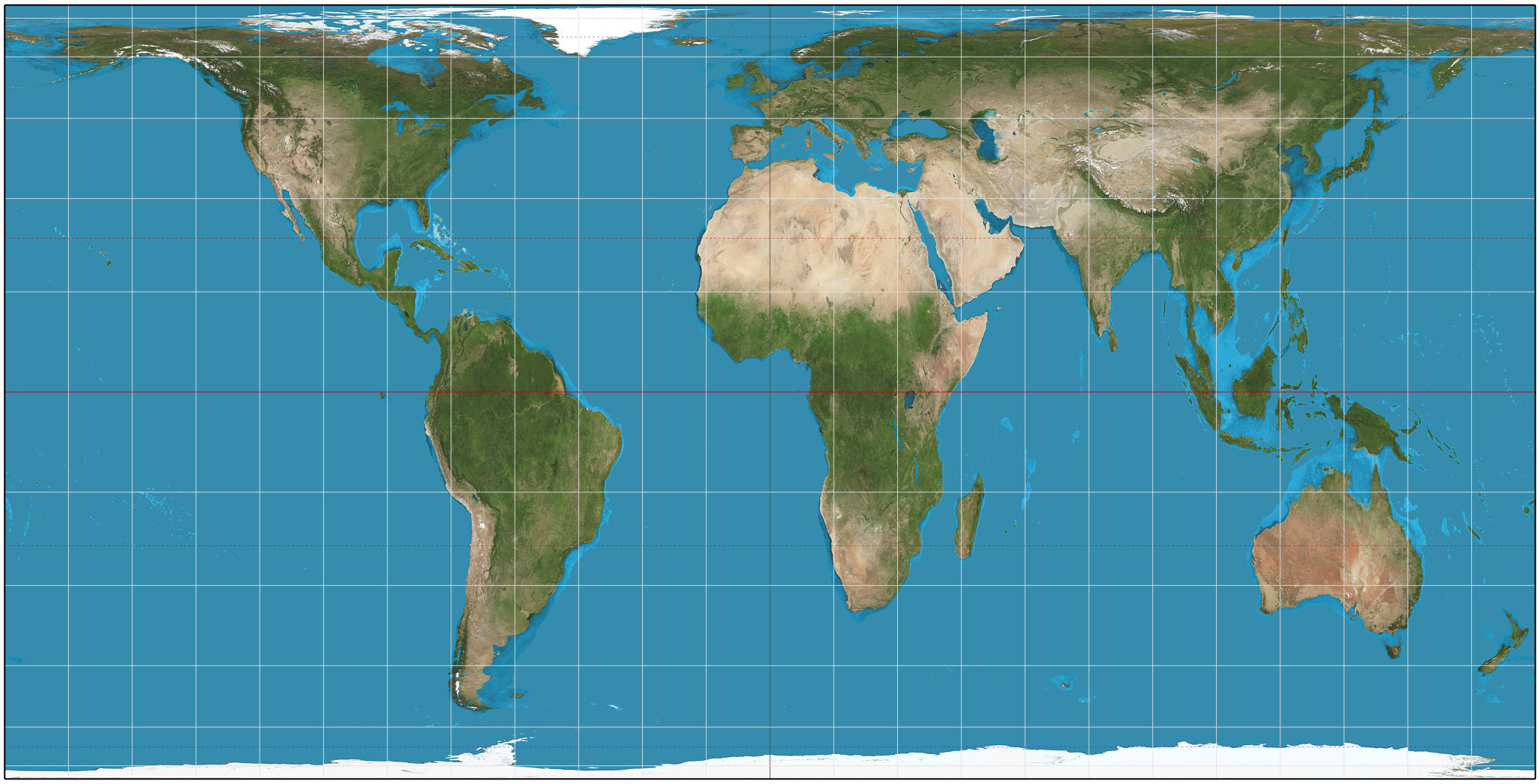
|
Equal-area Map
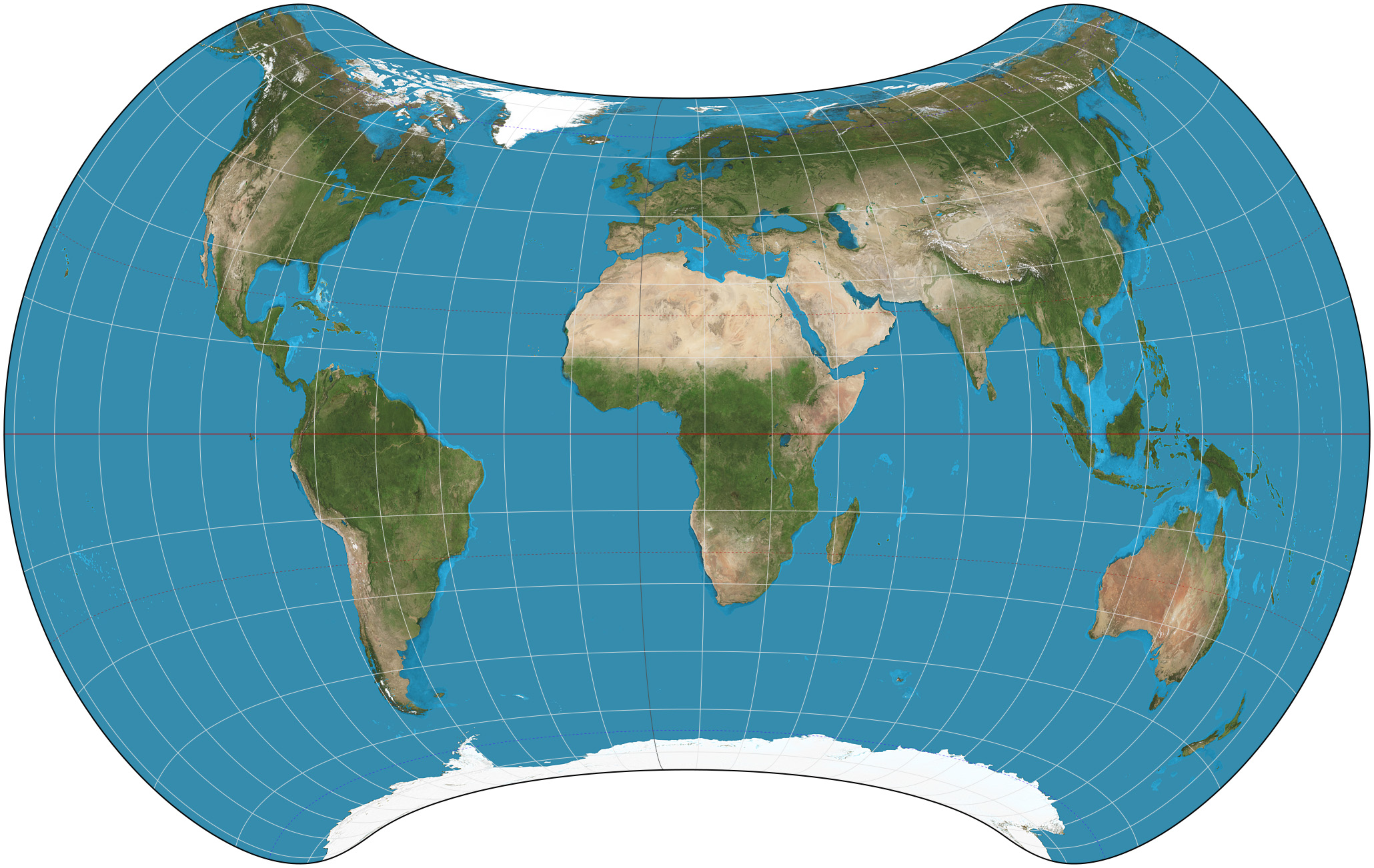
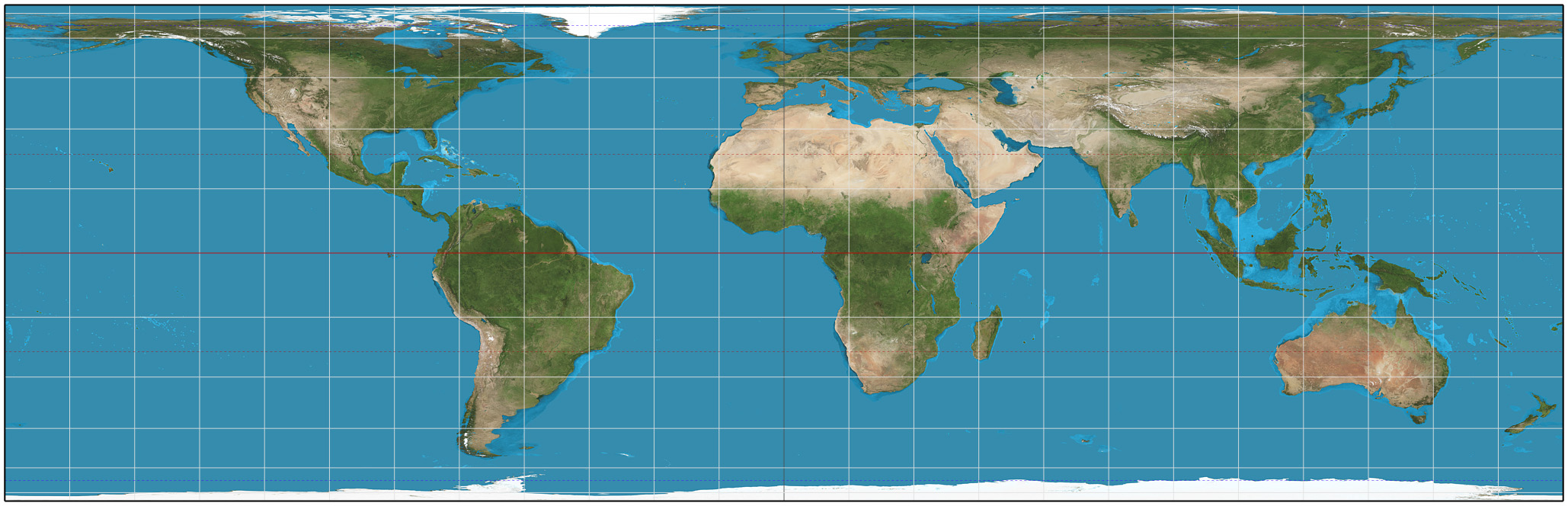
In map projection, equal-area maps preserve area measure, generally distorting shapes in order to do that. Equal-area maps are also called equivalent or authalic. An equal-area map projection cannot be conformal, nor can a conformal map projection be equal-area. Several equivalent projections were developed in an attempt to minimize the distortion of countries and continents of planet Earth, keeping the area constant. Equivalent projections are widely used for thematic maps showing scenario distribution such as population, farmland distribution, forested areas, etc. Applications Equal area representation implies that a region of interest in a particular portion of the map will share the same proportion of area as in any other part of the map. Statistical grid The term "statistical grid" refers to a discrete grid (global or local) of an equal-area surface representation, used for data visualization, geocode and statistical spatial analysis.IBGE (2016), “Grade Estatíst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollweide Projection SW
Mollweide may refer to: * Karl Mollweide, mathematician (1774-1825). :*Mollweide projection 400px, Mollweide projection of the world 400px, The Mollweide projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation The Mollweide projection is an equal-area, pseudocylindrical map projection generally used for maps of the world or celestial sph ..., a pseudocylindrical map projection. :* Mollweide Glacier, a glacier the Victoria region of Antarctica. :* Mollweide's formula, a mathematical equation. {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckert VI Projection
The Eckert VI projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. The length of polar line is half that of the equator, and lines of longitude are sinusoids. It was first described by Max Eckert in 1906 as one of a series of three pairs of pseudocylindrical projections. In each pair, the meridians have the same shape, and the odd-numbered projection has equally spaced parallels, whereas the even-numbered projection has parallels spaced to preserve area. The pair to Eckert VI is the Eckert V projection. See also * List of map projections *Eckert II projection The Eckert II projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. In the equatorial aspect (where the equator is shown as the horizontal axis) the network of longitude and latitude lines consists solely of straight lines, and the outer ... * Eckert IV projection References External links Eckert VI projection at Mathworld Map projections Equal-area projections {{Cartography-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
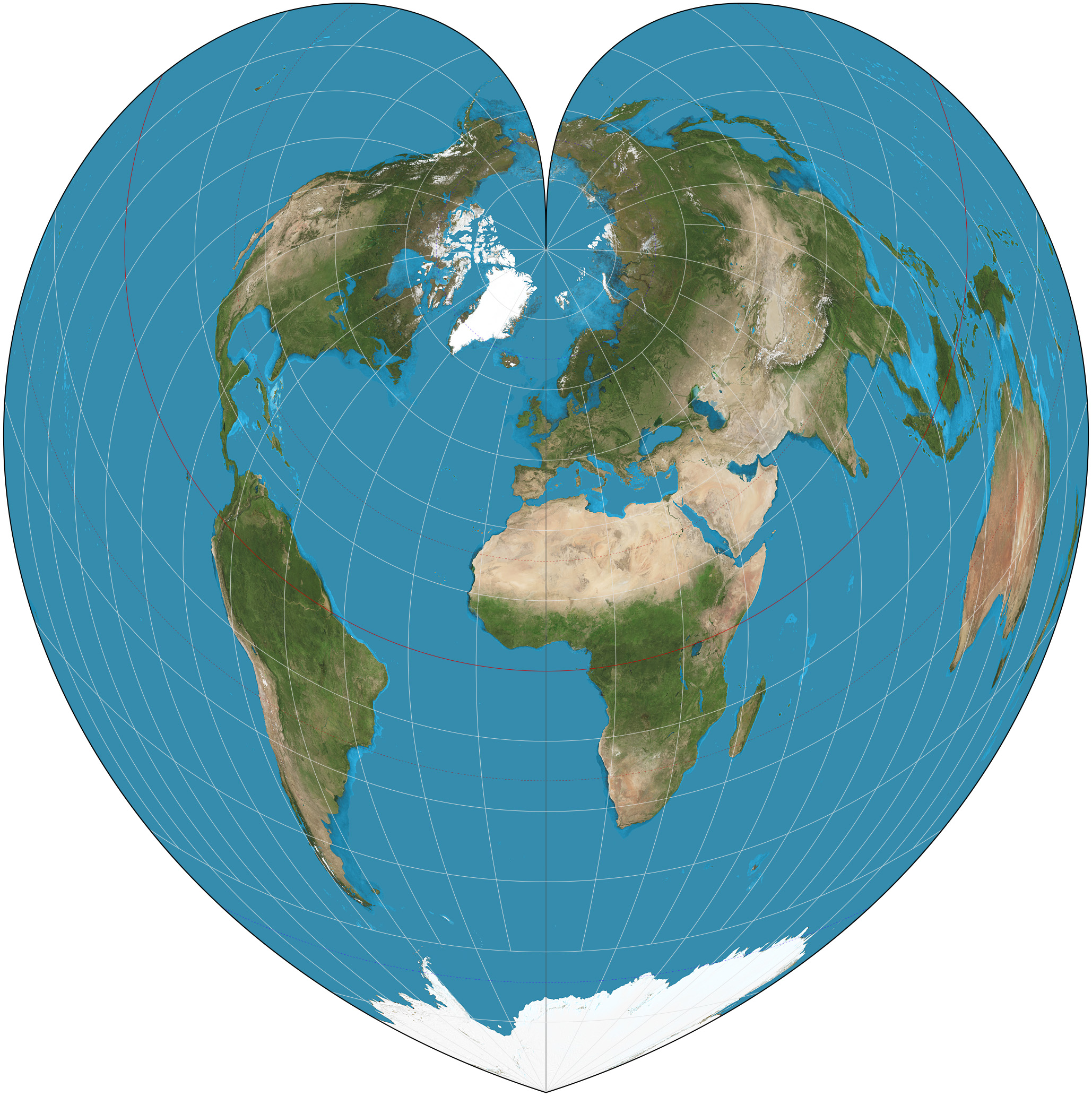
Werner Projection
The Werner projection is a pseudoconic equal-area map projection sometimes called the Stab-Werner or Stabius-Werner projection. Like other heart-shaped projections, it is also categorized as cordiform. ''Stab-Werner'' refers to two originators: Johannes Werner (1466–1528), a parish priest in Nuremberg, refined and promoted this projection that had been developed earlier by Johannes Stabius (Stab) of Vienna around 1500. The projection is a limiting form of the Bonne projection, having its standard parallel at one of the poles (90°N/S).. Distances along each parallel and along the central meridian are correct, as are all distances from the north pole. See also *List of map projections This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections, there can be no comprehensive list. Table of projections * ... References External links * *. {{Map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobler Hyperelliptical Projection
The Tobler hyperelliptical projection is a family of Map projection#Equal-area, equal-area Map projection#Pseudocylindrical, pseudocylindrical projections that may be used for world maps. Waldo R. Tobler introduced the construction in 1973 as the ''hyperelliptical'' projection, now usually known as the Tobler hyperelliptical projection. Overview As with any pseudocylindrical projection, in the projection’s normal aspect, the circle of latitude, parallels of latitude are parallel, straight lines. Their spacing is calculated to provide the equal-area property. The projection blends the cylindrical equal-area projection, which has straight, vertical Meridian (geography), meridians, with meridians that follow a particular kind of curve known as ''superellipses'' or ''Gabriel Lamé, Lamé curves'' or sometimes as ''hyperellipses''. A hyperellipse is described by x^k + y^k = \gamma^k, where \gamma and k are free parameters. Tobler's hyperelliptical projection is given as: :\begin &x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geodesic Grid
A geodesic grid is a spatial grid based on a geodesic polyhedron or Goldberg polyhedron. Construction A geodesic grid is a global Earth reference that uses triangular tiles based on the subdivision of a polyhedron (usually the icosahedron, and usually a Class I subdivision) to subdivide the surface of the Earth. Such a grid does not have a straightforward relationship to latitude and longitude, but conforms to many of the main criteria for a statistically valid discrete global grid. Primarily, the cells' area and shape are generally similar, especially near the poles where many other spatial grids have singularities or heavy distortion. The popular Quaternary Triangular Mesh (QTM) falls into this category. Geodesic grids may use the dual polyhedron of the geodesic polyhedron, which is the Goldberg polyhedron. Goldberg polyhedra are made up of hexagons and (if based on the icosahedron) 12 pentagons. One implementation that uses an icosahedron as the base polyhedron, hexagonal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
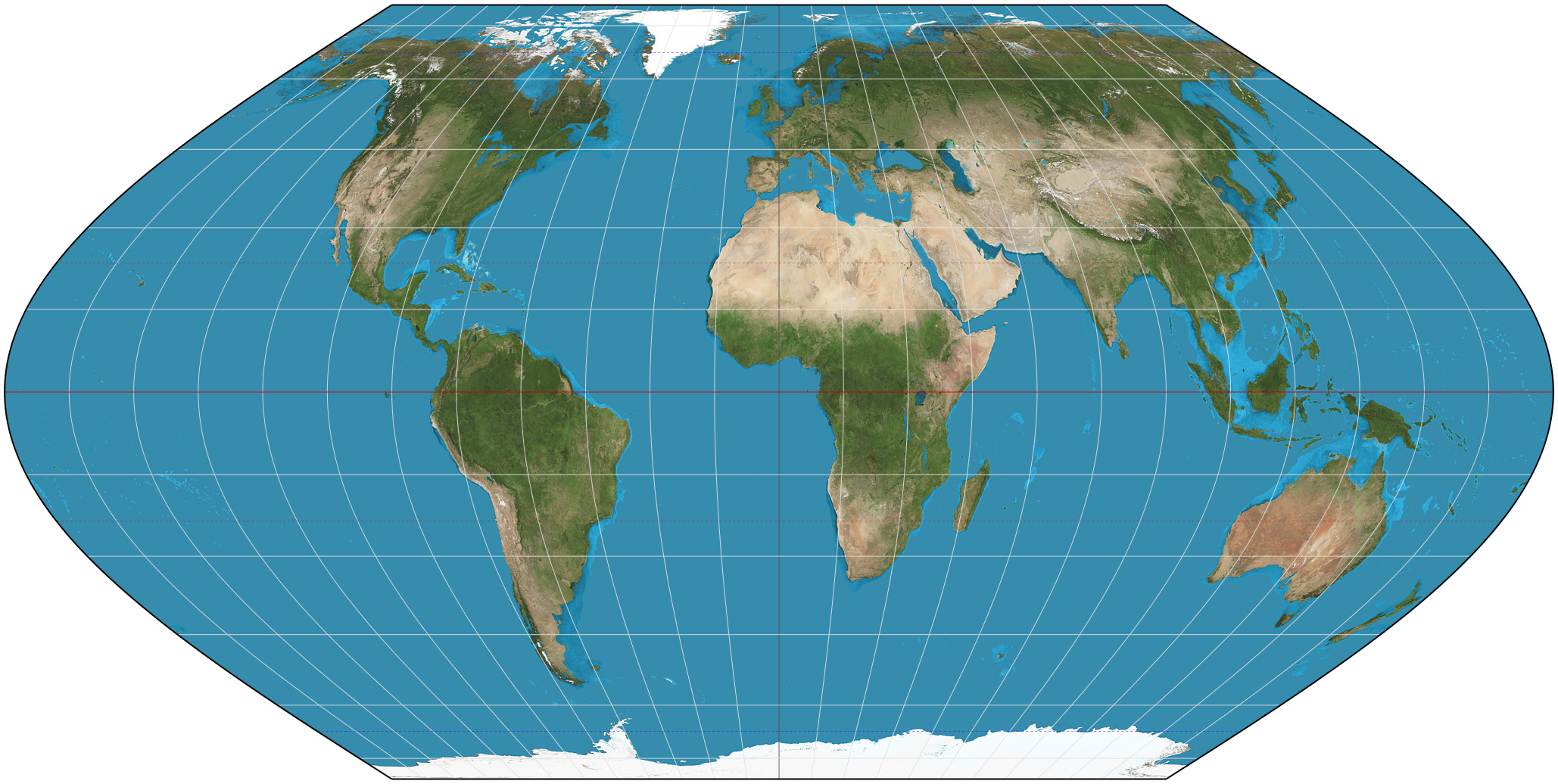
Strebe 1995 Projection
The Strebe 1995 projection, Strebe projection, Strebe lenticular equal-area projection, or Strebe equal-area polyconic projection is an equal-area map projection presented by Daniel "daan" Strebe in 1994. Strebe designed the projection to keep all areas proportionally correct in size; to push as much of the inevitable distortion as feasible away from the continental masses and into the Pacific Ocean; to keep a familiar equatorial orientation; and to do all this without slicing up the map. Description Strebe first presented the projection at a joint meeting of the Canadian Cartographic Association and the North American Cartographic Information Society (NACIS) in August 1994. Its final formulation was completed in 1995. The projection has been available in the map projection software Geocart since Geocart 1.2, released in October 1994. The projection is arrived at by a series of steps, each of which preserves areas. Because each step preserves areas, the entire process preserve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal Projection
The sinusoidal projection is a pseudocylindrical equal-area map projection, sometimes called the Sanson–Flamsteed or the Mercator equal-area projection. Jean Cossin of Dieppe was one of the first mapmakers to use the sinusoidal, appearing in a world map of 1570. The projection represents the poles as points, as they are on the sphere, but the meridians and continents are distorted. The equator and the prime meridian are the most accurate parts of the map, having no distortion at all, and the further away from those that one examines, the greater the distortion. The projection is defined by: :\begin x &= \left(\lambda - \lambda_0\right) \cos \varphi \\ y &= \varphi\,\end where \varphi is the latitude, ''λ'' is the longitude, and ''λ'' is the longitude of the central meridian. Scale is constant along the central meridian, and east–west scale is constant throughout the map. Therefore, the length of each parallel on the map is proportional to the cosine of the latitude, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollweide Projection
400px, Mollweide projection of the world 400px, The Mollweide projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation The Mollweide projection is an equal-area, pseudocylindrical map projection generally used for maps of the world or celestial sphere. It is also known as the Babinet projection, homalographic projection, homolographic projection, and elliptical projection. The projection trades accuracy of angle and shape for accuracy of proportions in area, and as such is used where that property is needed, such as maps depicting global distributions. The projection was first published by mathematician and astronomer Karl (or Carl) Brandan Mollweide (1774–1825) of Leipzig in 1805. It was reinvented and popularized in 1857 by Jacques Babinet, who gave it the name homalographic projection. The variation homolographic arose from frequent nineteenth-century usage in star atlases. Properties The Mollweide is a pseudocylindrical projection in which the equator is represented as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Cylindrical Equal-area Projection
In cartography, the Lambert cylindrical equal-area projection, or Lambert cylindrical projection, is a cylindrical equal-area projection. This projection is undistorted along the equator, which is its standard parallel, but distortion increases rapidly towards the poles. Like any cylindrical projection, it stretches parallels increasingly away from the equator. The poles accrue infinite distortion, becoming lines instead of points. History The projection was invented by the Swiss mathematician Johann Heinrich Lambert and described in his 1772 treatise, ''Beiträge zum Gebrauche der Mathematik und deren Anwendung'', part III, section 6: ''Anmerkungen und Zusätze zur Entwerfung der Land- und Himmelscharten'', translated as, ''Notes and Comments on the Composition of Terrestrial and Celestial Maps''. Lambert's projection is the basis for the cylindrical equal-area projection family. Lambert chose the equator as the parallel of no distortion. By multiplying the projection's h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Azimuthal Equal-area Projection
The Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection is a particular mapping from a sphere to a disk. It accurately represents area in all regions of the sphere, but it does not accurately represent angles. It is named for the Swiss mathematician Johann Heinrich Lambert, who announced it in 1772. "Zenithal" being synonymous with "azimuthal", the projection is also known as the Lambert zenithal equal-area projection. The Lambert azimuthal projection is used as a map projection in cartography. For example, the National Atlas of the US uses a Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection to display information in the online Map Maker application, and the European Environment Agency recommends its usage for European mapping for statistical analysis and display. It is also used in scientific disciplines such as geology for plotting the orientations of lines in three-dimensional space. This plotting is aided by a special kind of graph paper called a Schmidt net.Ramsay (1967) Definition To defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobo–Dyer Projection
The Hobo–Dyer map projection is a normal cylindrical equal-area projection, with standard parallels (there is no north-south or east-west distortion) at 37.5° north and south of the equator. The map was commissioned in 2002 by Bob Abramms and Howard Bronstein of ODT Inc. and drafted by cartographer Mick Dyer, as a modification of the 1910 Behrmann projection. The name ''Hobo–Dyer'' is derived from Bronstein and Abramms's first names (Howard and Bob) and Dyer's surname. The original ODT map is printed on two sides, one side with north upwards and the other with south upwards. That, together with its equal-area presentation, is intended to present a different perspective compared with more common non-equal area, north-up maps. The goal is similar to that of other equal-area projections (such as the Gall–Peters projection), but the Hobo-Dyer is billed by the publisher as "more visually satisfying". To that end, the map stretches the low latitudes vertically less than Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammer Projection
The Hammer projection is an equal-area map projection described by Ernst Hammer (cartographer), Ernst Hammer in 1892. Using the same 2:1 elliptical outer shape as the Mollweide projection, Hammer intended to reduce distortion in the regions of the outer meridians, where it is extreme in the Mollweide. Development Directly inspired by the Aitoff projection, Hammer suggested the use of the equatorial form of the Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection instead of Aitoff's use of the azimuthal equidistant projection: :\begin x &= \operatorname_x\left(\frac, \varphi\right) \\ y &= \tfrac12 \operatorname_y\left(\frac, \varphi\right) \end where laea and laea are the ''x'' and ''y'' components of the equatorial Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection. Written out explicitly: :\begin x &= \frac \\ y &= \frac \end The inverse is calculated with the intermediate variable :z \equiv \sqrt The longitude and latitudes can then be calculated by :\begin \lambda &= 2 \arctan \frac \\ \varphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |