|
Enmerkar And En-suhgir-ana
Enmerkar and En-suhgir-ana (also known as Enmerkar and Ensuhkeshdanna) is a text in Sumerian literature appearing as a sequel to '' Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'', and is second in a series of four accounts describing the contests of Aratta against Enmerkar, lord of Unug and Kulaba, and his successor Lugalbanda, father of Gilgamesh. Synopsis The name of the Lord of Aratta, which never appeared in ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'', is here provided in a brief introduction. Among scholars, the earlier cuneiform reading of this name, ''Ensuhgirana'', still enjoys currency alongside the more recent reading of it as '' Ensuhkeshdanna''. The introduction also gives the name of Ensuhkeshdanna's chief minister, ''Ansigaria'', and Enmerkar's chief minister, ''Namena-tuma''. Enmerkar is the Lord of both Unug and Kulaba, described as the "city which rises from heaven to earth" ic Following this introduction, the plot opens with Ensuhkeshdanna dictating a message to his envoy, to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian Literature
Sumerian literature constitutes the earliest known corpus of recorded literature, including the religious writings and other traditional stories maintained by the Sumerian civilization and largely preserved by the later Akkadian and Babylonian empires. These records were written in the Sumerian language in the 18th and 17th Centuries BC during the Middle Bronze Age. The Sumerians invented one of the first writing systems, developing Sumerian cuneiform writing out of earlier proto-writing systems by about the 30th century BC. The Sumerian language remained in official and literary use in the Akkadian and Babylonian empires, even after the spoken language disappeared from the population; literacy was widespread, and the Sumerian texts that students copied heavily influenced later Babylonian literature. Poetry Most Sumerian literature is written in left-justified lines, and could contain line-based organization such as the couplet or the stanza, but the Sumerian definit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enmerkar And The Lord Of Aratta
''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' is a legendary Sumerian account, preserved in early post-Sumerian copies, composed in the Neo-Sumerian period (ca. 21st century BC). It is one of a series of accounts describing the conflicts between Enmerkar, king of Unug-Kulaba, and the unnamed king of Aratta. Because it gives a Sumerian account of the "confusion of tongues", and also involves Enmerkar constructing temples at Eridu and Uruk, it has, since the time of Samuel Kramer, been compared with the Tower of Babel narrative in the Book of Genesis. Synopsis Near the beginning of the account, the following background is provided: "In those days of yore, when the destinies were determined, the great princes allowed Unug Kulaba's ''E-ana'' to lift its head high. Plenty, and carp floods and the rain which brings forth dappled barley were then increased in Unug Kulaba. Before the land of Dilmun yet existed, the ''E-ana'' of Unug Kulaba was well founded." '' E-ana'' was a temple in Uruk bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
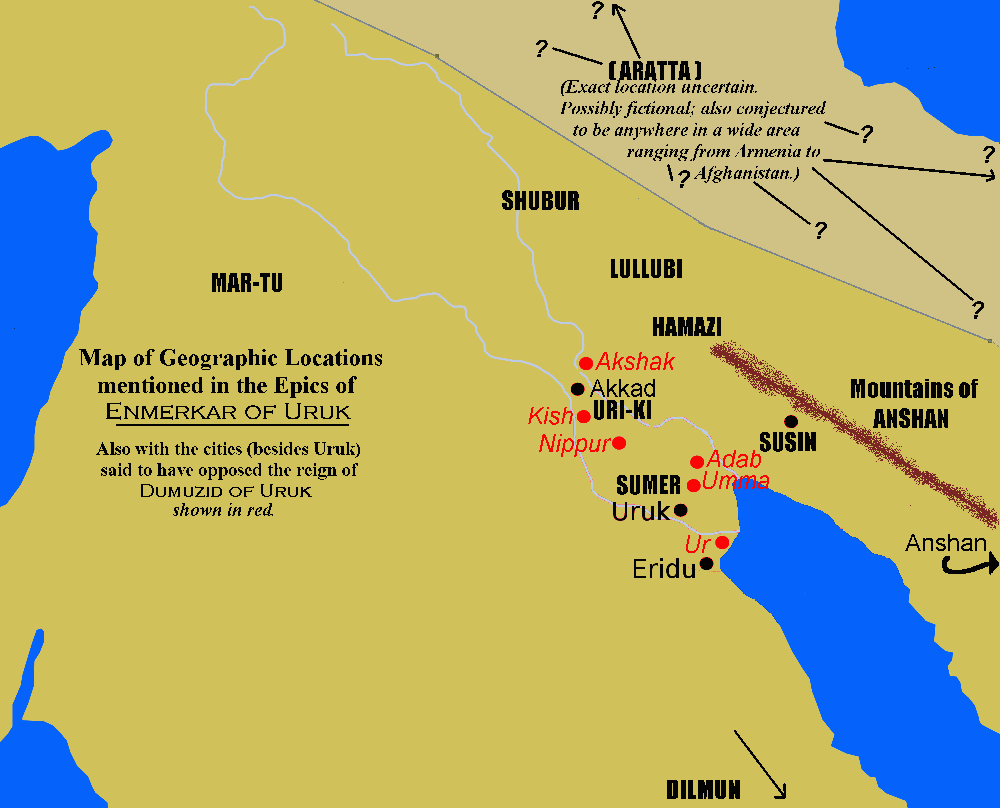
Aratta
Aratta is a land that appears in Sumerian myths surrounding Enmerkar and Lugalbanda, two early and possibly mythical kings of Uruk also mentioned on the Sumerian king list. Role in Sumerian literature Aratta is described as follows in Sumerian literature: *It is a fabulously wealthy place full of gold, silver, lapis lazuli and other precious materials, as well as the artisans to craft them. *It is remote and difficult to reach. *It is home to the goddess Inana, who transfers her allegiance from Aratta to Uruk. *It is conquered by Enmerkar of Uruk. Mentions in Sumerian literature ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' - The goddess Inanna resides in Aratta, but Enmerkar of Uruk pleases her more than does the lord of Aratta, who is not named in this epic. Enmerkar wants Aratta to submit to Uruk, bring stones down from the mountain, craft gold, silver and lapis lazuli, and send them, along with "kugmea" ore to Uruk to build a temple. Inana bids him send a messenger to Aratta, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enmerkar
Enmerkar was an ancient Sumerian ruler to whom the construction of Uruk and a 420-year reign was attributed. According to literary sources, he led various campaigns against the land of Aratta. Historical king Late Uruk period The tradition of Enmerkar as the founder of Uruk seems to date from the Jemdet Nasr period (3100-2900 BC) as found in the ''Ad-gi4 list''. The lexical list mentions Enmerkar and his wife Enmerkarzi as the builders of a town and the bringers of agriculture. A bilingual edition of the list has been found at Nineveh, indicating that the tradition was transmitted into the first millennium.''Enmerkar and (his) wife Enmerkar-zi,'' ''who know (how to build) towns (made) brick and brick pavements.'' ''When the yearly flood reached its proper level,'' ''(they made) irrigation canals and all kinds of irrigation ditches.''Despite his proclaimed divine descent from the poems, Enmerkar was not deified as his successors Lugalbanda and Gilgamesh. These two last k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Muthanna Governorate, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harmansah, 2007 Uruk is the type site for the Uruk period. Uruk played a leading role in the early urbanization of Sumer in the mid-4th millennium BC. By the final phase of the Uruk period around 3100 BC, the city may have had 40,000 residents, with 80,000-90,000 people living in its environs, making it the largest urban area in the world at the time. The legendary king Gilgamesh, according to the chronology presented in the Sumerian king list, ''Sumerian King List'' (henceforth ''SKL''), ruled Uruk in the 27th century BC. The city lost its prime importance around 2000 BC in the context of the struggle of Babylonia against Elam, but it remained inhabited throughout the Seleucid (312–63 BC) and Parthian Empire, Parth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugalbanda
Lugalbanda was a deified Sumerian king of Uruk who, according to various sources of Mesopotamian literature, was the father of Gilgamesh. Early sources mention his consort Ninsun and his heroic deeds in an expedition to Aratta by King Enmerkar. Lugalbanda is listed in the '' Sumerian King List'' as the second king of Uruk, saying he ruled for 1200 years, and providing him with the epithet of ''the Shepherd''. Lugalbanda's historicity is uncertain among scholars. Attempts to date him in the ED II period are based on an amalgamation of data from the epic traditions of the 2nd millennium with unclear archaeological observations. Mythology Lugalbanda appears in Sumerian literary sources as early as the mid-3rd millennium, as attested by the incomplete mythological text ''Lugalbanda and Ninsuna,'' found in Abu Salabikh, that describes a romantic relationship between Lugalbanda and Ninsun. In the earliest god-lists from Fara, his name appears separate and in a much lower ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilgamesh
sux, , label=none , image = Hero lion Dur-Sharrukin Louvre AO19862.jpg , alt = , caption = Possible representation of Gilgamesh as Master of Animals, grasping a lion in his left arm and snake in his right hand, in an Assyrian palace relief (713–706 BC), from Dur-Sharrukin, now held in the Louvre , reign=c. 2900–2700 BC ( EDI), predecessor = Dumuzid, the Fisherman (as Ensi of Uruk) , consort = , siblings = , successor = Ur-Nungal Gilgamesh ( akk, , translit=Gilgameš; originally sux, , translit= Bilgames)). His name translates roughly as "The Ancestor is a Young-man", from ''Bil.ga'' "Ancestor", Elder and ''Mes/Mesh3'' "Young-Man". See also . was a hero in ancient Mesopotamian mythology and the protagonist of the '' Epic of Gilgamesh'', an epic poem written in Akkadian during the late 2nd millennium BC. He was possibly a historical king of the Sumerian city-state of Uruk, who was posthumously deified. His rule probably would have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensuhkeshdanna
Aratta is a land that appears in Sumerian myths surrounding Enmerkar and Lugalbanda, two early and possibly mythical kings of Uruk also mentioned on the Sumerian king list. Role in Sumerian literature Aratta is described as follows in Sumerian literature: *It is a fabulously wealthy place full of gold, silver, lapis lazuli and other precious materials, as well as the artisans to craft them. *It is remote and difficult to reach. *It is home to the goddess Inana, who transfers her allegiance from Aratta to Uruk. *It is conquered by Enmerkar of Uruk. Mentions in Sumerian literature ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'' - The goddess Inanna resides in Aratta, but Enmerkar of Uruk pleases her more than does the lord of Aratta, who is not named in this epic. Enmerkar wants Aratta to submit to Uruk, bring stones down from the mountain, craft gold, silver and lapis lazuli, and send them, along with "kugmea" ore to Uruk to build a temple. Inana bids him send a messenger to Aratta, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inanna
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Sumer under the name "Inanna", and later by the Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians under the name Ishtar, (occasionally represented by the logogram ). She was known as the " Queen of Heaven" and was the patron goddess of the Eanna temple at the city of Uruk, which was her main cult center. She was associated with the planet Venus and her most prominent symbols included the lion and the eight-pointed star. Her husband was the god Dumuzid (later known as Tammuz) and her , or personal attendant, was the goddess Ninshubur (who later became conflated with the male deities Ilabrat and Papsukkal). Inanna was worshiped in Sumer at least as early as the Uruk period ( 4000 BCE – 3100 BCE), but she had little cult activity before the conqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamazi
Hamazi or Khamazi ( Sumerian: , ''ha-ma-zi''ki, or ''Ḫa-ma-zi2''ki) was an ancient kingdom or city-state of some importance that reached its peak c. 2500–2400 BC. Its exact location is unknown, but is thought to have been located in the western Zagros Mountains roughly between Elam and Assyria, possibly near Nuzi or modern Hamadan. Hamazi first came to the attention of archaeologists with the discovery of a vase with an inscription in very archaic cuneiform commemorating the victory of Uhub (or Utug), an early king of Kish, over this place, causing fringe theorist Laurence Waddell in 1929 to speculate that it was to be identified with Carchemish in Syria. It is now generally considered to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Diyala River. One of the earliest references to Hamazi is found in the epic ''Enmerkar and the Lord of Aratta'', where Enmerkar prays to Enki about the confusion of languages in the various inhabited lands, at the time of the building of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eresh (other)
Eresh can refer to: *A city in ancient Sumer, possibly Uruk or Abu Salabikh The low tells at Abu Salabikh, around northwest of the site of ancient Nippur in Al-Qādisiyyah Governorate, Iraq mark the site of a small Sumerian city state of the mid third millennium BCE, with cultural connections to the cities of Kish, ... *Akkadian pronunciation of NIN (cuneiform), a Sumerian word which can denote a "queen" or a "priestess". {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nisaba
Nisaba was the Mesopotamian goddess of writing and grain. She is one of the oldest Sumerian deities attested in writing, and remained prominent through many periods of Mesopotamian history. She was commonly worshiped by scribes, and numerous Sumerian texts end with the doxology "praise to Nisaba" as a result. She declined after the Old Babylonian period due to the rise of the new scribe god, Nabu, though she did not fully vanish from Mesopotamian religion and attestations from as late as the neo-Babylonian period are known. In myths and god lists, she was a part of the circle of Enlil, alongside her husband Haya. In the myth ''Enlil and Sud'' she plays an important role due to being the mother of the eponymous deity. Enlil seeks her permission to marry Sud with the help of his sukkal (attedant deity) Nuska. Both this narrative and other sources attest that she and her daughter were regarded as very close. Outside Mesopotamia her name was used to logographically represent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |