|
Endomembrane System
The endomembrane system is composed of the different membranes (endomembranes) that are suspended in the cytoplasm within a eukaryotic cell. These membranes divide the cell into functional and structural compartments, or organelles. In eukaryotes the organelles of the endomembrane system include: the nuclear membrane, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, endosomes, and plasma (cell) membrane among others. The system is defined more accurately as the set of membranes that forms a single functional and developmental unit, either being connected directly, or exchanging material through vesicle transport. Importantly, the endomembrane system does not include the membranes of plastids or mitochondria, but might have evolved partially from the actions of the latter (see below). The nuclear membrane contains a lipid bilayer that encompasses the contents of the nucleus. The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a synthesis and transport organelle that branches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
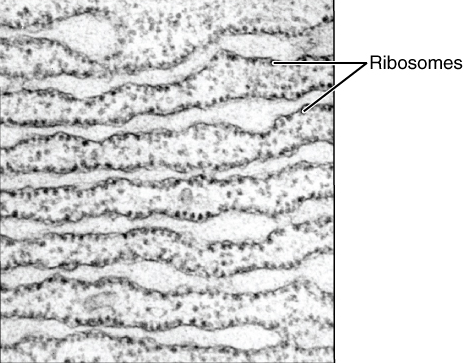
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are the cytosol (a gel-like substance), the cell's internal sub-structures, and various cytoplasmic inclusions. In eukaryotes the cytoplasm also includes the nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance, or cytoplasmic matrix, that remains after the exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, plant plasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzenkörper
The Spitzenkörper (German language, German for 'pointed body', SPK) is a structure found in fungal hyphae that is the organizing center for hyphal growth and morphogenesis. It consists of many small vesicle (biology), vesicles and is present in growing hyphal tips, during spore germination, and where branch formation occurs. Its position in the hyphal tip correlates with the direction of hyphal growth. The Spitzenkörper is a part of the endomembrane system in fungi. The vesicles are organized around a central area that contains a dense meshwork of microfilaments. Polysomes are often found closely to the posterior boundary of the Spitzenkörper core within the ''Ascomycota'', microtubules extend into and often through the Spitzenkörper and within the Ascomycota Woronin body, Woronin bodies are found in the apical region near the Spitzenkörper. The cytoplasm of the extreme apex is occupied almost exclusively by secretory vesicles. In the higher fungi (Ascomycota and Basidiomyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Envelope
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the nucleus, which encloses the genetic material. The nuclear envelope consists of two lipid bilayer membranes: an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. The space between the membranes is called the perinuclear space. It is usually about 10–50 nm wide. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. The nuclear envelope has many nuclear pores that allow materials to move between the cytosol and the nucleus. Intermediate filament proteins called lamins form a structure called the nuclear lamina on the inner aspect of the inner nuclear membrane and give structural support to the nucleus. Structure The nuclear envelope is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes, an inner nuclear membrane and an outer nuclear membrane. These membranes are connected to each other by nuclear pores. Two sets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diagram Human Cell Nucleus
A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word ''graph'' is sometimes used as a synonym for diagram. Overview The term "diagram" in its commonly used sense can have a general or specific meaning: * ''visual information device'' : Like the term "illustration", "diagram" is used as a collective term standing for the whole class of technical genres, including graphs, technical drawings and tables. * ''specific kind of visual display'' : This is the genre that shows qualitative data with shapes that are connected by lines, arrows, or other visual links. In science the term is used in both ways. For example, Anderson (1997) stated more generally: "diagrams are pictorial, yet abstract, represent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sterol
A sterol is any organic compound with a Skeletal formula, skeleton closely related to Cholestanol, cholestan-3-ol. The simplest sterol is gonan-3-ol, which has a formula of , and is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom on C3 position by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol (chemistry), alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the gonane structure, additional functional groups, and/or modified ring systems derived from gonane are called steroids. Therefore, sterols are a subgroup of the steroids. They occur naturally in most Eukaryote, eukaryotes, including plants, animals, and fungi, and can also be produced by some bacteria (however likely with different functions). The most familiar type of animal sterol is cholesterol, which is vital to the structure of the cell membrane, and functions as a precursor to fat-soluble vitamins and steroid hormones. While technically alcohols, sterols are classified by biochemists as lipids (f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated and unsaturated compounds#Organic chemistry, saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an Branched chain fatty acids, unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids (up to 70% by weight) in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important diet (nutrition), dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cell (biology), cells. History The concept of fatty acid (''acide gras'') was introduced in 1813 by Michel Eugène Chevreul, though he initially used some variant terms: ''graisse acide'' and ''acide huileux'' ("acid fat" and "oi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ether Lipid
In biochemistry, an ether lipid refers to any lipid in which the lipid "tail" group is attached to the glycerol backbone via an ether, ether bond at any position. In contrast, conventional glycerophospholipids and triglycerides are triesters. Structural types include: * Ether phospholipids: phospholipids are known to have ether-linked "tails" instead of the usual ester linkage. ** Ether on sn-1, ester on sn-2: "ether lipids" in the context of bacteria and eukaryotes refer to this class of lipids. Compared to the usual Phosphatidic acid, 1,2-diacyl-sn-glycerol (DAG), the sn-1 linkage is replaced with an ester bond.Based on whether the sn-1 lipid is unsaturated next to the ether linkage, they can be further divided into ''alkenyl-acylphospholipids'' ("plasmenylphospholipid", 1-0-alk-1’-enyl-2-acyl-sn-glycerol) and ''alkyl-acylphospholipids'' ("plasmanylphospholipid"). This class of lipids have important roles in human cell signaling and structure. ** Ether on sn-2 and sn-3: this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with a terminal hydroxyl group is a ceramide. Other common groups bonded to the terminal oxygen atom include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids. Structure The long-chain bases, sometimes simply known as sphingoid bases, are the first non-transient products of '' de novo'' sphingolipid synthesis in both yeast and mammals. These co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiomargarita Magnifica
'' Candidatus'' Thiomargarita magnifica is a species of sulfur-oxidizing gammaproteobacteria, found growing underwater on detached leaves of red mangroves from the Guadeloupe Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galant ... archipelago in the Lesser Antilles. These filament-shaped bacteria are the largest known, with an average length of 1 Centimetre, cm, and some individuals reaching , making the bacteria visible to humans by unaided eye. Discovery The bacterium was discovered during the early 2010s by Olivier Gros from the University of the French Antilles at Pointe-à-Pitre, but initially did not attract much attention as Gros thought his find to be a fungus; it took Gros and other researchers five years to determine that it was a bacterium, and a few more years until Jea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiomargarita
''Thiomargarita'' is a genus (family Thiotrichaceae) which includes the vacuolate sulfur bacteria species ''Thiomargarita namibiensis'', '' Candidatus'' Thiomargarita nelsonii, and ''Ca.'' Thiomargarita joergensii. In 2022, scientists working in a Caribbean mangrove discovered an extremely large member of the genus, provisionally named ''Ca.'' T. magnifica, whose cells are easily visible to the naked eye at up to long. Representatives of this genus can be found in a variety of environments that are rich in hydrogen sulfide, including methane seeps, mud volcanoes, brine pools, and organic-rich sediments such as those found beneath the Benguela Current and Humboldt Current. These bacteria are generally considered to be chemolithotrophs that utilize reduced inorganic species of sulfur as metabolic electron donors to produce energy for the fixation of carbon into biomass. Carbon fixation Biological carbon fixation, or сarbon assimilation, is the Biological proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Sulfur Bacteria
The green sulfur bacteria are a phylum, Chlorobiota, of obligately anaerobic photoautotrophic bacteria that metabolize sulfur. Green sulfur bacteria are nonmotile (except ''Chloroherpeton thalassium'', which may glide) and capable of anoxygenic photosynthesis. They live in anaerobic aquatic environments. In contrast to plants, green sulfur bacteria mainly use sulfide ions as electron donors. They are autotrophs that utilize the reverse tricarboxylic acid cycle to perform carbon fixation. They are also mixotrophs and reduce nitrogen. Characteristics Green sulfur bacteria are gram-negative rod or spherical shaped bacteria. Some types of green sulfur bacteria have gas vacuoles that allow for movement. They are photolithoautotrophs, and use light energy and reduced sulfur compounds as the electron source. Electron donors include , , S. The major photosynthetic pigment in these bacteria is Bacteriochlorophylls ''c'' or ''d'' in green species and ''e'' in brown species, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |