|
Electronic Fetal Monitoring
Cardiotocography (CTG) is a technique used to monitor the fetal heartbeat and the uterine contractions during pregnancy and labour. The machine used to perform the monitoring is called a cardiotocograph. Fetal heart sounds was described as early as 350 years ago and approximately 200 years ago mechanical stethoscopes, such as the Pinard horn, were introduced in clinical practice. Modern-day CTG was developed and introduced in the 1950s and early 1960s by Edward Hon, Roberto Caldeyro-Barcia and Konrad Hammacher. The first commercial fetal monitor (Hewlett-Packard 8020A) was released in 1968. CTG monitoring is widely used to assess fetal wellbeing by identifying babies at risk of hypoxia (lack of oxygen). CTG is mainly used during labour. A review found that in the antenatal period (before labour), there is no evidence to suggest that monitoring women with high-risk pregnancies benefits the mother or baby, although research around this is old and should be interpreted with caut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Heartbeat
Heart development, also known as cardiogenesis, refers to the prenatal development of the heart. This begins with the formation of two endocardial tubes which merge to form the tubular heart, also called the primitive heart tube. The heart is the first functional organ in vertebrate embryos. The tubular heart quickly differentiates into the truncus arteriosus, bulbus cordis, primitive ventricle, primitive atrium, and the sinus venosus. The truncus arteriosus splits into the ascending aorta and the pulmonary trunk. The bulbus cordis forms part of the ventricles. The sinus venosus connects to the fetal circulation. The heart tube elongates on the right side, looping and becoming the first visual sign of left-right asymmetry of the body. Septa form within the atria and ventricles to separate the left and right sides of the heart. Early development The heart derives from embryonic mesodermal germ layer cells that differentiate after gastrulation into mesothelium, endothel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association Of Women's Health, Obstetric And Neonatal Nurses
The Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit membership organization. The stated purpose of AWHONN is to promote the health of women and newborns. History AWHONN became a separate and independent organization in 1993. Using the Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN) guidelines correctly can make staffing the safest possible. When these staffing guidelines are followed appropriately they allow for quality care and more time for the nurse to spend at the bedside with the patient. The experience and skill mix of the nurses on the labor and delivery unit is another critical element of safe staffing. Nurses in labor and delivery units should have one patient to care for if the woman is having her labor induced or has chosen a birthing plan without pain medication or an epidural. Two nurses should be at every birth, one to care for the mom and the other to care for the baby. As far as post partum and mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Perinatology
The ''Journal of Perinatology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed medical journal covering perinatology. It was established in 1981 as the ''Journal of the California Perinatal Association'', obtaining its current name in 1984. It is published by Nature Publishing Group on behalf of the California Perinatal Association, of which it is the official journal. The editor-in-chief is Edward E. Lawson (Johns Hopkins Hospital). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.521. References External links * Pediatrics journals Nature Research academic journals Obstetrics and gynaecology journals Publications established in 1981 Monthly journals English-language journals Academic journals associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Obstetricia Et Gynecologica Scandinavica
''Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica'' is a peer-reviewed, open access, medical journal covering gynecology, female urology Urology (from Greek οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and '' -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of the urinary-tract system and the reproductive org ..., gynecologic oncology and fertility. The journal is published by Wiley-Blackwell, for the Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology. The editor in chief is Ganesh Acharya ( Karolinska Institute). Articles are published fully open access since 30 July 2021. According to the '' Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor of 4.544, ranking it 15th out of 85 journals in the category "Obstetrics & Gynecology". References External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica Publications established in 1921 English-language j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Hypoxia
Intrauterine hypoxia (also known as fetal hypoxia) occurs when the fetus is deprived of an adequate supply of oxygen. It may be due to a variety of reasons such as prolapse or occlusion of the umbilical cord, placental infarction, maternal diabetes (prepregnancy or gestational diabetes) and maternal smoking. Intrauterine growth restriction may cause or be the result of hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia can cause cellular damage that occurs within the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). This results in an increased mortality rate, including an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Oxygen deprivation in the fetus and neonate have been implicated as either a primary or as a contributing risk factor in numerous neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders such as epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, eating disorders and cerebral palsy. Presentation Maternal Consequences Complications arising from intrauterine hypoxia are some of the leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Acidemia
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys to excrete excess acids. Metabolic acidosis can lead to acidemia, which is defined as arterial blood pH that is lower than 7.35. Acidemia and acidosis are not mutually exclusive – pH and hydrogen ion concentrations also depend on the coexistence of other acid-base disorders; therefore, pH levels in people with metabolic acidosis can range from low to high. Acute metabolic acidosis, lasting from minutes to several days, often occurs during serious illnesses or hospitalizations, and is generally caused when the body produces an excess amount of organic acids (ketoacids in ketoacidosis, or lactic acid in lactic acidosis). A state of chronic metabolic acidosis, lasting several weeks to years, can be the result of impaired kidney function ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal (such as with exercise) or abnormal (such as with electrical problems within the heart). Complications Tachycardia can lead to fainting. When the rate of blood flow becomes too rapid, or fast blood flow passes on damaged endothelium, it increases the friction within vessels resulting in turbulence and other disturbances. According to the Virchow's triad, this is one of the three conditions that can lead to thrombosis (i.e., blood clots within vessels). Causes Some causes of tachycardia include: * Adrenergic storm * Anaemia * Anxiety * Atrial fibrillation * Atrial flutter * Atrial tachycardia * Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia * AV nodal reentrant tachycardia * Brugada syndrome * Circulatory shock and its various causes ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, and in athletes. In some people, bradycardia below 60 BPM may be associated with fatigue, weakness, dizziness, sweating, and fainting. The term "relative bradycardia" is used to refer to a heart rate slower than an individual's typical resting heart rate. Athletes may have athletic heart syndrome, which includes bradycardia as part of the cardiovascular adaptations to training and participation. The word "bradycardia" is from the Greek βραδύς ''bradys'' "slow", and καρδία ''kardia'' "heart". Classification Sinus Atrial bradycardias are divided into three types. The first, respiratory sinus arrhythmia, is usually found in young and healthy adults. Heart rate increases during inhalation and decreases during exhalation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
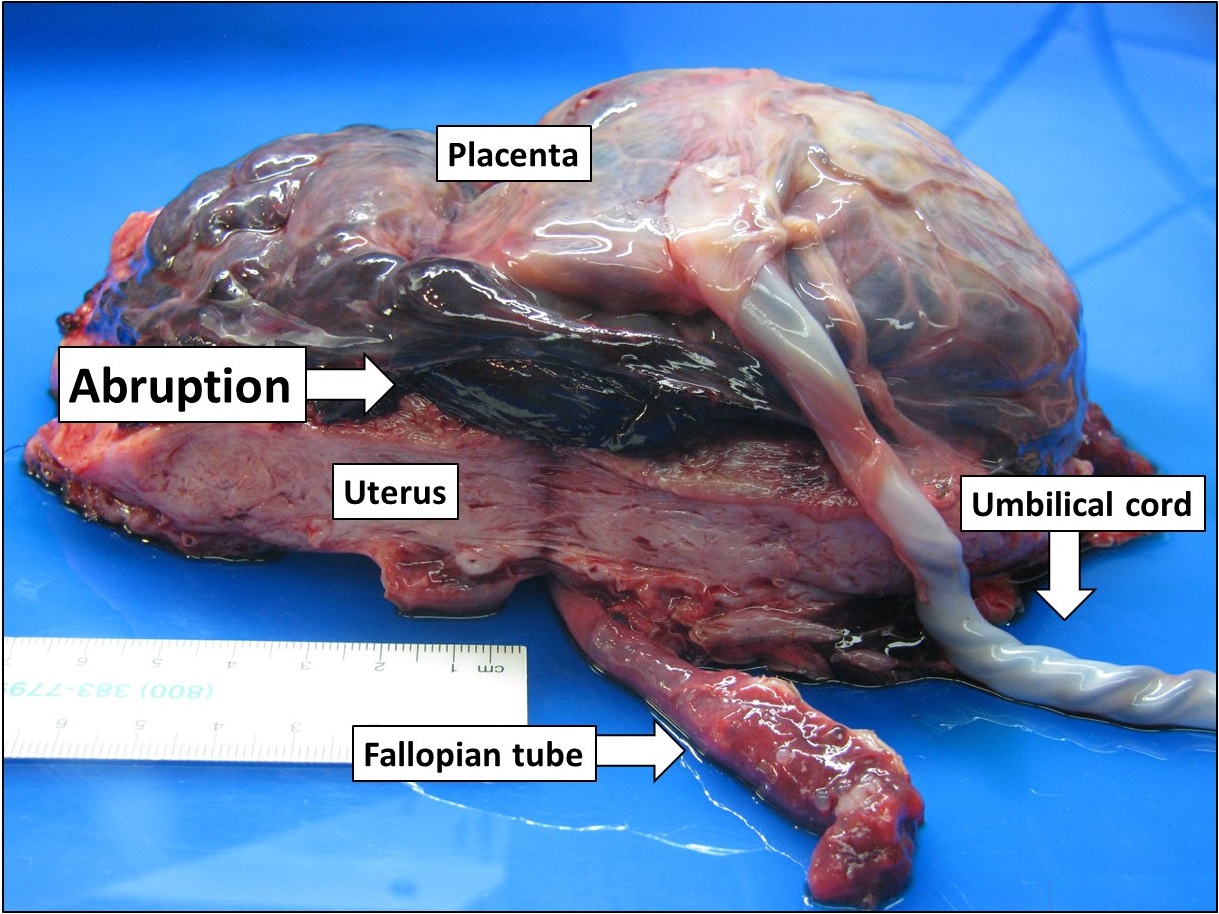
Uterine Tachysystole
Uterine Tachysystole is a condition of excessively frequent uterine contractions during pregnancy. It is most often seen in induced or augmented labor, though it can also occur during spontaneous labor, and this may result in fetal hypoxia and acidosis. This may have serious effects on both the mother and the fetus including hemorrhaging and death. There are still major gaps in understanding treatment as well as clinical outcomes of this condition. Uterine tachysystole is defined as more than 5 contractions in 10 minutes, averaged over a 30-minute period. Signs and Symptoms Excessive contractions may be a sign of placental abruption or obstructed labor potentially leading to Uterine Tachysystole. During a normal contraction, the mean intracerebral oxygen saturation may drop by about 54%. However, during tachysystole, the saturation may fall as low as 18%. Fetal hypoxia is often associated with uterine tachysystole as well aneonatal brachial plexusinjury. Cause and Correlati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Obstetricians And Gynaecologists Of Canada
The Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada (SOGC) is a national medical society in Canada, representing over 4,000 obstetricians/gynaecologists, family physicians, nurses, midwives, and allied health professionals in the field of sexual reproductive health. Having been operational for more than 7 decades, the number of participants might rise surpassing the original number making it one of the most valuable society of Obstetricians in the world. Status and activities The SOGC has been granted accreditation by the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada (RCPSC) as a Continued Professional Development provider for physicians and health care providers in Canada. The Society offers professional educational including the Annual Clinical Meeting, RCPSC-accredited Continuing Medical Education (CME) programs, e-learning modules, and its Managing Obstetrical Risk Efficiently (MOREOB) patient safety program. The SOGC produces national clinical guidelines for both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Obstetricians And Gynaecologists
The Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) is a professional association based in London, United Kingdom. Its members, including people with and without medical degrees, work in the field of obstetrics and gynaecology, that is, pregnancy, childbirth, and female sexual and reproductive health. The college has over 16,000 members in over 100 countries with nearly 50% of those residing outside the British Isles. Her Royal Highness the Princess of Wales became the RCOG's patron in 2018. The college's primary object is given as "The encouragement of the study and the advancement of the science and practice of obstetrics and gynaecology", although its governing documents impose no specific restrictions on its operation. Its present offices are based in London Bridge. Previously, the offices were located near Regent's Park in Central London. History The British College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists was founded in September 1929 by Professor William Blair-B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |