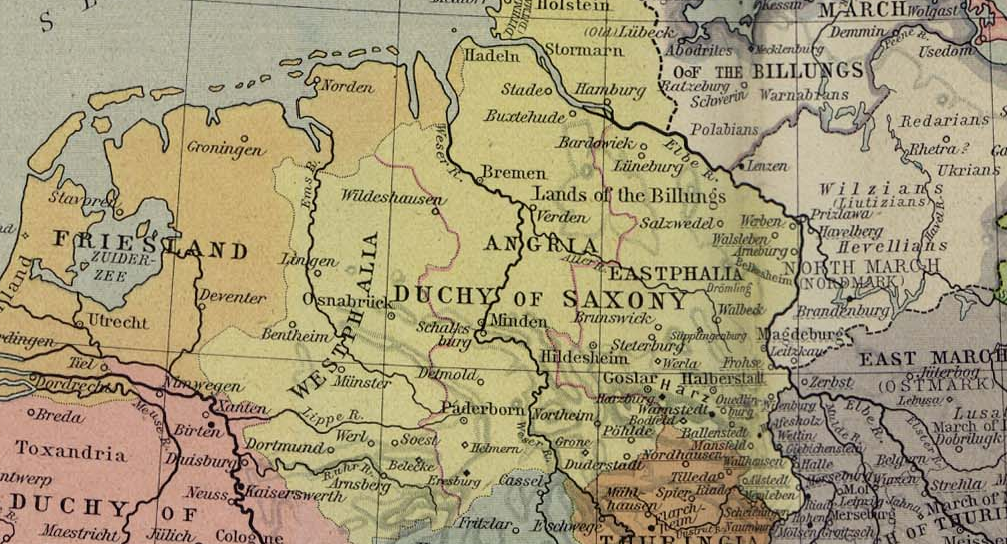
Lower Austria
Lower Austria (german: Niederösterreich; Austro-Bavarian: ''Niedaöstareich'', ''Niedaestareich'') is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Since 1986, the capital of Lower Austria has been Sankt Pölten, replacing Vienna which became a separate state in 1921. With a land area of and a population of 1.685 million people, Lower Austria is the second most populous state in Austria (after Vienna). Other large cities are Amstetten, Klosterneuburg, Krems an der Donau, Stockerau and Wiener Neustadt. Geography With a land area of situated east of Upper Austria, Lower Austria is the country's largest state. Lower Austria derives its name from its downriver location on the Enns River which flows from the west to the east. Lower Austria has an international border, long, with the Czech Republic ( South Bohemia and South Moravia Regions) and Slovakia ( Bratislava and Trnava Regions). The state has the second longest external border ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedi I, Margrave Of The Saxon Ostmark
Dedi (or Dedo) (1004 – October 1075) was the Margrave of the Saxon Ostmark (also called Lower Lusatia) from 1046 and a claimant for the title of Margrave of Meissen from 1069. He was the second son of Dietrich II of Wettin and Matilda, daughter of Eckard I of Meissen. Life Dedi inherited the Ostmark from its last dynast, the childless Odo II, because he had married his sister, Oda (died before 1068). Oda was herself the widow of William III of Weimar and mother of William and Otto, margraves of Meissen successively. When Otto his stepson died, Dedi married his widow, Adela of Louvain, and in her name claimed the Meissen March. Otto died in 1067 and was succeeded by Egbert I, but Dedi married his widow in 1069 and rebelled. In claiming the Meissen March through his wife, Dedi was challenging the royal prerogative in the marches. With him in his revolt was Albert II of Ballenstedt, who raided the monastery of Nienburg, a foundation of the family of Dedi's first wife. Adela o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Wettin
The House of Wettin () is a dynasty of German kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts that once ruled territories in the present-day German states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany. The family divided into two ruling branches in 1485 by the Treaty of Leipzig: the Ernestine and Albertine branches. The older Ernestine branch played a key role during the Protestant Reformation. Many ruling monarchs outside Germany were later tied to its cadet branch, the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. The Albertine branch, while l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxon Rebellion
The Saxon Rebellion or Rebellion of the Saxons (german: Sachsenkrieg), also commonly called the Saxon Uprising (not to be confused with the Saxon Wars, also called the Saxon Uprising), refers to the struggle between the Salian dynasty ruling the Holy Roman Empire and the rebel Saxons during the reign of Henry IV. The conflict reached its climax in the period from summer 1073 until the end of 1075, in a rebellion that involved several clashes of arms. Origins Undercurrents of discord between the Salian royal family and the Saxons already existed under Henry's father, Emperor Henry III. This may have been primarily due to his Rhenish Franconian origin as well as his numerous stays in the Imperial Palace of Goslar, which were associated with a disproportionately high economic burden on the surrounding population. With the accession of Henry IV in 1065 this conflict intensified, as Henry made demands on numerous Imperial domains (''Reichsgüter'') in the centre of the Saxon heartla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV (german: Heinrich IV; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son of Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor—the second monarch of the Salian dynasty—and Agnes of Poitou. After his father's death on 5 October 1056, Henry was placed under his mother's guardianship. She made grants to German aristocrats to secure their support. Unlike her late husband, she could not control the election of the popes, thus the idea of the "liberty of the Church" strengthened during her rule. Taking advantage of her weakness, Archbishop Anno II of Cologne kidnapped Henry in April 1062. He administered Germany until Henry came of age in 1065. Henry endeavoured to recover the royal estates that had been lost during his minority. He employed low-ranking officials to carry out his new policies, causing discontent in Saxony and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, also called Investiture Contest ( German: ''Investiturstreit''; ), was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops ( investiture) and abbots of monasteries and the pope himself. A series of popes in the 11th and 12th centuries undercut the power of the Holy Roman Emperor and other European monarchies, and the controversy led to nearly 50 years of conflict. It began as a power struggle between Pope Gregory VII and Henry IV (then King, later Holy Roman Emperor) in 1076. The conflict ended in 1122, when Pope Callixtus II and Emperor Henry V agreed on the Concordat of Worms. The agreement required bishops to swear an oath of fealty to the secular monarch, who held authority "by the lance" but left selection to the church. It affirmed the right of the church to invest bishops with sacred authority, symbolized by a ring and staff. In Germany (but not Italy and Burgundy), the Emper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Of Hersfeld
Lambert of Hersfeld (also called Lampert; – 1082/85) was a medieval chronicler. His work represents a major source for the history of the German kingdom of Henry IV and the incipient Investiture Controversy in the eleventh century. Life What little is known of his life is revealed in scattered details from his own historical writings. Probably a Franconian by birth, of good family, he prepared for an ecclesiastical career at the cathedral school in Bamberg, where he received tuition by Anno of Steusslingen, the later Archbishop of Cologne. On 15 March 1058 Lambert entered the Benedictine abbey of Hersfeld as a monk. On September 16, he was also ordained as a priest in Aschaffenburg and therefore sometimes called Lampert of Aschaffenburg. After his elevation to the priesthood, he made a pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Back in Hersfeld in October 1059, Lambert worked in the cloister library and taught at the monastery school. In 1071 he visited the Benedictine abbeys of Siegburg and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon, King Of Hungary
Solomon, also Salomon ( hu, Salamon; 1053–1087) was King of Hungary from 1063. Being the elder son of Andrew I, he was crowned king in his father's lifetime in 1057 or 1058. However, he was forced to flee from Hungary after his uncle, Béla I, dethroned Andrew in 1060. Assisted by German troops, Solomon returned and was again crowned king in 1063. On this occasion he married Judith, sister of Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor. In the following year he reached an agreement with his cousins, the three sons of Béla I. Géza, Ladislaus and Lampert acknowledged Solomon's rule, but in exchange received one-third of the kingdom as a separate duchy. In the following years, Solomon and his cousins jointly fought against the Czechs, the Cumans and other enemies of the kingdom. Their relationship deteriorated in the early 1070s and Géza rebelled against him. Solomon could only maintain his rule in a small zone along the western frontiers of Hungary after his defeat in the Battle of Mogyor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Géza I Of Hungary
Géza I (; hu, I. Géza; 104025 April 1077) was King of Hungary from 1074 until his death. He was the eldest son of King Béla I. His baptismal name was Magnus. With German assistance, Géza's cousin Solomon acquired the crown when his father died in 1063, forcing Géza to leave Hungary. Géza returned with Polish reinforcements and signed a treaty with Solomon in early 1064. In the treaty, Géza and his brother Ladislaus acknowledged the rule of Solomon, who granted them their father's former duchy, which encompassed one-third of the Kingdom of Hungary. Géza closely cooperated with Solomon, but their relationship became tense from 1071. The king invaded the duchy in February 1074 and defeated Géza in a battle. However, Géza was victorious at the decisive battle of Mogyoród on 14 March 1074. He soon acquired the throne, although Solomon maintained his rule in the regions of Moson and Pressburg (present-day Bratislava, Slovakia) for years. Géza initiated peace negotia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béla I Of Hungary
Béla I the Boxer or the Wisent ( hu, I. Bajnok or Bölény Béla, sk, Belo I.; – 11 September 1063) was King of Hungary from 1060 until his death. He descended from a younger branch of the Árpád dynasty. Béla's baptismal name was Adalbert. He left Hungary in 1031, together with his brothers, Levente and Andrew, after the execution of their father, Vazul. Béla settled in Poland and married Richeza (or Adelaide), daughter of Polish king Mieszko II Lambert. He returned to his homeland upon the invitation of his brother Andrew, who had in the meantime been crowned King of Hungary. Andrew assigned the administration of the so-called '' ducatus'' or "duchy", which encompassed around one-third of the territory of the Kingdom of Hungary, to Béla. The two brothers' relationship became tense when Andrew had his own son, Solomon, crowned king, and forced Béla to publicly confirm Solomon's right to the throne in 1057 or 1058. Béla, assisted by his Polish relatives, rebe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epithet
An epithet (, ), also byname, is a descriptive term (word or phrase) known for accompanying or occurring in place of a name and having entered common usage. It has various shades of meaning when applied to seemingly real or fictitious people, divinities, objects, and binomial nomenclature. It can also be a descriptive title: for example, Pallas Athena, Phoebus Apollo, Alfred the Great, Suleiman the Magnificent, and Władysław I the Elbow-high. Many English monarchs have traditional epithets: some of the best known are Edward the Confessor, William the Conqueror, Richard the Lionheart, Æthelred the Unready, John Lackland and Bloody Mary. The word ''epithet'' can also refer to an abusive, defamatory, or derogatory phrase. This use as a euphemism is criticized by Martin Manser and other proponents of linguistic prescription. H. W. Fowler complained that "epithet is suffering a vulgarization that is giving it an abusive imputation." Linguistics Epithets are sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

