|
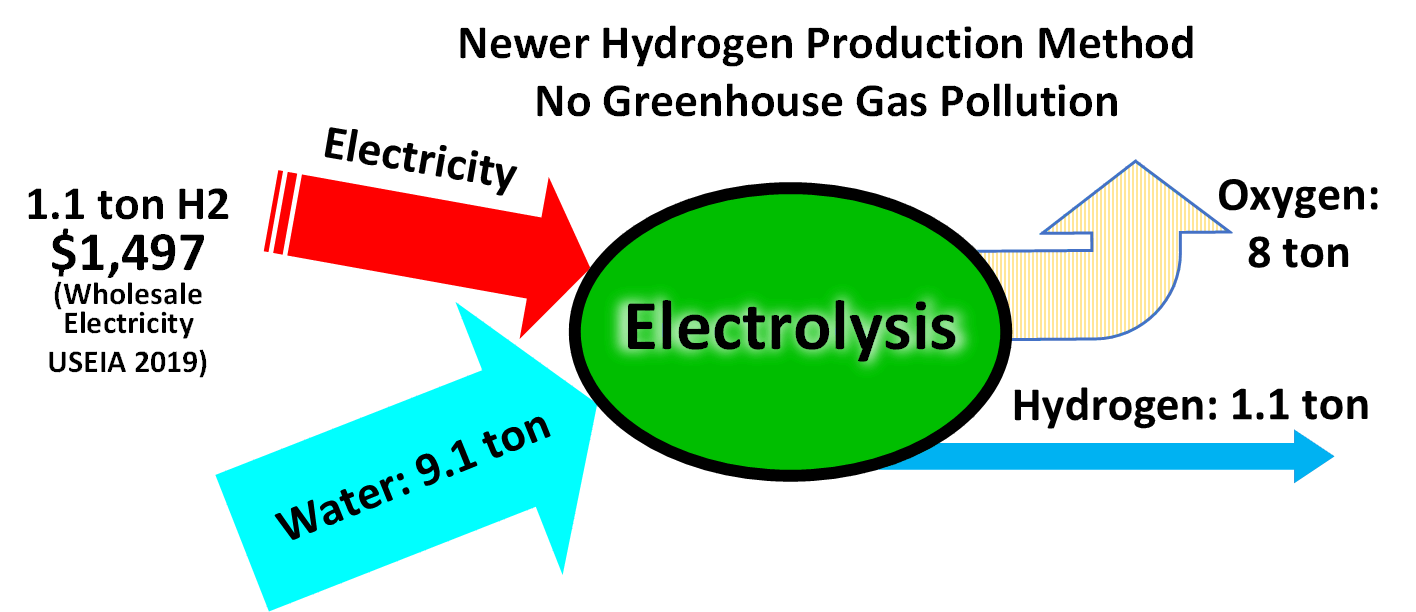
Electrolysis Of Water
Electrolysis of water is using electricity to Water splitting, split water into oxygen () and hydrogen () gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, but must be kept apart from the oxygen as the mixture would be extremely explosive. Separately pressurised into convenient 'tanks' or 'gas bottles', hydrogen can be used for oxyhydrogen welding and other applications, as the hydrogen / oxygen flame can reach approximately 2,800°C. Water electrolysis requires a minimum potential difference of 1.23 volts, although at that voltage external heat is also required. Typically 1.5 volts is required. Electrolysis is rare in industrial applications since hydrogen can be produced less expensively from fossil fuels. Most of the time, hydrogen is made by splitting methane (CH4) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen (H2) via steam reforming. This is a carbon-intensive process that means for every kilogram of “grey” hydrogen produced, approximatel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriaan Paets Van Troostwijk
Adriaan Paets van Troostwijk (4 March 1752 – 3 April 1837) was a Dutch businessman and an amateur chemist. He conducted experiments and theorized on the nature of substances, conduct some of the earliest experiments on the electrolysis of water in collaboration with physician Johan Rudolph Deiman (1743–1808). Van Troostwijk was born in Utrecht to cloth-merchant Wouter van Troostwijk and Johanna Dolphina Paets. He married Marie Cornelia Loten in 1770 and joined the business of his father-in-law in Amsterdam until 1816 and lived in Niewersluis subsequently. Here he became a member of the ''Felix Meritis'', an Amsterdam organization of polymaths founded in 1777. Along with his physician friend Jan Deiman, he conducted experiments and wrote 35 papers between 1778 and 1818. The director of the Haarlem Teylers museum Martinus van Marum also collaborated with Paets van Troostwijk. Using an electrostatic generator, he was able to split water with gold as an electrode (acting as a cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a variety of materials (chemicals) depending on the type of cell. An electrode may be called either a cathode or anode according to the direction of the electric current, unrelated to the potential difference between electrodes. Michael Faraday coined the term "" in 1833; the word recalls the Greek ἤλεκτρον (, "amber") and ὁδός (, "path, way"). The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke in 1762, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saints Cyrill And Methodius
Cyril (; born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (; born Michael, 815–885) were brothers, Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs". They are credited with devising the Glagolitic alphabet, the first alphabet used to transcribe Old Church Slavonic. After their deaths, their pupils continued their missionary work among other Slavs. Both brothers are venerated in the Eastern Orthodox Church as saints with the title of "equal-to-apostles". In 1880, Pope Leo XIII introduced their feast into the calendar of the Roman Rite of the Catholic Church. In 1980, the first Slav pope, Pope John Paul II declared them co-patron saints of Europe, together with Benedict of Nursia. Apostolic letter of Pope John Paul II, 31 December 1980 Early career Early life The two brothers were born in Thessalonica, at that time in the Byzantine province of the same name (today in Greece) – Cyril in 827–8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Lachinov
Dmitry Aleksandrovich Lachinov () (10 May 1842 – 15 October 1902) was a physicist, electrical engineer, inventor, meteorologist and climatologist from the Russian Empire. Biography Dmitry Lachinov studied in the St. Petersburg University, where he was a pupil of Heinrich Lenz, Pafnuty Chebyshev, and Feodor Petrushevsky. In 1862, when the University was closed because of the students' unrest, Lachinov went to Germany and for two and a half years studied there under the guidance of Gustav Kirchhoff, Robert Bunsen and Hermann von Helmholtz, Hermann Helmholtz, attending practical lessons in their laboratories in Heidelberg and Tübingen. In a paper released in 1880, Lachinov became the first one to point out the possibility of electricity transmission over long distances, and to propose the means of achieving it — 18 months before the first publication of the article with similar conclusions by Marcel Deprez. In 1889 Lachinov wrote the first textbook on meteorology and climato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. When carbon capture and storage is used to remove a large fraction of these emissions, the product is known as ''blue hydrogen''. ''Green hydrogen'' is usually understood to be produced from Renewable energy, renewable electricity via electrolysis of water. Less frequently, definitions of ''green hydrogen'' include hydrogen produced from other low-emission sources such as Biomass (energy), biomass. Producing green hydrogen is currently more expensive than producing gray hydrogen, and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gramme Machine
A Gramme machine, Gramme ring, Gramme magneto, or Gramme dynamo is an electrical generator that produces direct current, named for its Belgian inventor, Zénobe Gramme, and was built as either a dynamo or a magneto. It was the first generator to produce power on a commercial scale for industry. Inspired by a machine invented by Antonio Pacinotti in 1860, Gramme was the developer of a new induced rotor in form of a wire-wrapped ring (Gramme ring) and demonstrated this apparatus to the Academy of Sciences in Paris in 1871. Although popular in 19th century electrical machines, the Gramme winding principle is no longer used since it makes inefficient use of the conductors. The portion of the winding on the interior of the ring cuts no flux and does not contribute to energy conversion in the machine. The winding requires twice the number of turns and twice the number of commutator bars as an equivalent drum-wound armature. Description The Gramme machine used a ring armature, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zénobe Gramme
Zénobe Théophile Gramme (; 4 April 1826 – 20 January 1901) was a Belgian electrical engineer. He was born at Jehay-Bodegnée on 4 April 1826, the sixth child of Mathieu-Joseph Gramme, and died at Bois-Colombes on 20 January 1901. He invented the Gramme machine, a type of direct current dynamo capable of generating smoother (less AC) and much higher voltages than the dynamos known to that point. Career Gramme was poorly educated and semi-literate throughout his life. His talent was in handicraft and when he left school he became a joiner. After moving to Paris he took a job as a model maker at a company that manufactured electrical equipment and there became interested in technology. Having built an improved dynamo, Gramme, in association with Hippolyte Fontaine, opened a factory to develop the device. The business, called Société des Machines Magnéto-Électriques Gramme, manufactured the Gramme dynamo, Gramme ring, Gramme armature and other devices. In 1873 a Gramme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitric Acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% , it is referred to as ''fuming nitric acid''. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%, or white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%. Nitric acid is the primary reagent used for nitration – the addition of a nitro group, typically to an organic molecule. While some resulting nitro compounds are shock- and thermally-sensitive explosives, a few are stable enough to be used in munitions and demolition, while others are still more stable and used as synthetic dyes and medicines (e.g. metronidazole). Nitric acid is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several Chemical element, elements for the first time: potassium and sodium in 1807 and calcium, strontium, barium, magnesium and boron the following year, as well as for discovering the elemental nature of chlorine and iodine. Davy also studied the forces involved in these separations, inventing the new field of electrochemistry. Davy is also credited with discovering clathrate hydrates. In 1799, he experimented with nitrous oxide and was astonished at how it made him laugh. He nicknamed it "laughing gas" and wrote about its potential as an Anesthesia, anaesthetic to relieve pain during surgery. Davy was a baronet, President of the Royal Society (PRS), Member of the Royal Irish Academy (MRIA), a founder member and Fellow of the Geological Society of London, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Carlisle
Sir Anthony Carlisle FRCS, FRS (15 February 1768 in Stillington, County Durham, England – 2 November 1840 in London) was an English surgeon. Life He was born in Stillington, County Durham, the third son of Thomas Carlisle and his first wife, and the half-brother of Nicholas Carlisle. He was apprenticed to medical practitioners in York and Durham, including his uncle Anthony Hubback and William Green. He later studied in London under John Hunter. In 1793 he was appointed Surgeon at Westminster Hospital in 1793, remaining there for 47 years. He also studied art at the Royal Academy. In 1800, he and William Nicholson discovered electrolysis by passing a voltaic current through water, decomposing it into its constituent elements of hydrogen and oxygen. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1804. He was Professor of Anatomy of the Society from 1808 to 1824. In 1815 he became a member of the council of the Royal College of Surgeons, and served as president of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Nicholson (chemist)
William Nicholson (13 December 175321 May 1815) was an English writer, translator, publisher, scientist, inventor, patent agent and civil engineer. He launched the first monthly scientific journal in Britain, ''Journal of Natural Philosophy, Chemistry, and the Arts'', in 1797, and remained its editor until 1814. In 1800, he and Anthony Carlisle were the first to achieve electrolysis, the splitting of water into hydrogen and oxygen, using a voltaic pile. Nicholson also wrote extensively on natural philosophy and chemistry. Early life Nicholson was educated in Yorkshire, and after leaving school, he made two voyages as a midshipman in the service of the British East India Company. His first voyage was to India and the second voyage was to China on board the ''Gatton,'' (1772-1773). Subsequently, having become acquainted with Josiah Wedgwood in 1775, he moved to Amsterdam, where he made a living for a few years as Wedgwood's agent. On his return to England he was persuaded by T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |