|
Environmental Policy Of The Government Of India
Environment policies of the Government of India include legislations related to environment. In the Directive Principles of State Policy, Article 48A says "the state shall endeavour to protect and improve the environment and to safeguard the forests and wildlife of the country"; Article 51-A states that "it shall be the duty of every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife and to have compassion for living creatures." India is one of the parties of the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) treaty. Prior to the CBD, India had different laws to govern the environment. The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, Indian Wildlife Protection Act 1972 protected the biodiversity. It was amended later multiple times. The National Forest Policy, 1988, 1988 National Forest Policy had conservation as its fundamental principle. In addition to these acts, the government passed the Environment Protection Act, 1986, Environment (Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention On Biological Diversity
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), known informally as the Biodiversity Convention, is a multilateral treaty. The Convention has three main goals: the conservation of biological diversity (or biodiversity); the sustainable use of its components; and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising from genetic resources. Its objective is to develop national strategies for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity, and it is often seen as the key document regarding sustainable development. The Convention was opened for signature at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro on 5 June 1992 and entered into force on 29 December 1993. The United States is the only UN member state which has not ratified the Convention. It has two supplementary agreements, the Cartagena Protocol and Nagoya Protocol. Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety, The Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety to the Convention on Biological Diversity is an international treaty governing the movements of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife Protection Act Of 1972
The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted for the protection of plants and animal species. Before 1972, India had only five designated national parks. Among other reforms, the Act established scheduled protected plant and hunting certain animal species or harvesting these species was largely outlawed. The Act provides for the protection of wild animals, birds and plants; and for matters connected or incidental thereto. It extends to the whole of India. It has six schedules which give varying degrees of protectionSchedule Iand part II oprovide absolute protection - offences under these are prescribed the highest penalties. Species listed ianare also protected, but the penalties are much lower. Animals unde(e.g. common crows, fruit bats, rats, and mice) are legally considered vermin and may be hunted freely. The specified endemic plants iare prohibited from cultivation and planting. The Enforcement authorities have the power to compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry In India
Forestry in India is a significant rural industry and a major environmental resource. India is one of the ten most forest-rich countries of the world. Together, India and 9 other countries account for 67 percent of the total forest area of the world. India's forest cover grew at 0.20% annually over 1990–2000,Global Forest Resources Assessment 2010 FAO Forestry Paper 163, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (2011), , page 21 and has grown at the rate of 0.7% per year over 2000–2010, after decades where forest degradation was a matter of serious concern. As of 2010, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations estimates Forest cover in India, India's forest cover to be about 68 million hectares, or 22% of the country's area [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Policies Of India
Policy is a deliberate system of guidelines to guide decisions and achieve rational outcomes. A policy is a statement of intent and is implemented as a procedure or protocol. Policies are generally adopted by a governance body within an organization. Policies can assist in both ''subjective'' and ''objective'' decision making. Policies used in subjective decision-making usually assist senior management with decisions that must be based on the relative merits of a number of factors, and as a result, are often hard to test objectively, e.g. work–life balance policy. Moreover, governments and other institutions have policies in the form of laws, regulations, procedures, administrative actions, incentives and voluntary practices. Frequently, resource allocations mirror policy decisions. Policies intended to assist in objective decision-making are usually operational in nature and can be objectively tested, e.g. a password policy. The term may apply to government, public sector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of India
The environment of India comprises some of the world's most biodiverse ecozones. The Deccan Traps, Gangetic Plains and the Himalayas are the major geographical features. The country faces different forms of pollution as its major environmental issue and is more vulnerable to the effects of climate change being a developing nation. India has laws protecting the environment and is one of the countries that signed the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) treaty. The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change and each particular state forest departments plan and implement environmental policies throughout the country. Features Biota India has some of the world's most biodiverse ecozones—desert, high mountains, highlands, tropical and temperate forests, swamplands, plains, grasslands, areas surrounding rivers and an island archipelago. It hosts three biodiversity hotspots: the Western Ghats, the Himalayas and the Indo-Burma region. These hotspots have numerous e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Council Of Forestry Research And Education
The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) is an autonomous organisation or governmental agency under the MoEFCC, Government of India. Headquartered in Dehradun, its functions are to conduct forestry research; transfer the technologies developed to the states of India and other user agencies; and to impart forestry education. The council has 9 research institutes and 4 advanced centres to cater to the research needs of different bio-geographical regions. These are located at Dehradun, Shimla, Ranchi, Jorhat, Jabalpur, Jodhpur, Bengaluru, Coimbatore, Prayagraj, Chhindwara, Aizawl, Hyderabad and Agartala. It's also the administrator and implementor of India's Green Credits Program. History ICFRE is the largest organisation responsible for forestry research in India. ICFRE was created in 1986, under the Central Ministry of Environment and Forests (Indians), to direct and manage research and education in forestry sector in India. ICFRE is headed by a Director ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Policy Of Narendra Modi
Narendra Damodardas Modi (born 17 September 1950) is an Indian politician who has served as the prime minister of India since 2014. Modi was the chief minister of Gujarat from 2001 to 2014 and is the member of parliament (MP) for Varanasi. He is a member of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) and of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS), a right-wing Hindutva paramilitary volunteer organisation. He is the longest-serving prime minister outside the Indian National Congress. Modi was born and raised in Vadnagar, Bombay State (present-day Gujarat), where he completed his secondary education. He was introduced to the RSS at the age of eight. Modi became a full-time worker for the RSS in Gujarat in 1971. The RSS assigned him to the BJP in 1985 and he rose through the party hierarchy, becoming general secretary in 1998. In 2001, Modi was appointed chief minister of Gujarat and elected to the legislative assembly soon after. His administration is considered complicit in the 2002 G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
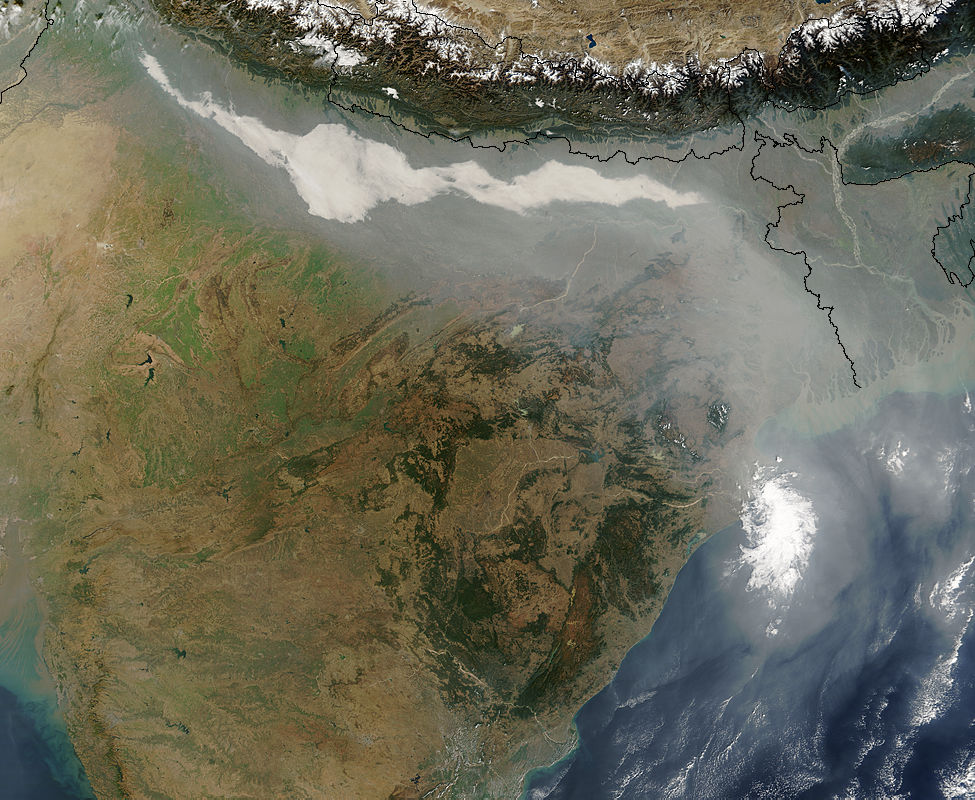
Environmental Issues In India
There are multiple environmental issues in India. Air pollution, water pollution, garbage, domestically prohibited goods and pollution of the natural environment are all challenges for India. Nature is also causing some drastic effects on India. The situation was worse between 1947 through 1995. According to data collected and environmental assessments studied by World Bank experts, between 1995 through 2010, India has made some of the fastest progress in addressing its environmental issues and improving its environmental quality in the world. However, pollution still remains a major challenge and opportunity for the country. Environmental issues are one of the primary causes of disease, health issues and long term livelihood impact for India. Law and policies British rule of India saw several laws related to the environment. Amongst the earliest ones were Shore Nuisance (Bombay and Kolkata) Act of 1853 and the Oriental Gas Company Act of 1857. The Indian Penal Code of 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Conservation Act, 1980
The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 an Act of the Parliament of India to provide for the conservation of forests and for matters connected therewith or ancillary or incidental thereto. It was further amended in 1988. This law extends to the whole of India. It was enacted by Parliament of India to control further deforestation Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ... of Forest Areas in India. The act came into force on 25 October 1980. It has five sections. History for conservation of forest This act was enacted by Parliament of India on 25 October 1980. SECTION Section 1 of the Act explains Short Title, Extent, and the Date of commencement. It states that: (1) This Act may be called the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980. (2) It extends to the whole of India. (3) It s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poaching
Poaching is the illegal hunting or capturing of wild animals, usually associated with land use rights. Poaching was once performed by impoverished peasants for subsistence purposes and to supplement meager diets. It was set against the hunting privileges of nobility and territorial rulers. Since the 1980s, the term "poaching" has also been used to refer to the illegal harvesting of wild plants. In agricultural terms, the term 'poaching' is also applied to the loss of soils or grass by the damaging action of feet of livestock, which can affect availability of productive land, water pollution through increased runoff and welfare issues for cattle. Stealing livestock, as in cattle raiding, classifies as theft rather than poaching. The United Nations' Sustainable Development Goal 15 enshrines the sustainable use of all wildlife. It targets the taking of action on dealing with poaching and trafficking of protected species of flora and fauna to ensure their availability for present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife Sanctuaries Of India
A wildlife sanctuary in India is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or other interest, which is reserved and managed for conservation and to provide opportunities for study or research. The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 provides for the establishment of protected areas in India. Wildlife sanctuaries of India, are classified as IUCN Category IV protected areas. 573 wildlife sanctuaries have been established, covering . Among these, Project Tiger governs 53 tiger reserves, which are of special significance for the conservation of the Bengal tiger. Additionally, there are 33 elephant reserves covering established under the Project Elephant, some of which overlap with the boundaries of declared wildlife sanctuaries and tiger reserves. Established in 1936, Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu was the first bird sanctuary in the country and the Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary was established later in 1940. Spanning , Kutch Desert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Parks Of India
National parks in India are International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) category II protected areas. India's first national park was established in 1936, now known as Jim Corbett National Park, in Uttarakhand. In 1970, India had only five national parks. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger in 1973 to safeguard the habitats of conservation reliant species. Further legislation strengthening protection for wildlife was introduced in the 1980s. There are 107 existing national parks in India covering an area of 44,402.95 km2 which is 1.35% of the geographical area of the country. In addition to the above, 75 other national parks covering an area of are proposed in the Protected Area Network Report. The network of parks will go up 176 after full implementation of the above report. State-wise List of National Parks Source: Andaman and Nicobar Islands(6) Andhra Pradesh(3) Arunachal Pradesh(2) Assam(8) Bihar(1) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |