|
Encyclopedia Of Mathematics
The ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'' (also ''EOM'' and formerly ''Encyclopaedia of Mathematics'') is a large reference work in mathematics. Overview The 2002 version contains more than 8,000 entries covering most areas of mathematics at a graduate level, and the presentation is technical in nature. The encyclopedia is edited by Michiel Hazewinkel and was published by Kluwer Academic Publishers until 2003, when Kluwer became part of Springer. The CD-ROM contains animations and three-dimensional objects. The encyclopedia has been translated from the Soviet ''Matematicheskaya entsiklopediya'' (1977) originally edited by Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov and extended with comments and three supplements adding several thousand articles. Until November 29, 2011, a static version of the encyclopedia could be browsed online free of charge. This URL now redirects to the new wiki A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and manage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michiel Hazewinkel
Michiel Hazewinkel (born 22 June 1943) is a Dutch mathematician, and Emeritus Professor of Mathematics at the Centre for Mathematics and Computer Science and the University of Amsterdam, particularly known for his 1978 book ''Formal groups and applications'' and as editor of the ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''. Biography Born in Amsterdam to Jan Hazewinkel and Geertrude Hendrika Werner, Hazewinkel studied at the University of Amsterdam. He received his BA in mathematics and physics in 1963, his MA in mathematics with a minor in philosophy in 1965 and his PhD in 1969 under supervision of Frans Oort and Albert Menalda for the thesis "Maximal Abelian Extensions of Local Fields".Michiel Hazewinkel, Curriculum vitae at michhaz.home.xs4all.nl. Accessed September 10, 2013 After graduation Hazewinkel started h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kluwer Academic Publishers
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second-largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov
Ivan Matveevich Vinogradov ( rus, Ива́н Матве́евич Виногра́дов, p=ɪˈvan mɐtˈvʲejɪvʲɪtɕ vʲɪnɐˈɡradəf, a=Ru-Ivan_Matveyevich_Vinogradov.ogg; 14 September 1891 – 20 March 1983) was a Soviet mathematician, who was one of the creators of modern analytic number theory, and also a dominant figure in mathematics in the USSR. He was born in the Velikiye Luki district, Pskov Oblast. He graduated from the University of St. Petersburg, where in 1920 he became a Professor. From 1934 he was a Director of the Steklov Institute of Mathematics, a position he held for the rest of his life, except for the five-year period (1941–1946) when the institute was directed by Academician Sergei Sobolev. In 1941 he was awarded the Stalin Prize. He was elected to the American Philosophical Society in 1942. In 1951 he became a foreign member of the Polish Academy of Sciences and Letters in Kraków. Mathematical contributions In analytic number theory, ''V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
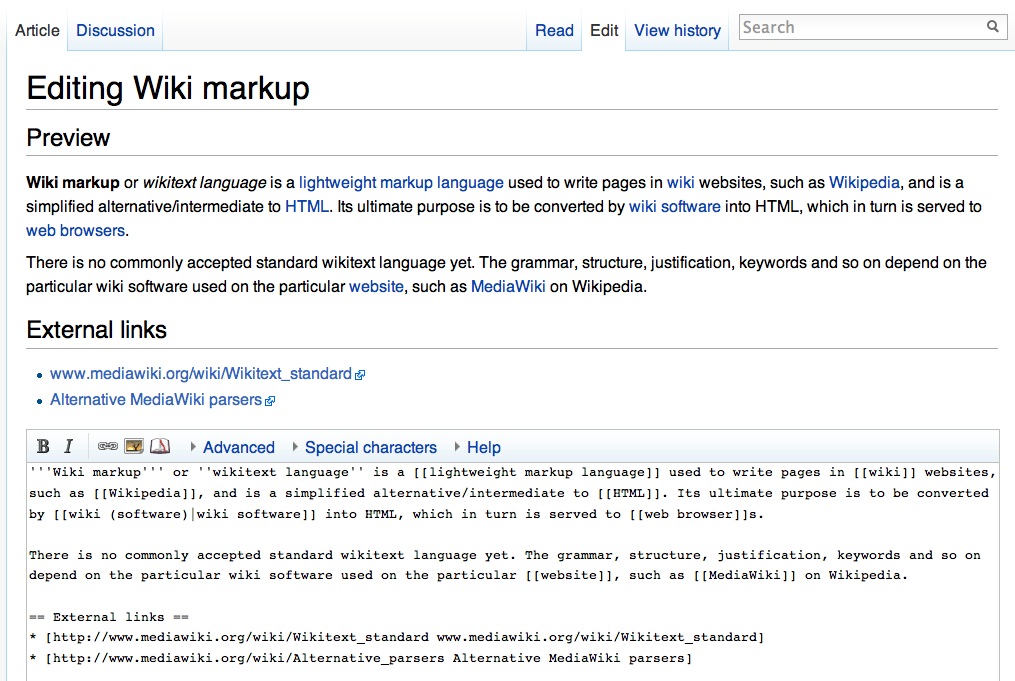
Wiki
A wiki ( ) is a form of hypertext publication on the internet which is collaboratively edited and managed by its audience directly through a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages that can either be edited by the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Its name derives from the first user-editable website called " WikiWikiWeb," with "wiki" being a Hawaiian word meaning "quick." Wikis are powered by wiki software, also known as wiki engines. Being a form of content management system, these differ from other web-based systems such as blog software or static site generators in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader. Wikis have little inherent structure, allowing one to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a lightweight markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Mathematical Society
The European Mathematical Society (EMS) is a European organization dedicated to the development of mathematics in Europe. Its members are different mathematical societies in Europe, academic institutions and individual mathematicians. The current president is Jan Philip Solovej, professor at the Department of Mathematics at the University of Copenhagen. Goals The Society seeks to serve all kinds of mathematicians in universities, research institutes and other forms of higher education. Its aims are to #Promote mathematical research, both pure and applied, #Assist and advise on problems of mathematical education, #Concern itself with the broader relations of mathematics to society, #Foster interaction between mathematicians of different countries, #Establish a sense of identity amongst European mathematicians, #Represent the mathematical community in supra-national institutions. The EMS is itself an Affiliate Member of the International Mathematical Union and an Associate Member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedia Of Mathematics, Complete Set
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Online Encyclopedias
This is a list of well-known online encyclopedias that are accessible or formerly accessible on the Internet. The largest online encyclopedias are general reference works, though there are also many specialized ones. Some online encyclopedias are editions of a print encyclopedia, such as ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', whereas others have always existed online, such as Wikipedia. General reference Biography Antiquities, arts, and literature Regional interest US-specific Pop culture and fiction Mathematics Media Philosophy Politics, law, and history Religion and theology Science and technology Life sciences Medical See also * Chinese encyclopedia * List of academic databases and search engines * List of blogs * List of Danish online encyclopedic resources * List of encyclopedias by branch of knowledge * List of online databases * List of online dictionaries * List of multilingual MediaWiki sites * List of wikis * List of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopedias Of Mathematics
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles or entries that are arranged alphabetically by article name or by thematic categories, or else are hyperlinked and searchable. Encyclopedia entries are longer and more detailed than those in most dictionaries. Generally speaking, encyclopedia articles focus on ''factual information'' concerning the subject named in the article's title; this is unlike dictionary entries, which focus on linguistic information about words, such as their etymology, meaning, pronunciation, use, and grammatical forms.Béjoint, Henri (2000)''Modern Lexicography'', pp. 30–31. Oxford University Press. Encyclopedias have existed for around 2,000 years and have evolved considerably during that time as regards language (written in a major international or a vernacular language), size (few or many volumes), intent (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Online Encyclopedias
German(s) may refer to: * Germany, the country of the Germans and German things **Germania (Roman era) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizenship in Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman era) *German diaspora * German language * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (disambiguati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics Websites
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, theories and theorems that are developed and proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of abstract objects that consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstracti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |