|
Ephedra Californica
''Ephedra californica'' is a species of ''Ephedra'', known by the common names California jointfir, California ephedra, desert tea, Mormon tea, and ''cañatillo''. Distribution The plant is native to many diverse areas of central and southern California, Baja California, and west Arizona. It grows in varied scrub and open habitats, including chaparral, arid grassland, and Creosote scrub.Jepson . accessed 1.10.2013 It is found at elevations from .Flora of North America . accessed 1.10.2013 Regions and landforms of distribution include: * |
Sereno Watson
Sereno Watson (December 1, 1826 in East Windsor Hill, Connecticut – March 9, 1892 in Cambridge, Massachusetts) was an American botanist. Graduating from Yale in 1847 in Biology, he drifted through various occupations until, in California, he joined the Clarence King Expedition and eventually became its expedition botanist. Appointed by Asa Gray as assistant in the Gray Herbarium of Harvard University in 1873, he later became its curator, a position he maintained until his death. Watson was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1874, and a member of the National Academy of Sciences in 1889. Works * ''Botany'', in ''Report of the geological exploration of the 40th parallel made ... by Clarence King'', 1871 * * Publications by and about S. Watsoon WorldCat References External linksBiographical sketch at the Gray Herbarium site [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
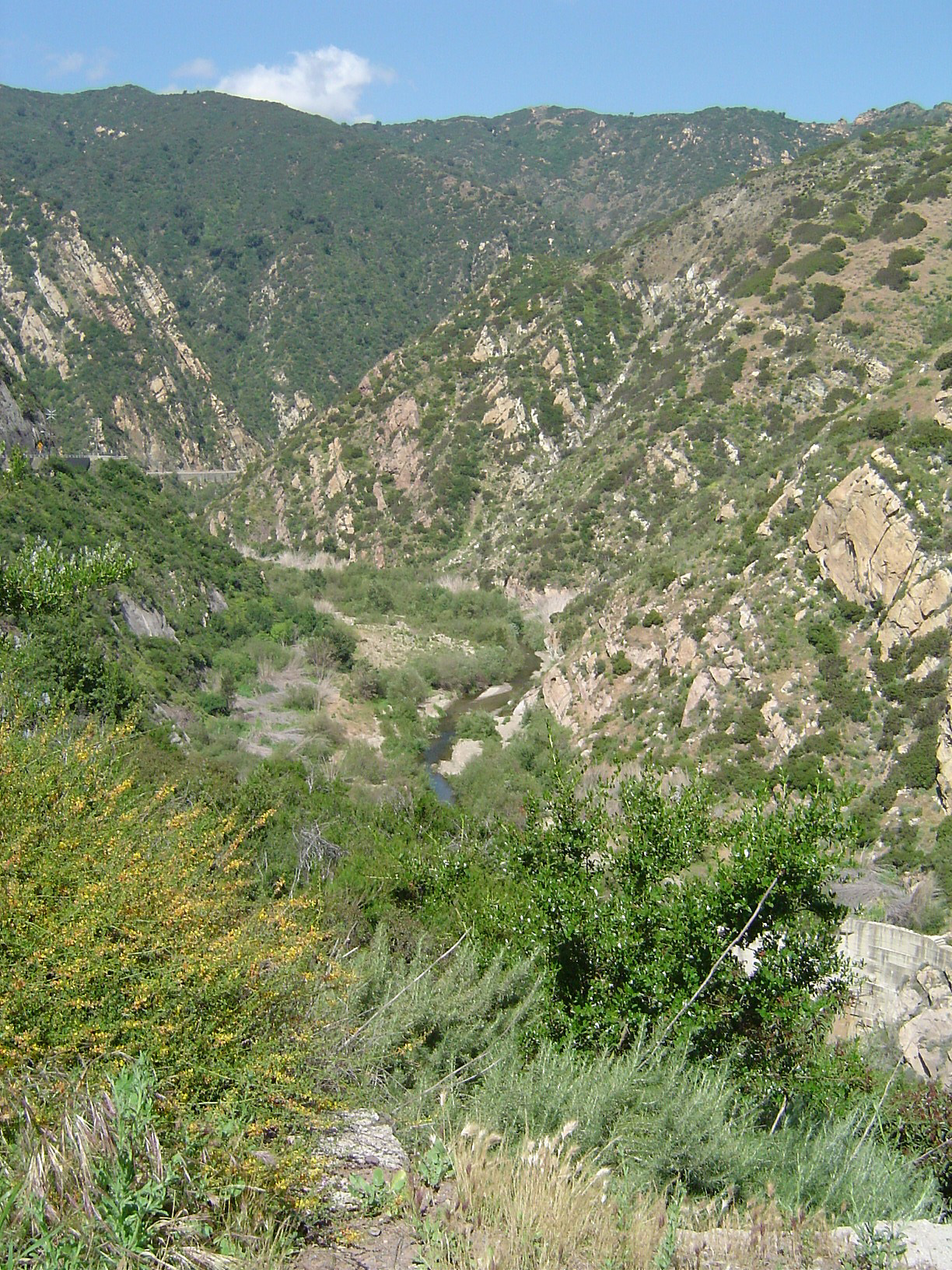
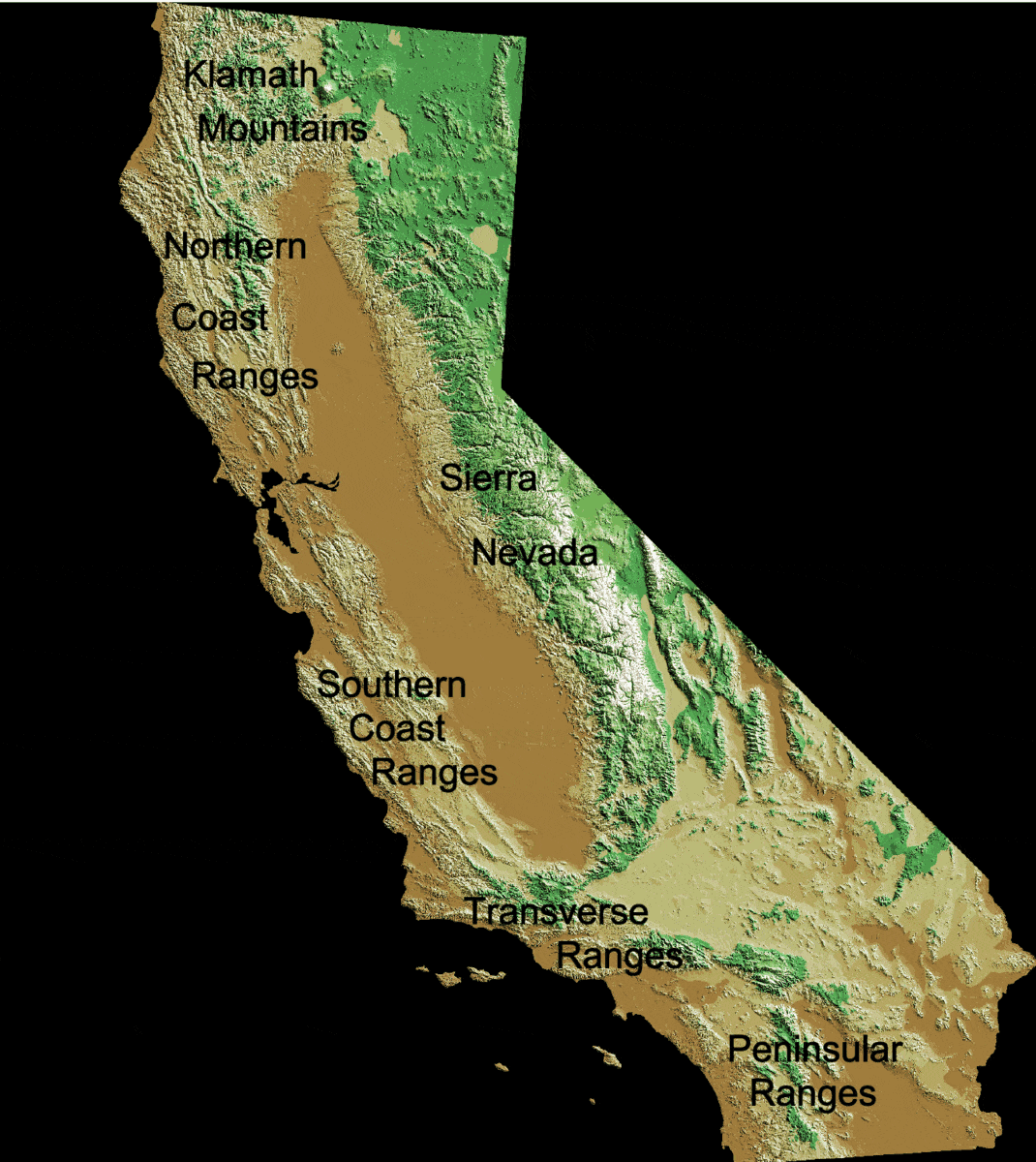
California Coast Ranges
The Coast Ranges of California span from Del Norte or Humboldt County, California, south to Santa Barbara County. The other three coastal California mountain ranges are the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges and the Klamath Mountains. Physiographically, they are a section of the larger Pacific Border province, which in turn is part of the larger Pacific Mountain System physiographic division. UNESCO has included the " California Coast Ranges Biosphere Reserve" in its Man and the Biosphere Programme of World Network of Biosphere Reserves since 1983. * Physiography The northern end of the California Coast Ranges overlap the southern end of the Klamath Mountains for approximately 80 miles on the west. They extend southward for more than 600 miles to where the coastline turns eastward along the Santa Barbara Channel, around the area of Point Conception. Here the southern end meets the Los Angeles Transverse Ranges, or ''Sierras de los Angeles''. The rocks themselves that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumeyaay
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the United States. Their Kumeyaay language belongs to the Yuman–Cochimí language family. The Kumeyaay consist of three related groups, the Ipai, Tipai and Kamia. The San Diego River loosely divided the Ipai and the Tipai historical homelands, while the Kamia lived in the eastern desert areas. The Ipai lived to the north, from Escondido to Lake Henshaw, while the Tipai lived to the south, in lands including the Laguna Mountains, Ensenada, and Tecate. The Kamia lived to the east in an area that included Mexicali and bordered the Salton Sea. Name The Kumeyaay or Tipai-Ipai were formerly known as the Kamia or Diegueños, the former Spanish name applied to the Mission Indians living along the San Diego River. They are referred to as the Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawaiisu
The Kawaiisu (pronounced: ″ka-wai-ah-soo″) are a Native Californian ethnic group in the United States who live in the Tehachapi Valley and to the north across the Tehachapi Pass in the southern Sierra Nevada, toward Lake Isabella and Walker Pass. Historically, the Kawaiisu also traveled eastward on food-gathering trips to areas in the northern Mojave Desert, to the north and northeast of the Antelope Valley, Searles Valley, as far east as the Panamint Valley, the Panamint Mountains, and the western edge of Death Valley. Today, some Kawaiisu people are enrolled in the Tule River Indian Tribe. Language The Kawaiisu language, or Tehachapi, is a member of the Southern Numic division of the Uto-Aztecan language family. The Kawaiisu homeland was bordered by speakers of non-Numic Uto-Aztecan languages. The Kitanemuk to the south spoke Takic, the Tübatulabal to the north spoke the Tübatulabal language, a linguistic isolate. The Yokuts (''Monilabal'') to the west were non-Uto-A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumeyaay People
The Kumeyaay, also known as Tipai-Ipai or by their historical Spanish name Diegueño, is a tribe of Indigenous peoples of the Americas who live at the northern border of Baja California in Mexico and the southern border of California in the United States. Their Kumeyaay language belongs to the Yuman–Cochimí language family. The Kumeyaay consist of three related groups, the Ipai, Tipai and Kamia. The San Diego River loosely divided the Ipai and the Tipai historical homelands, while the Kamia lived in the eastern desert areas. The Ipai lived to the north, from Escondido to Lake Henshaw, while the Tipai lived to the south, in lands including the Laguna Mountains, Ensenada, and Tecate. The Kamia lived to the east in an area that included Mexicali and bordered the Salton Sea. Name The Kumeyaay or Tipai-Ipai were formerly known as the Kamia or Diegueños, the former Spanish name applied to the Mission Indians living along the San Diego River. They are referred to as the Kumia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicinal Plant
Medicinal plants, also called medicinal herbs, have been discovered and used in traditional medicine practices since prehistoric times. Plants synthesize hundreds of chemical compounds for various functions, including defense and protection against insects, fungi, diseases, and herbivorous mammals. The earliest historical records of herbs are found from the Sumerian civilization, where hundreds of medicinal plants including opium are listed on clay tablets, c. 3000 BC. The Ebers Papyrus from ancient Egypt, c. 1550 BC, describes over 850 plant medicines. The Greek physician Dioscorides, who worked in the Roman army, documented over 1000 recipes for medicines using over 600 medicinal plants in ''De materia medica'', c. 60 AD; this formed the basis of pharmacopoeias for some 1500 years. Drug research sometimes makes use of ethnobotany to search for pharmacologically active substances, and this approach has yielded hundreds of useful compounds. These include the common drugs aspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of California
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. With over forty groups seeking to be federally recognized tribes, California has the second-largest Native American population in the United States. The California cultural area does not conform exactly to the state of California's boundaries. Many tribes on the eastern border with Nevada are classified as Great Basin tribes, and some tribes on the Oregon border are classified as Plateau tribes. Tribes in Baja California who do not cross into California are classified as indigenous peoples of Mexico. History Pre-contact Evidence of human occupation of California dates from at least 19,000 years ago. Prior to European contact, indigenous Californians had 500 distinct sub-tribes or groups, each consisting of 50 to 500 individual memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Interior Chaparral And Woodlands
The California interior chaparral and woodlands ecoregion covers in an elliptical ring around the California Central Valley. It occurs on hills and mountains ranging from to . It is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, with cool, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures within the coast can range from 53° to 65 °F and 32° to 60 °F within the mountains. Many plant and animal species in this ecoregion are adapted to periodic fire. Geography The California interior chaparral and woodlands ecoregion extends from as far north as Shasta Lake in Northern California to as far south as the Santa Barbara Channel in Southern California. Despite being termed as "inland", this ecoregion features extensive coastline between the Central Coast towns of Goleta and San Simeon, as well as within the Monterey and San Francisco Bay areas. These coastal regions are broken up by isolated patches of Northern California coastal forests and California mont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Montane Chaparral And Woodlands
The California montane chaparral and woodlands is an ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund, spanning of mountains in the Transverse Ranges, Peninsular Ranges, and Coast Ranges of southern and central California. The ecoregion is part of the larger California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion, and belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome. Geography The ecoregion spreads from low foothills up to the highest peaks of the following ranges: San Bernardino Mountains, San Jacinto Mountains, San Gabriel Mountains, Santa Susana Mountains, Santa Monica Mountains, Sierra Pelona, Topatopa Mountains, Tehachapi Mountains, San Rafael Mountains, Santa Ynez Mountains, and the long Santa Lucia Mountains. The wide elevation range and characteristic climate produce a variety of natural communities, from chaparral to mixed evergreen forest to alpine tundra. File:Angelesnationalforest.jpg, Montane woodlands in the San Gabriel Mountains File:Vasquez Rocks chaparral.j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Coastal Sage And Chaparral Ecoregion
The California coastal sage and chaparral ( es, Salvia y chaparral costero de California) is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion located in southwestern California ( United States) and northwestern Baja California ( Mexico). It is part of the larger California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion. Geography The California coastal sage and chaparral ecoregion covers about of coastal terraces, plains, and foothills between Carpinteria Beach in California and Punta Banda in Baja California. This includes the southwestern slopes of the Transverse and Peninsular Ranges, the entirety of the Santa Susana and Santa Monica Mountains, the Channel Islands, Guadalupe Island, and Cedros Island. Major urban centers located within this ecoregion include Greater Los Angeles, San Diego-Tijuana, Ensenada, and Tecate. Climate The climate is Mediterranean, with mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers with fog. Flora The plant species of the California coastal sage and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
California Chaparral And Woodlands
The California chaparral and woodlands is a terrestrial ecoregion of southwestern Oregon, northern, central, and southern California (United States) and northwestern Baja California (Mexico), located on the west coast of North America. It is an ecoregion of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, and part of the Nearctic realm. Setting Three sub-ecoregions The California chaparral and woodlands ecoregion is subdivided into three smaller ecoregions. * California coastal sage and chaparral ecoregion: In southern coastal California and northwestern coastal Baja California, as well as all the Channel Islands of California and Guadalupe Island. * California montane chaparral and woodlands: In southern and central coast adjacent and inland California, covering some of the mountains of: the Coast Ranges; the Transverse Ranges; and the western slopes of the northern Peninsular Ranges. * California interior chaparral and woodlands: In central interior California su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



