|
Electrical Phenomena
This is a list of electrical phenomena. Electrical phenomena are a somewhat arbitrary division of electromagnetic phenomenon, electromagnetic phenomena. Some examples are: *Atmospheric electricity *Biefeld–Brown effect — Thought by the person who coined the name, Thomas Townsend Brown, to be an anti-gravity effect, it is generally attributed to electrohydrodynamics (EHD) or sometimes electro-fluid-dynamics, a counterpart to the well-known magneto-hydrodynamics. *Bioelectrogenesis — The generation of electricity by living organisms. *Capacitive coupling — Transfer of energy within an electrical network or between distant networks by means of displacement current. *Contact electrification — The phenomenon of electrification by contact. When two objects were touched together, sometimes the objects became spontaneously charged (οne negative charge, one positive charge). *Corona discharge, Corona effect — Build-up of charges in a high-voltage conductor (common i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of either a positive or negative electric charge produces an electric field. The motion of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. In most applications, Coulomb's law determines the force acting on an electric charge. Electric potential is the Work (physics), work done to move an electric charge from one point to another within an electric field, typically measured in volts. Electricity plays a central role in many modern technologies, serving in electric power where electric current is used to energise equipment, and in electronics dealing w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, electrical insulation, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron beam, electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A archaism, term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains Electronics, electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joule Heating
Joule heating (also known as resistive heating, resistance heating, or Ohmic heating) is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor (material), conductor produces heat. Joule's first law (also just Joule's law), also known in countries of the former Soviet Union, USSR as the Joule–Lenz law, Assuming the element behaves as a perfect resistor and that the power is completely converted into heat, the formula can be re-written by substituting Ohm's law, V = I R , into the generalized power equation: P = IV = I^2R = V^2/R where ''R'' is the electrical resistance and conductance, resistance. Voltage can be increased in DC circuits by connecting batteries or solar panels in series. Alternating current When current varies, as it does in AC circuits, P(t) = U(t) I(t) where ''t'' is time and ''P'' is the instantaneous active power being converted from electrical energy to heat. Far more often, the ''average'' power is of more interest than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Induction Heating
Induction heating is the process of heating electrically conductive materials, namely metals or semi-conductors, by electromagnetic induction, through heat transfer passing through an inductor that creates an electromagnetic field within the coil to heat up and possibly melt steel, copper, brass, graphite, gold, silver, aluminum, or carbide. An important feature of the induction heating process is that the heat is generated inside the object itself, instead of by an external heat source via heat conduction. Thus objects can be heated very rapidly. In addition, there need not be any external contact, which can be important where contamination is an issue. Induction heating is used in many industrial processes, such as heat treatment in metallurgy, Czochralski process, Czochralski crystal growth and zone refining used in the semiconductor industry, and to melt refractory metals that require very high temperatures. It is also used in induction cooking, induction cooktops. An induct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the electric current, and therefore follows any changes in the magnitude of the current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) (voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called ''back EMF''. Inductance is defined as the ratio of the induced voltage to the rate of change of current causing it. It is a proportionality constant that depends on the geometry of circuit conductors (e.g., cross-section area and length) and the magnetic permeability of the conductor and nearby materials. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage, potential difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is wikt:transverse, transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field wikt:perpendicular, perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879. The ''Hall coefficient'' is defined as the ratio of the induced electric field to the product of the current density and the applied magnetic field. It is a characteristic of the material from which the conductor is made, since its value depends on the type, number, and properties of the charge carriers that constitute the current. Discovery Wires carrying current in a magnetic field experience a mechanical force perpendicular to both the current and magnetic field. In the 1820s, André-Marie Ampère observed this underlying mechanism that led to the discovery of the Hall effect. However it was not until a solid mathematical basis for electromagnetism was system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferroelectric Effect
In physics and materials science, ferroelectricity is a characteristic of certain materials that have a Spontaneous process, spontaneous Polarization density, electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field. All ferroelectrics are also Piezoelectricity, piezoelectric and Pyroelectricity, pyroelectric, with the additional property that their natural electrical polarization is reversible. The term is used in analogy to ferromagnetism, in which a material exhibits a permanent magnetic moment. Ferromagnetism was already known when ferroelectricity was discovered in 1920 in Rochelle salt by American physicist Joseph Valasek.See and Thus, the prefix ''ferro'', meaning iron, was used to describe the property despite the fact that most ferroelectric materials do not contain iron. Materials that are both ferroelectric ''and'' ferromagnetic are known as multiferroics. Polarization When most materials are Polarization density, electrically pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmission must be taken into account. This applies especially to radio-frequency engineering because the short wavelengths mean that wave phenomena arise over very short distances (this can be as short as millimetres depending on frequency). However, the Telegrapher's equations, theory of transmission lines was historically developed to explain phenomena on very long electrical telegraph, telegraph lines, especially submarine telegraph cables. Transmission lines are used for purposes such as connecting Transmitter, radio transmitters and Radio receiver, receivers with their antenna (radio), antennas (they are then called feed lines or feeders), distributing cable television signals, trunking, trunklines routing calls between telephone switchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferranti Effect
In electrical engineering, the Ferranti effect is the increase in voltage occurring at the receiving end of a very long (> 200 km) AC electric power transmission line, relative to the voltage at the sending end, when the load is very small, or no load is connected. It can be stated as a factor, or as a percent increase. It was first observed during the installation of underground cables in Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti's 10,000-volt AC power distribution system in 1887. The capacitive line charging current produces a voltage drop across the line inductance that is in-phase with the sending-end voltage, assuming negligible line resistance. Therefore, both line inductance and capacitance are responsible for this phenomenon. This can be analysed by considering the line as a transmission line where the source impedance is lower than the load impedance (unterminated). The effect is similar to an electrically short version of the quarter-wave impedance transformer, but with smaller vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
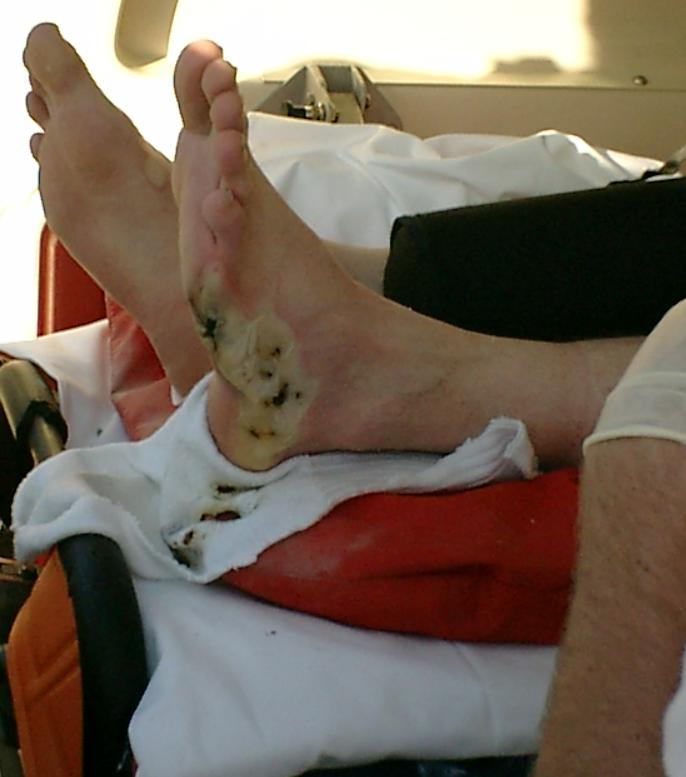
Electric Shock
An electrical injury (electric injury) or electrical shock (electric shock) is damage sustained to the skin or internal organs on direct contact with an electric current. The injury depends on the Current density, density of the current, tissue resistance and duration of contact. Very small currents may be imperceptible or only produce a light tingling sensation. However, a shock caused by low and otherwise harmless current could startle an individual and cause injury due to jerking away or falling. A strong electric shock can often cause painful Spasm, muscle spasms severe enough to Joint dislocation, dislocate joints or even to Bone fracture, break bones. The loss of muscle control is the reason that a person may be unable to release themselves from the electrical source; if this happens at a height as on a Overhead power line, power line they can be thrown off. Larger currents can result in tissue damage and may trigger ventricular fibrillation or cardiac arrest. If death res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Conduction
Electrical resistivity (also called volume resistivity or specific electrical resistance) is a fundamental specific property of a material that measures its electrical resistance or how strongly it resists electric current. A low resistivity indicates a material that readily allows electric current. Resistivity is commonly represented by the Greek letter (rho). The SI unit of electrical resistivity is the ohm-metre (Ω⋅m). For example, if a solid cube of material has sheet contacts on two opposite faces, and the resistance between these contacts is , then the resistivity of the material is . Electrical conductivity (or specific conductance) is the reciprocal of electrical resistivity. It represents a material's ability to conduct electric current. It is commonly signified by the Greek letter (sigma), but ( kappa) (especially in electrical engineering) and (gamma) are sometimes used. The SI unit of electrical conductivity is siemens per metre (S/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |