|
European Contribution To The International Space Station
The European contribution to the International Space Station comes from 10 members of the European Space Agency (ESA) and amounts to an 8% share in the programme. It consists of a number of modules (primarily the Columbus (ISS module), ''Columbus'' laboratory) in the US Orbital Segment, ATV supply ships, launchers, software and €8 billion. History In the 1980s, ESA devised plans for its own space station called Columbus Man-Tended Free Flyer, ''Columbus'' Man-Tended Free Flyer which could be attached to NASA's Space Station Freedom, Space Station ''Freedom''. America objected to ESA's using ''Columbus'' as a building block of a future European space station, and were concerned that they would facilitate the creation of a potential competitor if the crewed space outpost fulfilled its promise as supplier of commercially viable products, such as new materials and pharmaceuticals. Plans were scaled down as a result, and by 1988, Europe proposed to participate with three eleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
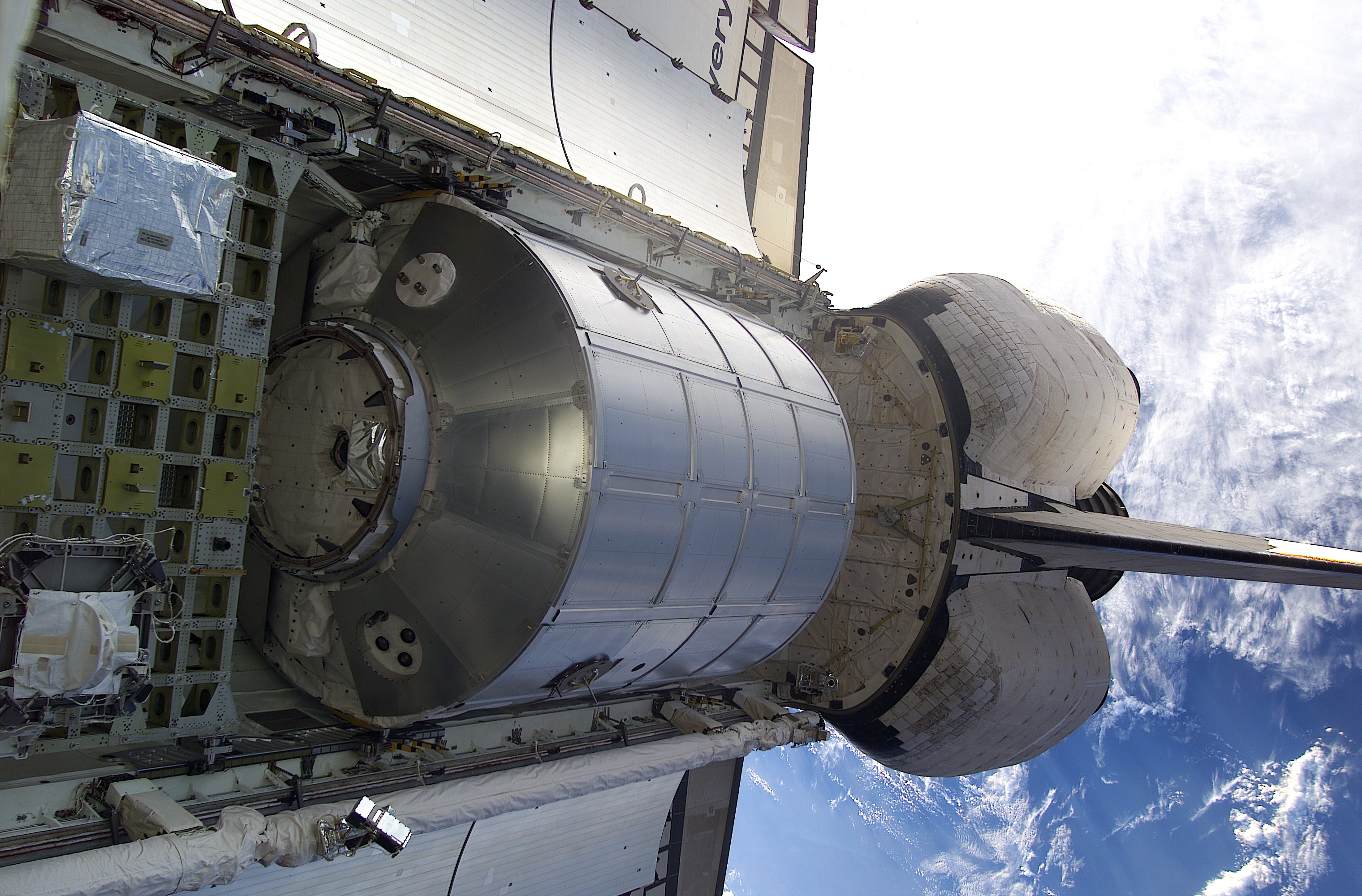
Columbus (ISS Module)
''Columbus'' is a science laboratory that is part of the International Space Station (ISS) and is the largest single contribution to the ISS made by the European Space Agency (ESA). Like the ''Harmony (ISS module), Harmony'' and ''Tranquility (ISS module), Tranquility'' modules, the ''Columbus'' laboratory was constructed in Turin, Italy by Thales Alenia Space. The functional equipment and software of the lab was designed by Airbus, EADS in Bremen, Germany. It was also integrated in Bremen before being flown to the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida in an Airbus Beluga. It was launched aboard on 7 February 2008, on flight STS-122. It is designed for ten years of operation. The module is controlled by the Columbus Control Centre, located at the German Space Operations Center, part of the German Aerospace Center in Oberpfaffenhofen near Munich, Germany. The European Space Agency has spent Euro, €1.4 billion (about United States dollar, US$2 billion) on building ''Columbu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-135 Final Flyaround Of ISS 1
STS-135 ( ISS assembly flight ULF7) was the 135th and final mission of the American Space Shuttle program. It used the orbiter ''Atlantis'' and hardware originally processed for the STS-335 contingency mission, which was not flown. STS-135 launched on July 8, 2011, and landed on July 21, 2011, following a one-day mission extension. The four-person crew was the smallest of any shuttle mission since STS-6 in April 1983. The mission's primary cargo was the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) '' Raffaello'' and a Lightweight Multi-Purpose Carrier (LMC), which were delivered to the International Space Station (ISS). The flight of ''Raffaello'' marked the only time that ''Atlantis'' carried an MPLM. Although the mission was authorized, it initially had no appropriation in the NASA budget, raising questions about whether the mission would fly. On January 20, 2011, program managers changed STS-335 to STS-135 on the flight manifest. This allowed for training and other mission speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space () is a joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (company), Leonardo (33%). The company is headquartered in Cannes, France. It provides space-based systems, including satellites and ground segments, used for telecommunications, navigation, earth observation, space exploration and scientific purposes. The company is the second largest industrial participant in the International Space Station (ISS), having produced numerous pressurized modules for the European Space Agency (ESA) including the Cupola (ISS module), Cupola, the node modules Harmony (ISS module), Harmony and Tranquility (ISS module), Tranquility, and the structure of the Columbus (ISS module), Columbus laboratory. It is a key contributor to Galileo (satellite navigation), Galileo, a European Satellite navigation, global satellite navigation system, being responsible for the ground segment in particular. In 2021, the company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATV-4 "Albert Einstein" Approaching The ISS
The ''Albert Einstein'' ATV, or Automated Transfer Vehicle 004 (ATV-004), was a European Space Agency, European uncrewed cargo spacecraft, cargo resupply spacecraft, named after the German-born physicist Albert Einstein. It was built to supply the International Space Station (ISS) with propellant, water, air, and dry cargo, and also to reboost the station's altitude with its thrusters. It was the fourth and penultimate ATV to be built, following the Edoardo Amaldi ATV, ''Edoardo Amaldi'', which was launched in March 2012. ''Albert Einstein'''s components were constructed in Turin, Italy, and Bremen, Germany, and underwent final assembly and testing in Bremen in 2012. The spacecraft left Bremen for Kourou on 31 August 2012 to begin launch preparations. ''Albert Einstein'' was launched on an Ariane 5ES rocket from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana at 21:52:11 UTC on 5 June 2013. The launch was conducted by Arianespace on behalf of the European Space Agency (ESA). At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iss016e034176
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, storage, spacecraft control, and airlock operations. The ISS has eight docking and berthing ports for visiting spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadarm-2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS) is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supports astronauts working in space, services instruments and other payloads attached to the ISS, and is used for external maintenance. Astronauts receive specialized training to perform these functions with the various systems of the MSS. The MSS is composed of three components: * the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), known as Canadarm2. * the Mobile Remote Servicer Base System (MBS). * the Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM, also known as "Dextre" or "Canada hand"). The system can move along rails on the Integrated Truss Structure on top of the US-provided Mobile Transporter cart, which hosts the MRS Base System. The system's control software was written in the Ada 95 programming language. The MSS was designed an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nauka (ISS Module)
''Nauka'' (), also known as the ''Multipurpose Laboratory Module, Upgrade'' (MLM-U, ), is the primary laboratory of the Russian Orbital Segment of the International Space Station (ISS). Serving alongside the ''Rassvet'' and ''Poisk'' mini-research modules, Nauka conducts scientific experiments and stores research equipment. Originally built as a backup for ''Zarya'', the very first module of the ISS, ''Nauka'''s construction was halted in the late 1990s, when it was about 70% complete. After exploring various options, Roscosmos decided to convert the partially completed module into a laboratory. While the initial target launch date was set for 2007, and outfitting equipment for Nauka was delivered by Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' in 2010 attached to the ''Rassvet'' module, numerous delays and technical issues delayed the launch by 14 years. ''Nauka'' finally launched on 21 July 2021 at 14:58:25UTC from the Baikonur Cosmodrome atop a Proton-M rocket. Like most of the Russian mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Robotic Arm
The European Robotic Arm (ERA) is a robotic arm that is attached to the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) of the International Space Station. Launched to the ISS in July 2021; it is the first robotic arm that is able to work on the Russian Segment of the station. The arm supplements the two Russian ''Strela'' cargo cranes that were originally installed on the '' Pirs'' module, but were later moved to the docking compartment ''Poisk'' and '' Zarya'' module. The ERA was developed for the European Space Agency (ESA) by a number of European space companies. Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands (formerly Dutch Space) designed and assembled the arm and was the prime contractor; it worked along with subcontractors in 8 countries. In 2010, a spare elbow joint for the arm and ERA's Portable Workpost was launched preemptively, attached to ''Rassvet'' or Mini Research Module 1(MRM-1). The '' Nauka Module'' and Prichal module serves as home base for ERA; originally, the arm was going to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadarm
Canadarm or Canadarm1 (officially Shuttle Remote Manipulator System or SRMS, also SSRMS) is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, the Canadarm was always paired with the Orbiter Boom Sensor System (OBSS), which was used to inspect the exterior of the shuttle for damage to the thermal protection system. Development In 1969, Canada was invited by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) to participate in the Space Shuttle program. At the time what that participation would entail had not yet been decided but a manipulator system was identified as an important component. Canadian company DSMA ATCON had developed a robot to load fuel into CANDU nuclear reactors; this robot attracted NASA's attention. In 1975, NASA and the Canadian National Research Council (NRC) signed a memorandum of understanding that Canada would develop and constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupola (ISS Module)
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout. The word derives, via Italian, from lower Latin ''cupula'' (classical Latin ''cupella''), (Latin ''cupa''), indicating a vault resembling an upside-down cup. The cylindrical drum underneath a larger cupola is called a tholobate. Background The cupola evolved during the Renaissance from the older oculus. Being weatherproof, the cupola was better suited to the wetter climates of northern Europe. The chhatri, seen in Indian architecture, fits the definition of a cupola when it is used atop a larger structure. Cupolas often serve as a belfry, belvedere, or roof lantern above a main roof. In other cases they may crown a spire, tower, or turret. Barns often have cupolas for ventilation. Cupolas can also appear as small buildings in their own right. The sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multi-Purpose Logistics Module
A Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) is a large pressurized container that was used on Space Shuttle missions to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station (ISS). Two MPLMs made a dozen trips in the Shuttle cargo bay and initially berthed to the ''Unity (ISS module), Unity'' and later the ''Harmony (ISS module), Harmony'' module on the ISS. Once attached, supplies were offloaded, and finished experiments and waste were reloaded. The MPLM was then transferred back into the Shuttle’s cargo bay for return to Earth. Three modules were built by Alenia Aeronautica for the Italian Space Agency (ASI). They were named ''Leonardo (ISS module), Leonardo'', Raffaello MPLM, ''Raffaello'', and ''Donatello''. The ''Leonardo'' module was modified in 2010 to turn it into the Leonardo (ISS module), Permanent Multipurpose Module (PMM) and was permanently attached to the ISS during the STS-133 mission in March 2011. In July 2011, the ''Raffaello'' module was the primary payload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Space Agency
The Italian Space Agency (; ASI) is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy. The agency cooperates with numerous national and international entities who are active in aerospace research and technology. Nationally, ASI is responsible for both drafting the National Aerospace Plan and ensuring it is carried out. To do this the agency operates as the owner/coordinator of a number of Italian space research agencies and assets such as CIRA as well as organising the calls and opportunities process for Italian industrial contractors on spaceflight projects. Internationally, the ASI provides Italy's delegation to the Council of the European Space Agency and to its subordinate bodies as well as representing the country's interests in foreign collaborations. ASI's main headquarters are located in Rome, Italy, and the agency also has direct control over two operational centres: the Centre for Space Geodesy (CGS) located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |