|
Early Expansions Of Hominins Out Of Africa
Several expansions of populations of archaic humans (genus ''Homo'') out of Africa and throughout Eurasia took place in the course of the Lower Paleolithic, and into the beginning Middle Paleolithic, between about 2.1 million and 0.2 million years ago (Ma). These expansions are collectively known as Out of Africa I, in contrast to the expansion of ''Homo sapiens'' (anatomically modern humans) into Eurasia, which may have begun shortly after 0.2 million years ago (known in this context as "Out of Africa II"). The earliest presence of ''Homo'' (or indeed any hominin) outside of Africa dates to close to 2 million years ago. A 2018 study claims human presence at Shangchen, central China, as early as 2.12 Ma based on magnetostratigraphic dating of the lowest layer containing stone artefacts. "Eight major magnetozones are recorded in the Shangchen section, four of which have normal polarity (N1 to N4) and four of which have reversed polarity (R1 to R4). By comparison with the geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreading Homo Sapiens La
Spread may refer to: Places * Spread, West Virginia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Spread'' (film), a 2009 film. * ''$pread'', a quarterly magazine by and for sex workers * "Spread", a song by OutKast from their 2003 album ''Speakerboxxx/The Love Below'' * Spreadability, a concept in media studies * Page spread, an aspect of book design Finance * Spread, the difference in price between related securities, as in: ** Bid–offer spread, between the buying and selling price of a commodity and/or security ** Credit spread (bond), on bonds ** Option-adjusted spread, on mortgage backed securities where the borrower has the right to repay in full ** Options spread, building blocks of option trading strategies. ** Spread trade, between two related securities or commodities *** Spread option, payoff is based on the difference in price between two underlying assets ** Yield spread, difference in percentage rate of return of two instruments ** Z-spread, on mortgage backed securit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Antecessor
''Homo antecessor'' (Latin "pioneer man") is an extinct species of archaic human recorded in the Spanish Sierra de Atapuerca, a productive archaeological site, from 1.2 to 0.8 million years ago during the Early Pleistocene. Populations of this species may have been present elsewhere in Western Europe, and were among the first to colonise that region of the world (hence, the name). The first fossils were found in the Gran Dolina cave in 1994, and the species was formally described in 1997 as the last common ancestor of modern humans and Neanderthals, supplanting the more conventional '' H. heidelbergensis'' in this position. ''H. antecessor'' has since been reinterpreted as an offshoot from the modern human line, although probably one branching off just before the modern human/Neanderthal split. Despite being so ancient, the face is unexpectedly similar to that of modern humans rather than other archaic humans—namely in its overall flatness as well as the curving of the cheek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 revision of the geologic time sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomekwi
Lomekwi 3 is the name of an archaeological site in Kenya where ancient stone tools have been discovered dating to 3.3 million years ago, which make them the oldest ever found. Discovery In July 2011, a team of archeologists led by Sonia Harmand and Jason Lewis of Stony Brook University, United States, were heading to a site near Kenya's Lake Turkana near where ''Kenyanthropus platyops'' fossils had previously been found. The group made a wrong turn on the way and ended up at a previously unexplored region and decided to do some surveying. They quickly found some stone artifacts on the site, which they named Lomekwi 3. A year later they returned to the site for a full excavation. Harmand presented her findings at the annual meeting of the Paleoanthropology Society on April 14, 2015 and published the full announcement and results on the cover of Nature on May 21, 2015. Artifacts Around 20 well preserved artifacts have been dug up at Lomekwi 3 including anvils, cores, and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecus Afarensis
''Australopithecus afarensis'' is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not take place until the 1970s. From 1972 to 1977, the International Afar Research Expedition—led by anthropologists Maurice Taieb, Donald Johanson and Yves Coppens—unearthed several hundreds of hominin specimens in Hadar, Ethiopia, the most significant being the exceedingly well-preserved skeleton AL 288-1 ("Lucy") and the site AL 333 ("the First Family"). Beginning in 1974, Mary Leakey led an expedition into Laetoli, Tanzania, and notably recovered fossil trackways. In 1978, the species was first described, but this was followed by arguments for splitting the wealth of specimens into different species given the wide range of variation which had been attributed to sexual dimorphism (normal differences between males and females). ''A. a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gracile Australopithecines
''Australopithecus'' (, ; ) is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genus ''Homo'' (which includes modern humans) emerged within ''Australopithecus'', as sister to e.g. ''Australopithecus sediba''. Also the genera '' Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' emerged within ''Australopithecus''. ''Australopithecus'' is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes ''Ardipithecus'', though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of ''Australopithecus''. Species include '' A. garhi'', '' A. africanus'', '' A. sediba'', '' A. afarensis, A. anamensis, A. bahrelghazali'' and '' A. deyiremeda''. Debate exists as to whether some ''Australopithecus'' species should be reclassified into new genera, or if ''Paranthropus'' and ''Kenyanthropus'' are synonymous with ''Australopithecus'', in part because of the taxonomic inconsistency. The earliest known member of the genus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
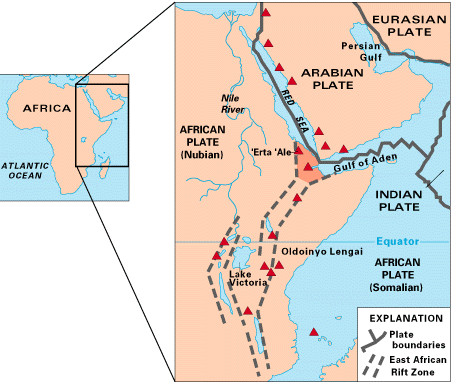
Afar Depression
The Afar Triangle (also called the Afar Depression) is a geological depression caused by the Afar Triple Junction, which is part of the Great Rift Valley in East Africa. The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans. The Depression overlaps the borders of Eritrea, Djibouti and the entire Afar Region of Ethiopia; and it contains the lowest point in Africa, Lake Assal, Djibouti, at below sea level. The Awash River is the main waterflow into the region, but it runs dry during the annual dry season, and ends as a chain of saline lakes. The northern part of the Afar Depression is also known as the Danakil Depression. The lowlands are affected by heat, drought, and minimal air circulation, and contain the hottest places (year-round average temperatures) of anywhere on Earth. The Afar Triangle is bordered as follows (see the top ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australopithecina
Australopithecina or Hominina is a subtribe in the tribe Hominini. The members of the subtribe are generally ''Australopithecus'' (cladistically including the genera ''Homo'', ''Paranthropus'', and ''Kenyanthropus''), and it typically includes the earlier '' Ardipithecus'', '' Orrorin'', '' Sahelanthropus'', and '' Graecopithecus''. All these closely related species are now sometimes collectively termed australopiths or homininians. They are the extinct, close relatives of humans and, with the extant genus ''Homo'', comprise the human clade. Members of the human clade, i.e. the Hominini after the split from the chimpanzees, are now called Hominina (''see Hominidae; terms "hominids" and hominins''). While none of the groups normally directly assigned to this group survived, the australopiths do not appear to be literally extinct (in the sense of having no living descendants) as the genera ''Kenyanthropus'', ''Paranthropus'' and ''Homo'' probably emerged as sister of a late ''Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trachilos Footprints
The Trachilos footprints are possibly tetrapod footprints which show hominin-like characteristics from the late Miocene on the western Crete, close to the village of Trachilos, west of Kissamos, in the Chania Prefecture. Researchers describe the tracks as representing at least one apparent bipedal hominin or an unknown primate. The stratum in which the footprints were found was dated to about 5.7 million years ago, which predates the previously earliest discovered hominin footprints by about two million years. Later studies show that the footprints might be more than 6 million years old. The researchers of the tracks suggest that it may imply the possibility of hominin evolution outside of Africa, contrary to the current theory. Discovery The tracks were originally discovered by Gerard D. Gierliński, from the Polish Research Institute in Warsaw in 2002. During a visit to Trachilos on Crete, Gierliński found the tracks, and as he was not planning on staying in Trachilos, Gierl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homininae
Homininae (), also called "African hominids" or "African apes", is a subfamily of Hominidae. It includes two tribes, with their extant as well as extinct species: 1) the tribe Hominini (with the genus ''Homo'' including modern humans and numerous extinct species; the subtribe Hominina, comprising at least two extinct genera; and the subtribe Panina, represented only by the genus ''Pan'', which includes chimpanzees and bonobos)―and 2) the tribe Gorillini (gorillas). Alternatively, the genus '' Pan'' is sometimes considered to belong to its own third tribe, Panini. Homininae comprises all hominids that arose after orangutans (subfamily Ponginae) split from the line of great apes. The Homininae cladogram has three main branches, which lead to gorillas (through the tribe Gorillini), and to humans and chimpanzees via the tribe Hominini and subtribes Hominina and Panina (see the evolutionary tree below). There are two living species of Panina (chimpanzees and bonobos) and two livin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ouranopithecus
''Ouranopithecus'' ("celestial ape" from Ancient Greek οὐρανός (ouranós), "sky, heaven" + πίθηκος (píthēkos),"ape") is a genus of extinct Eurasian great ape represented by two species, ''Ouranopithecus macedoniensis'', a late Miocene (9.6–8.7 mya) hominoid from Greece and ''Ouranopithecus turkae'', also from the late Miocene (8.7–7.4 mya) of Turkey. The first specimen ''O. macedoniensis'' was discovered by French palaeontologists Louis de Bonis and Jean Melentis in 1977, and ''O. turkae'' by Turkish team led by Erksin Savaş Güleç in 2007. For a long time it was considered as similar (synonymous) to ''Graecopithecus'' and member of the genus ''Sivapithecus,'' which more discoveries proved otherwise. Description and systematics Based on ''O. macedoniensis dental and facial anatomy, it has been suggested that ''Ouranopithecus'' was actually a dryopithecine. However, it is probably more closely related to the Ponginae. Some researchers consider ''O. macedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
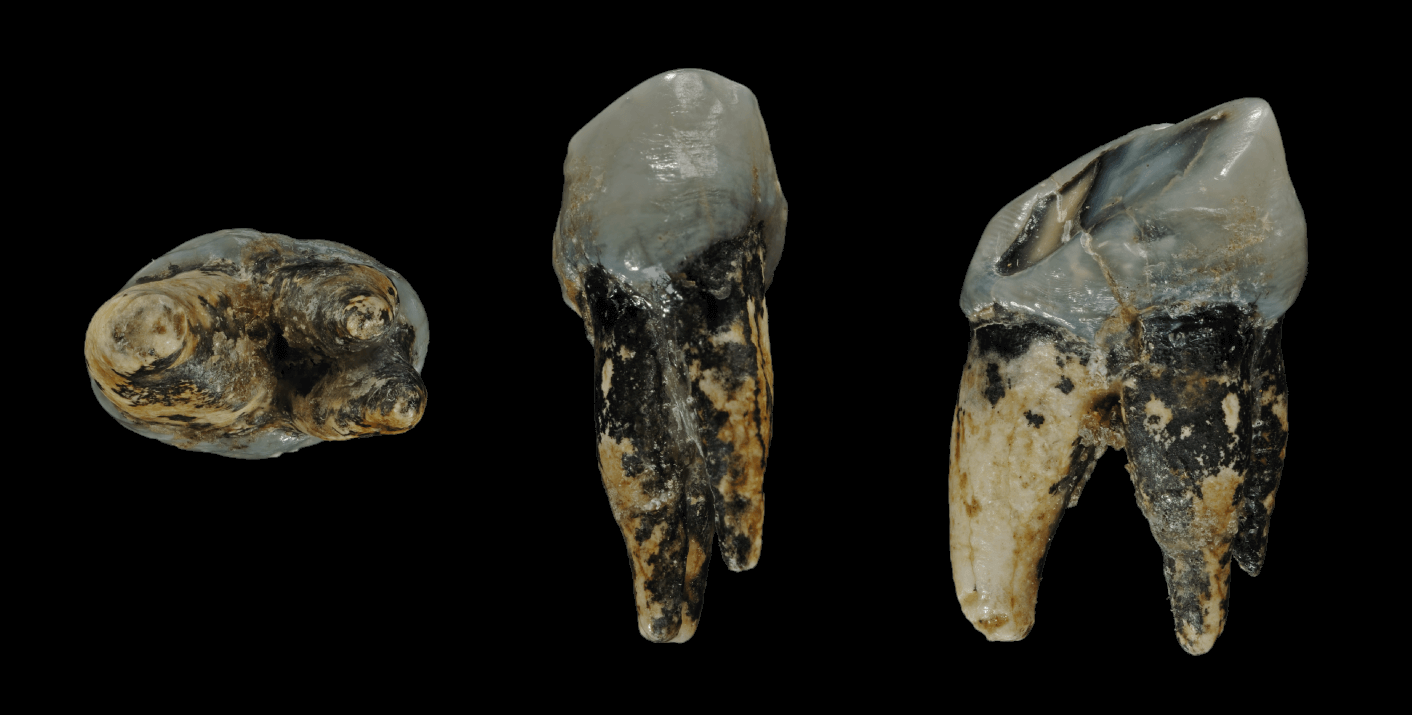
Graecopithecus
''Graecopithecus'' is an extinct species of hominid that lived in southeast Europe during the late Miocene around 7.2 million years ago. Originally identified by a single lower jaw bone bearing a molar tooth found in Pyrgos Vasilissis, Athens, Greece, in 1944, other tooth specimens were discovered from Azmaka quarry in Bulgaria in 2012. With only little and badly preserved materials to reveal its nature, it is considered as "the most poorly known European Miocene hominoids." The creature was popularly nicknamed 'El Graeco' (word play on the Spanish painter El Greco) by scientists. In 2017, an international team of palaeontologists led by Madelaine Böhme of the Eberhard-Karls-University Tübingen, Germany, published a detailed analysis of the teeth and age of the specimens, and came to the conclusion that it could be the oldest hominin, meaning that it could be the oldest direct ancestors of humans after splitting from that of the chimpanzees. Their simultaneous study also cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)