|
ELIZA
ELIZA is an early natural language processing computer program created from 1964 to 1966 at the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory by Joseph Weizenbaum. Created to demonstrate the superficiality of communication between humans and machines, Eliza simulated conversation by using a "pattern matching" and substitution methodology that gave users an illusion of understanding on the part of the program, but had no built in framework for contextualizing events. Directives on how to interact were provided by "scripts", written originally in MAD-Slip, which allowed ELIZA to process user inputs and engage in discourse following the rules and directions of the script. The most famous script, DOCTOR, simulated a Rogerian psychotherapist (in particular, Carl Rogers, who was well known for simply parroting back at patients what they had just said), and used rules, dictated in the script, to respond with non-directional questions to user inputs. As such, ELIZA was one of the first chatterb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELIZA Conversation
ELIZA is an early natural language processing computer program created from 1964 to 1966 at the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory by Joseph Weizenbaum. Created to demonstrate the superficiality of communication between humans and machines, Eliza simulated conversation by using a "pattern matching" and substitution methodology that gave users an illusion of understanding on the part of the program, but had no built in framework for contextualizing events. Directives on how to interact were provided by "scripts", written originally in MAD-Slip, which allowed ELIZA to process user inputs and engage in discourse following the rules and directions of the script. The most famous script, DOCTOR, simulated a Rogerian psychotherapist (in particular, Carl Rogers, who was well known for simply parroting back at patients what they had just said), and used rules, dictated in the script, to respond with non-directional questions to user inputs. As such, ELIZA was one of the first chatter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turing Test
The Turing test, originally called the imitation game by Alan Turing in 1950, is a test of a machine's ability to artificial intelligence, exhibit intelligent behaviour equivalent to, or indistinguishable from, that of a human. Turing proposed that a human evaluator would judge natural language conversations between a human and a machine designed to generate human-like responses. The evaluator would be aware that one of the two partners in conversation was a machine, and all participants would be separated from one another. The conversation would be limited to a text-only channel, such as a computer keyboard and screen, so the result would not depend on the machine's ability to render words as speech. If the evaluator could not reliably tell the machine from the human, the machine would be said to have passed the test. The test results would not depend on the machine's ability to give correct question answering, answers to questions, only on how closely its answers resembled t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chatterbot
A chatbot or chatterbot is a software application used to conduct an on-line chat conversation via text or text-to-speech, in lieu of providing direct contact with a live human agent. Designed to convincingly simulate the way a human would behave as a conversational partner, chatbot systems typically require continuous tuning and testing, and many in production remain unable to adequately converse, while none of them can pass the standard Turing test. The term "ChatterBot" was originally coined by Michael Mauldin (creator of the first Verbot) in 1994 to describe these conversational programs. Chatbots are used in dialog systems for various purposes including customer service, request routing, or information gathering. While some chatbot applications use extensive word-classification processes, natural-language processors, and sophisticated AI, others simply scan for general keywords and generate responses using common phrases obtained from an associated library or database. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Weizenbaum
Joseph Weizenbaum (8 January 1923 – 5 March 2008) was a German American computer scientist and a professor at MIT. The Weizenbaum Award is named after him. He is considered one of the fathers of modern artificial intelligence. Life and career Born in Berlin, Germany to Jewish parents, he escaped Nazi Germany in January 1936, immigrating with his family to the United States. He started studying mathematics in 1941 at Wayne State University, in Detroit, Michigan. In 1942, he interrupted his studies to serve in the U.S. Army Air Corps as a meteorologist, having been turned down for cryptology work because of his "enemy alien" status. After the war, in 1946, he returned to Wayne State, obtaining his B.S. in Mathematics in 1948, and his M.S. in 1950. Around 1952, as a research assistant at Wayne, Weizenbaum worked on analog computers and helped create a digital computer. In 1956 he worked for General Electric on ERMA, a computer system that introduced the use of the magnetically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PARRY
PARRY was an early example of a chatbot, implemented in 1972 by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby. History PARRY was written in 1972 by psychiatrist Kenneth Colby, then at Stanford University. While ELIZA was a tongue-in-cheek simulation of a Rogerian therapist, PARRY attempted to simulate a person with paranoid schizophrenia. The program implemented a crude model of the behavior of a person with paranoid schizophrenia based on concepts, conceptualizations, and beliefs (judgements about conceptualizations: accept, reject, neutral). It also embodied a conversational strategy, and as such was a much more serious and advanced program than ELIZA. It was described as "ELIZA with attitude". PARRY was tested in the early 1970s using a variation of the Turing Test. A group of experienced psychiatrists analysed a combination of real patients and computers running PARRY through teleprinters. Another group of 33 psychiatrists were shown transcripts of the conversations. The two groups were then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to process and analyze large amounts of natural language data. The goal is a computer capable of "understanding" the contents of documents, including the contextual nuances of the language within them. The technology can then accurately extract information and insights contained in the documents as well as categorize and organize the documents themselves. Challenges in natural language processing frequently involve speech recognition, natural-language understanding, and natural-language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
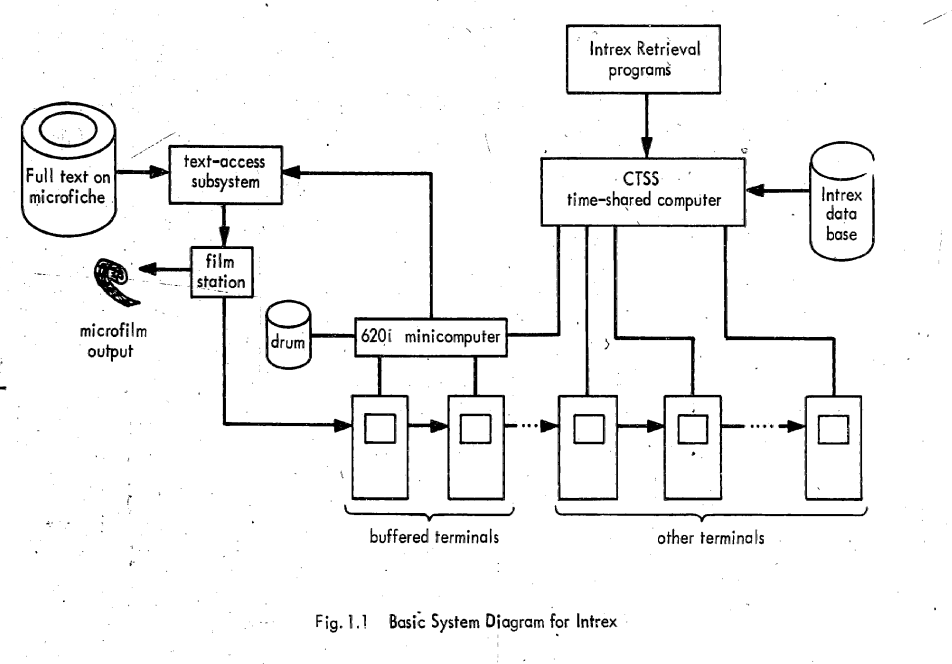
Compatible Time-Sharing System
The Compatible Time-Sharing System (CTSS) was the first general purpose time-sharing operating system. Compatible Time Sharing referred to time sharing which was compatible with batch processing; it could offer both time sharing and batch processing concurrently. CTSS was developed at the MIT Computation Center ("Comp Center"). CTSS was first demonstrated on MIT's modified IBM 709 in November 1961. The hardware was replaced with a modified IBM 7090 in 1962 and later a modified IBM 7094 called the "blue machine" to distinguish it from the Project MAC CTSS IBM 7094. Routine service to MIT Comp Center users began in the summer of 1963 and was operated there until 1968. A second deployment of CTSS on a separate IBM 7094 that was received in October 1963 (the "red machine") was used early on in Project MAC until 1969 when the red machine was moved to the Information Processing Center and operated until July 20, 1973. CTSS ran on only those two machines however there were remote CTSS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Emacs
GNU Emacs is a free software text editor. It was created by GNU Project founder Richard Stallman, based on the Emacs editor developed for Unix operating systems. GNU Emacs has been a central component of the GNU project and a flagship project of the free software movement. Its name has occasionally been shortened to GNUMACS. The tag line for GNU Emacs is "the extensible self-documenting text editor". History In 1976, Stallman wrote the first Emacs (“Editor MACroS”), and in 1984, began work on GNU Emacs, to produce a free software alternative to the proprietary Gosling Emacs. GNU Emacs was initially based on Gosling Emacs, but Stallman's replacement of its Mocklisp interpreter with a true Lisp interpreter required that nearly all of its code be rewritten. This became the first program released by the nascent GNU Project. GNU Emacs is written in C and provides Emacs Lisp, also implemented in C, as an extension language. Version 13, the first public release, was made on Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIT Computer Science And Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) is a research institute at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) formed by the 2003 merger of the Laboratory for Computer Science (LCS) and the Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (AI Lab). Housed within the Ray and Maria Stata Center, CSAIL is the largest on-campus laboratory as measured by research scope and membership. It is part of the Schwarzman College of Computing but is also overseen by the MIT Vice President of Research. Research activities CSAIL's research activities are organized around a number of semi-autonomous research groups, each of which is headed by one or more professors or research scientists. These groups are divided up into seven general areas of research: * Artificial intelligence * Computational biology * Graphics and vision * Language and learning * Theory of computation * Robotics * Systems (includes computer architecture, databases, distributed systems, networks and networked sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygmalion (play)
''Pygmalion'' is a play by Irish playwright George Bernard Shaw, named after the Greek mythological figure. It premiered at the Hofburg Theatre in Vienna on 16 October 1913 and was first presented in German on stage to the public in 1913. Its English-language premiere took place at Her Majesty's Theatre in the West End in April 1914 and starred Herbert Beerbohm Tree as phonetics professor Henry Higgins and Mrs Patrick Campbell as Cockney flower girl Eliza Doolittle. In ancient Greek mythology, Pygmalion fell in love with one of his sculptures, which then came to life. The general idea of that myth was a popular subject for Victorian era British playwrights, including one of Shaw's influences, W. S. Gilbert, who wrote a successful play based on the story called '' Pygmalion and Galatea'' that was first presented in 1871. Shaw would also have been familiar with the musical ''Adonis'' and the burlesque version, ''Galatea, or Pygmalion Reversed''. Shaw's play has been adapted nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLIP (programming Language)
SLIP is a list processing computer programming language, invented by Joseph Weizenbaum in the 1960s. The name ''SLIP'' stands for Symmetric LIst Processor. It was first implemented as an extension to the Fortran programming language, and later embedded into MAD and ALGOL. The best known program written in the language is ELIZA, an early natural language processing computer program created by Weizenbaum at the MIT Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. General overview In a nutshell, SLIP consisted of a set of FORTRAN "accessor" functions which operated on circular doubly linked lists with fixed-size data fields. The "accessor" functions had direct and indirect addressing variants. List representation The list representation had four types of cell: a ''reader'', a ''header'', a ''sublist indicator'', and a ''payload'' cell. The header included a reference count field for garbage collection purposes. The sublist indicator allowed it to be able to represent nested lists, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogerian Psychotherapy
Person-centered therapy, also known as person-centered psychotherapy, person-centered counseling, client-centered therapy and Rogerian psychotherapy, is a form of psychotherapy developed by psychologist Carl Rogers beginning in the 1940s and extending into the 1980s. Person-centered therapy seeks to facilitate a client's self-actualizing tendency, "an inbuilt proclivity toward growth and fulfillment", via acceptance (''unconditional positive regard''), therapist ''congruence'' (genuineness), and empathic understanding. History and influences Person-centered therapy was developed by Carl Rogers in the 1940s and 1950s, and was brought to public awareness largely through his highly influential book ''Client-centered Therapy'', published in 1951. It has been recognized as one of the major types of psychotherapy (theoretical orientations), along with psychodynamic psychotherapy, psychoanalysis, classical Adlerian psychology, cognitive behavioral therapy, existential therapy, and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)