|
Environmental Issues In Israel
The State of Israel is one of the smallest countries in the world, at around 20,000 sq. km, and has relatively few natural resources. Due to its limited space, semi-arid climate, high population growth and resource scarcity, Israel is highly susceptible to Ecological crisis, environmental crises. These include water shortages and pollution, shrinking of the Dead Sea, waste production and disposal, air pollution and population density. As a result, resource development, in particular water, has benefited from relatively high government support throughout most of the country's history. For example, Israel's water conservation and reclamation infrastructure is one of the most advanced in the world, with approximately half its water supply derived from reclaimed and treated waste water, brackish water and desalinated water. Additionally, Israel is party to several international agreements regarding air pollution and climate change, including the Kyoto Protocol, the UN Framework C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Desert Climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of Earth's land area, hot deserts are the second-most common type of climate on Earth after the Polar climate. There are two variations of a desert climate according to the Köppen climate classification: a hot desert climate (''BWh''), and a cold desert climate (''BWk''). To delineate "hot desert climates" from "cold desert climates", a mean annual temperature of is used as an isotherm so that a location with a ''BW'' type climate with the appropriate temperature above this isotherm is classified as "hot arid subtype" (''BWh''), and a location with the appropriate temperature below the isotherm is classified as "cold ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliyah
''Aliyah'' (, ; ''ʿălīyyā'', ) is the immigration of Jews from Jewish diaspora, the diaspora to, historically, the geographical Land of Israel or the Palestine (region), Palestine region, which is today chiefly represented by the Israel, State of Israel. Traditionally described as "the act of going up" (towards the Jerusalem in Judaism, Jewish holy city of Jerusalem), moving to the Land of Israel or "making aliyah" is one of the most basic tenets of Zionism. The opposite action – emigration by Jews from the Land of Israel – is referred to in the Hebrew language as ''yerida'' (). The Law of Return that was passed by the Knesset, Israeli parliament in 1950 gives all diaspora Jews, as well as their children and grandchildren, the right to relocate to Israel and acquire Israeli citizenship on the basis of connecting to their Jewish identity. For much of Jewish history, their history, most Jews have lived in the diaspora outside of the Land of Israel due to Jewish militar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish National Fund
The Jewish National Fund (JNF; , ''Keren Kayemet LeYisrael''; previously , ''Ha Fund HaLeumi'') is a non-profit organizationProfessor Alon Tal, The Mitrani Department of Desert Ecology, The Blaustein Institutes for Desert Research, Ben Gurion University of the Negev"National Report of Israel, Years 2003–2005, to the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD)"; State of Israel, July 2006 founded in 1901 to buy land and encourage Jewish settlement () in Ottoman Syria (later Mandatory Palestine, subsequently Israel and the Palestinian territories) for Jewish settlement. By 2007, it owned 13% of the total land in Israel. Since its inception, the JNF has planted over 240 million trees in Israel. It has also built 180 dams and reservoirs, developed of land and established more than 1,000 parks. In 2002, the Israeli government awarded the JNF the Israel Prize for lifetime achievement and special contribution to society and the State of Israel. The JNF has faced num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Templer Colonies In Palestine
The German Templer colonies in Palestine were the settlements established in Ottoman Palestine and Mandatory Palestine by the German Templers (Pietist sect), Pietist Templer movement in the late 19th and early 20th century. During and shortly after World War II, these colonies were depopulated, and its German residents deported to Australia. At its height, the Templer community in Palestine numbered 2,000. History Templer Colony in Haifa On 6 August 1868, the founders of the Templers, Christoph Hoffmann and Georg David Hardegg, their families and a group of fellow Templers, left Germany for Palestine, landing in Haifa on 30 October. They had already come to the conclusion that basing themselves in Jerusalem wouldn't be practical, planning to settle nearby, close to Nazareth, but during their journey they were advised that Haifa would be more suitable, having a good harbor and climate. Hoffmann and Hardegg purchased land at the foot of Mount Carmel and established German Colony, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afforestation
Afforestation is the establishment of a forest or stand of trees in an area where there was no recent tree cover. There are three types of afforestation: natural Regeneration (biology), regeneration, agroforestry and Tree plantation, tree plantations. Afforestation has many benefits. In the context of climate change, afforestation can be helpful for climate change mitigation through the route of carbon sequestration. Afforestation can also improve the local climate through increased rainfall and by being a barrier against high winds. The additional trees can also prevent or reduce topsoil erosion (from water and wind), floods and landslides. Finally, additional trees can be a habitat for wildlife, and provide employment and wood products. In comparison, reforestation means re-establishing forest that have either been cut down or lost due to natural causes, such as fire, storm, etc. Nowadays, the boundaries between afforestation and reforestation projects can be blurred as it ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Conifer And Mixed Forests
Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests is an ecoregion, in the Temperate coniferous forests, temperate coniferous forest biome, which occupies the high mountain ranges of North Africa. The term is also a botanically recognized plant association in the African and Mediterranean literature. Geography The Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests ecoregion consists of a series of enclaves in the coastal Rif Mountains and interior Middle Atlas and High Atlas of Morocco, the eastern Tell Atlas and eastern Saharan Atlas of Algeria, and the Kroumerie and Mogods, Mogod ranges of Tunisia. The Mediterranean woodlands and forests ecoregion surrounds the Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests at lower elevations. In the High Atlas, the Mediterranean conifer and mixed forests yield to the Mediterranean High Atlas juniper steppe at the highest elevations. Flora * Atlas cedar forests: These forests occur in the Rif Mountains, the Middle Atlas and the Tellien Atlas at elevations from 1200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
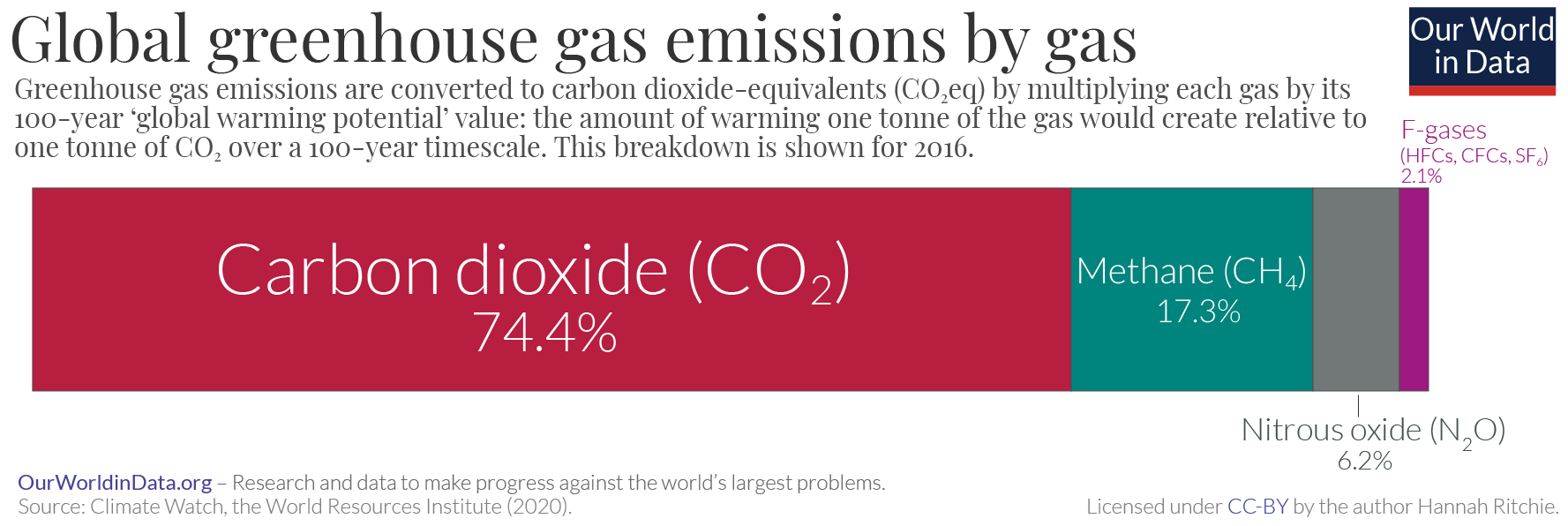
GHG Emissions
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from human activities intensify the greenhouse effect. This contributes to climate change. Carbon dioxide (), from burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, is the main cause of climate change. The largest annual emissions are from China followed by the United States. The United States has higher emissions per capita. The main producers fueling the emissions globally are large oil and gas companies. Emissions from human activities have increased atmospheric carbon dioxide by about 50% over pre-industrial levels. The growing levels of emissions have varied, but have been consistent among all greenhouse gases. Emissions in the 2010s averaged 56 billion tons a year, higher than any decade before. Total cumulative emissions from 1870 to 2022 were 703 (2575 ), of which 484±20 (1773±73 ) from fossil fuels and industry, and 219±60 (802±220 ) from land use change. Land-use change, such as deforestation, caused about 31% of cumulati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (also called the Paris Accords or Paris Climate Accords) is an international treaty on climate change that was signed in 2016. The treaty covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance. The Paris Agreement was negotiated by 196 parties at the 2015 United Nations Climate Change Conference near Paris, France. As of February 2023, 195 members of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are parties to the agreement. Of the three UNFCCC member states which have not ratified the agreement, the only major emitter is Iran. The United States, the second largest emitter, withdrew from the agreement in 2020, rejoined in 2021, and announced its withdrawal again in 2025. The Paris Agreement has a long-term temperature goal which is to keep the rise in global surface temperature to well below above pre-industrial levels. The treaty also states that preferably the limit of the increase should only be . These limits are defin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Oxides
Sulfur oxide Sulfur oxides (SOx) are a group of chemical compounds formed by the combination of sulfur and oxygen. The most common SOx are sulfur dioxide (SO2) and sulfur trioxide (SO3). SOx are produced naturally through volcanic activity and are also released into the atmosphere from human activities like burning fossil fuels and industrial processes. Sulfur oxide (SO''x'') refers to one or more of the following: * Lower sulfur oxides (S''n''O, S7O2 and S6O2) * Sulfur monoxide (SO) and its dimer, Disulfur dioxide (S2O2) * Sulfur dioxide (SO2) * Sulfur trioxide Sulfur trioxide (alternative spelling sulphur trioxide) is the chemical compound with the formula SO3. It has been described as "unquestionably the most conomicallyimportant sulfur oxide". It is prepared on an industrial scale as a precursor to ... (SO3) * Higher sulfur oxides (SO3 and SO4 and polymeric condensates of them) * Disulfur monoxide (S2O) {{Authority control * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Oxides
In atmospheric chemistry, is shorthand for nitric oxide () and nitrogen dioxide (), the nitrogen oxides that are most relevant for air pollution. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone. gases are usually produced from the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen during combustion of fuels, such as hydrocarbons, in air; especially at high temperatures, such as in car engines. In areas of high motor vehicle traffic, such as in large cities, the nitrogen oxides emitted can be a significant source of air pollution. gases are also produced naturally by lightning. does not include nitrous oxide (), a fairly inert oxide of nitrogen that contributes less severely to air pollution, notwithstanding its involvement in ozone depletion and high global warming potential. is the class of compounds comprising and the compounds produced from the oxidation of which include nitric acid, nitrous acid (HONO), din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alon Tal
Alon Tal (; born 12 July 1960) is an Israeli politician, academic and environmentalist. He was a member of the 24th Knesset between 2021 and 2022, representing the Blue and White political party; founder of the Israel Union for Environmental Defense and the Arava Institute for Environmental Studies; and co-founder of Ecopeace: Friends of the Earth–Middle East, This Is My Earth, the Israel Forum for Demography, Environment and Society, Aytzim: Ecological Judaism, and the Green Movement. Tal was appointed chair of the Department of Public Policy at Tel Aviv University in 2017. Early life Tal was born on July 12, 1960, and grew up in Raleigh, North Carolina, as Albert Rosenthal. He was active in the Young Judaea youth movement, served on its national executive board, and participated in its Israel program in 1977. After graduating from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 1980, he moved to Israel and enlisted in the Israeli army. He changed his name to Alon Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |