|
Entity Linking
In natural language processing, entity linking, also referred to as named-entity linking (NEL), named-entity disambiguation (NED), named-entity recognition and disambiguation (NERD) or named-entity normalization (NEN) is the task of assigning a unique identity to entities (such as famous individuals, locations, or companies) mentioned in text. For example, given the sentence ''"Paris is the capital of France"'', the idea is to determine that ''"Paris"'' refers to the city of Paris and not to Paris Hilton or any other entity that could be referred to as ''"Paris"''. Entity linking is different from named-entity recognition (NER) in that NER identifies the occurrence of a named entity in text but it does not identify which specific entity it is (see Differences from other techniques). Introduction In entity linking, words of interest (names of persons, locations and companies) are mapped from an input text to corresponding unique entities in a target knowledge base. Words of inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled " Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Negative
A false positive is an error in binary classification in which a test result incorrectly indicates the presence of a condition (such as a disease when the disease is not present), while a false negative is the opposite error, where the test result incorrectly indicates the absence of a condition when it is actually present. These are the two kinds of errors in a binary test, in contrast to the two kinds of correct result (a and a ). They are also known in medicine as a false positive (or false negative) diagnosis, and in statistical classification as a false positive (or false negative) error. In statistical hypothesis testing the analogous concepts are known as type I and type II errors, where a positive result corresponds to rejecting the null hypothesis, and a negative result corresponds to not rejecting the null hypothesis. The terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences in detail and interpretation due to the differences between medical testing and stati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coreference
In linguistics, coreference, sometimes written co-reference, occurs when two or more expressions refer to the same person or thing; they have the same referent. For example, in ''Bill said Alice would arrive soon, and she did'', the words ''Alice'' and ''she'' refer to the same person. Co-reference is often non-trivial to determine. For example, in ''Bill said he would come'', the word ''he'' may or may not refer to Bill. Determining which expressions are coreferences is an important part of analyzing or understanding the meaning, and often requires information from the context, real-world knowledge, such as tendencies of some names to be associated with particular species ("Rover"), kinds of artifacts ("Titanic"), grammatical genders, or other properties. Linguists commonly use indices to notate coreference, as in ''Billi said hei would come''. Such expressions are said to be ''coindexed'', indicating that they should be interpreted as coreferential. When expressions are corefer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Named-entity Recognition
Named-entity recognition (NER) (also known as (named) entity identification, entity chunking, and entity extraction) is a subtask of information extraction that seeks to locate and classify named entities mentioned in unstructured text into pre-defined categories such as person names, organizations, locations, medical codes, time expressions, quantities, monetary values, percentages, etc. Most research on NER/NEE systems has been structured as taking an unannotated block of text, such as this one: And producing an annotated block of text that highlights the names of entities: In this example, a person name consisting of one token, a two-token company name and a temporal expression have been detected and classified. State-of-the-art NER systems for English produce near-human performance. For example, the best system entering MUC-7 scored 93.39% of F-measure while human annotators scored 97.60% and 96.95%. Named-entity recognition platforms Notable NER platforms include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Linkage
Record linkage (also known as data matching, data linkage, entity resolution, and many other terms) is the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources (e.g., data files, books, websites, and databases). Record linkage is necessary when joining different data sets based on entities that may or may not share a common identifier (e.g., database key, URI, National identification number), which may be due to differences in record shape, storage location, or curator style or preference. A data set that has undergone RL-oriented reconciliation may be referred to as being ''cross-linked''. Naming conventions "Record linkage" is the term used by statisticians, epidemiologists, and historians, among others, to describe the process of joining records from one data source with another that describe the same entity. However, many other terms are used for this process. Unfortunately, this profusion of terminology has led to few cross-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Record Linkage
Record linkage (also known as data matching, data linkage, entity resolution, and many other terms) is the task of finding records in a data set that refer to the same entity across different data sources (e.g., data files, books, websites, and databases). Record linkage is necessary when joining different data sets based on entities that may or may not share a common identifier (e.g., database key, URI, National identification number), which may be due to differences in record shape, storage location, or curator style or preference. A data set that has undergone RL-oriented reconciliation may be referred to as being ''cross-linked''. Naming conventions "Record linkage" is the term used by statisticians, epidemiologists, and historians, among others, to describe the process of joining records from one data source with another that describe the same entity. However, many other terms are used for this process. Unfortunately, this profusion of terminology has led to few cross-r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Size Of Wikipedia
The size of the English Wikipedia can be measured in terms of the number of articles, number of words, number of pages, and the size of the database, among other ways. As of , there are articles in the English Wikipedia containing over 4 billion words (giving an average of about 644 words per article). Including articles, the total number of pages is . Being pages themselves, articles make up percent of all pages on Wikipedia. As of 21 September 2022, the size of the current version of all articles compressed is about 21.23 GB without media. Wikipedia continues to grow, and the number of articles on Wikipedia is increasing by over 17,000 a month. The number of articles added to Wikipedia every month reached its peak in 2006, at over 50,000 new articles a month, and has been slowly but steadily declining since then. While this might seem to show that Wikipedia's growth is slowing or stopping, it should be noted that the amount of text added to Wikipedia articles every year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysemy
Polysemy ( or ; ) is the capacity for a sign (e.g. a symbol, a morpheme, a word, or a phrase) to have multiple related meanings. For example, a word can have several word senses. Polysemy is distinct from ''monosemy'', where a word has a single meaning. Polysemy is distinct from homonymy—or homophony—which is an accidental similarity between two or more words (such as '' bear'' the animal, and the verb ''bear''); whereas homonymy is a mere linguistic coincidence, polysemy is not. In discerning whether a given set of meanings represent polysemy or homonymy, it is often necessary to look at the history of the word to see whether the two meanings are historically related. Dictionary writers often list polysemes (words or phrases with different, but related, senses) in the same entry (that is, under the same headword) and enter homonyms as separate headwords (usually with a numbering convention such as ''¹bear'' and ''²bear''). Polysemes A polyseme is a word or phrase w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Search
Semantic search denotes search with meaning, as distinguished from lexical search where the search engine looks for literal matches of the query words or variants of them, without understanding the overall meaning of the query. Semantic search seeks to improve search accuracy by understanding the searcher's intent and the contextual meaning of terms as they appear in the searchable dataspace, whether on the Web or within a closed system, to generate more relevant results. Content that ranks well in semantic search is well-written in a natural voice, focuses on the user's intent, and considers related topics that the user may look for in the future. Some authors regard semantic search as a set of techniques for retrieving knowledge from richly structured data sources like ontologies and XML as found on the Semantic Web. Such technologies enable the formal articulation of domain knowledge Domain knowledge is knowledge of a specific, specialized discipline or field, in contrast t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maarten De Rijke
Maarten de Rijke (born 1 August 1961) is a Dutch computer scientist. His work initially focused on modal logic and knowledge representation, but since the early years of the 21st century he has worked mainly in information retrieval. His work is supported by grants from the Nederlandse Organisatie voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek (NWO), public-private partnerships, and the European Commission (under the Sixth and Seventh Framework programmes). Biography Maarten de Rijke was born in Vlissingen. He studied philosophy (MSc 1989) and mathematics (MSc 1990) and wrote a PhD thesis, defended in 1993, on extended modal logics, under the supervision of Johan van Benthem. De Rijke worked as a postdoc at the Centrum Wiskunde & Informatica, before becoming a Warwick Research Fellow at the University of Warwick. He joined the University of Amsterdam in 1998, and was appointed professor of Information Processing and Internet at the Informatics Institute of the University of Amsterdam in 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user or searcher enters a query into the system. Queries are formal statements of information needs, for example search strings in web search engines. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infobox
An infobox is a digital or physical table used to collect and present a subset of information about its subject, such as a document. It is a structured document containing a set of attribute–value pairs, and in Wikipedia represents a summary of information about the subject of an article. In this way, they are comparable to data tables in some aspects. When presented within the larger document it summarizes, an infobox is often presented in a sidebar format. An infobox may be implemented in another document by transcluding it into that document and specifying some or all of the attribute–value pairs associated with that infobox, known as parameterization. Wikipedia An infobox may be used to summarize the information of an article on Wikipedia. They are used on similar articles to ensure consistency of presentation by using a common format. Originally, infoboxes (and templates in general) were used for page layout purposes. An infobox may be transcluded into an artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
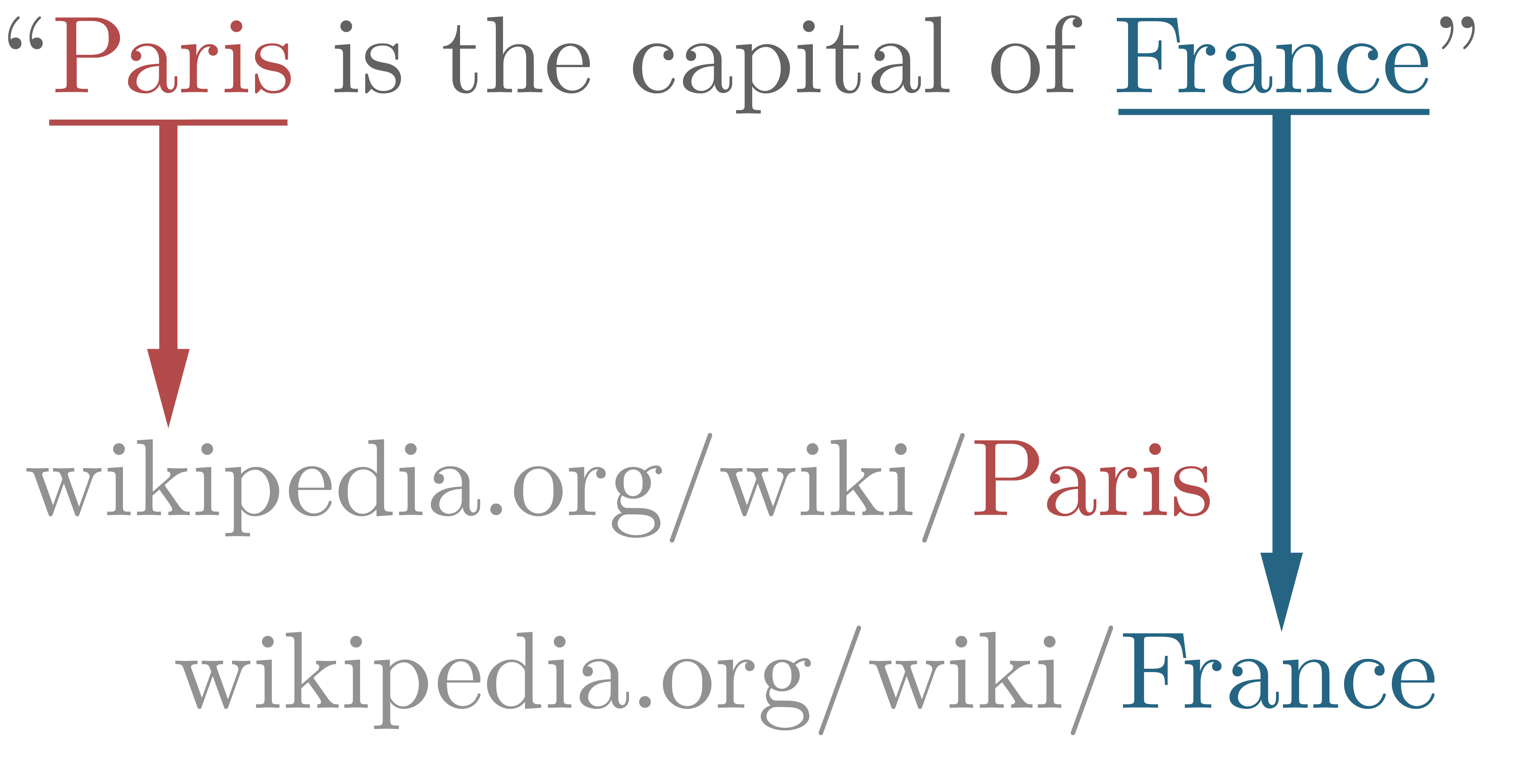

.jpg)

