|
EcoRII
EcoRII (pronounced 'eco R two') is an Restriction endonuclease enzyme (REase) of the restriction modification system (RM) naturally found in ''Escherichia coli'', a Gram-negative bacteria. Its molecular mass is 45.2 Atomic mass unit, kDa, being composed of 402 amino acids. Mode of action EcoRII is a bacterial Type IIE restriction endonuclease, REase that interacts with two othreeref name="pmid17845057"> copies of the pseudopalindromic dsDNA, DNA Restriction enzyme#Recognition site, recognition sequence 5' end, 5'-Cytosine, CCWGuanine, GG-3' end, 3' (W = Adenine, A or Thymine, T), one being the actual target of cleavage, the other(s) serving as the Allosteric regulation#Allosteric activation and inhibition, allosteric activator(s). EcoRII cuts the target dsDNA, DNA sequence CCWGG, generating sticky ends. Cut diagram Structure The apo structure, apo X-ray crystallography, crystal structure of EcoRII Point mutation, mutant R88A () has been solved at 2.1 Angstrom, Å Resolution ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Restriction Endonuclease
A restriction enzyme, restriction endonuclease, REase, ENase or'' restrictase '' is an enzyme that cleaves DNA into fragments at or near specific recognition sites within molecules known as restriction sites. Restriction enzymes are one class of the broader endonuclease group of enzymes. Restriction enzymes are commonly classified into five types, which differ in their structure and whether they cut their DNA enzyme substrate (biology), substrate at their recognition site, or if the recognition and cleavage sites are separate from one another. To cut DNA, all restriction enzymes make two incisions, once through each backbone chain, sugar-phosphate backbone (i.e. each strand) of the DNA double helix. These enzymes are found in bacteria and archaea and provide a defense mechanism against invading viruses. Inside a prokaryote, the restriction enzymes selectively cut up ''foreign'' DNA in a process called ''restriction digestion''; meanwhile, host DNA is protected by a modification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
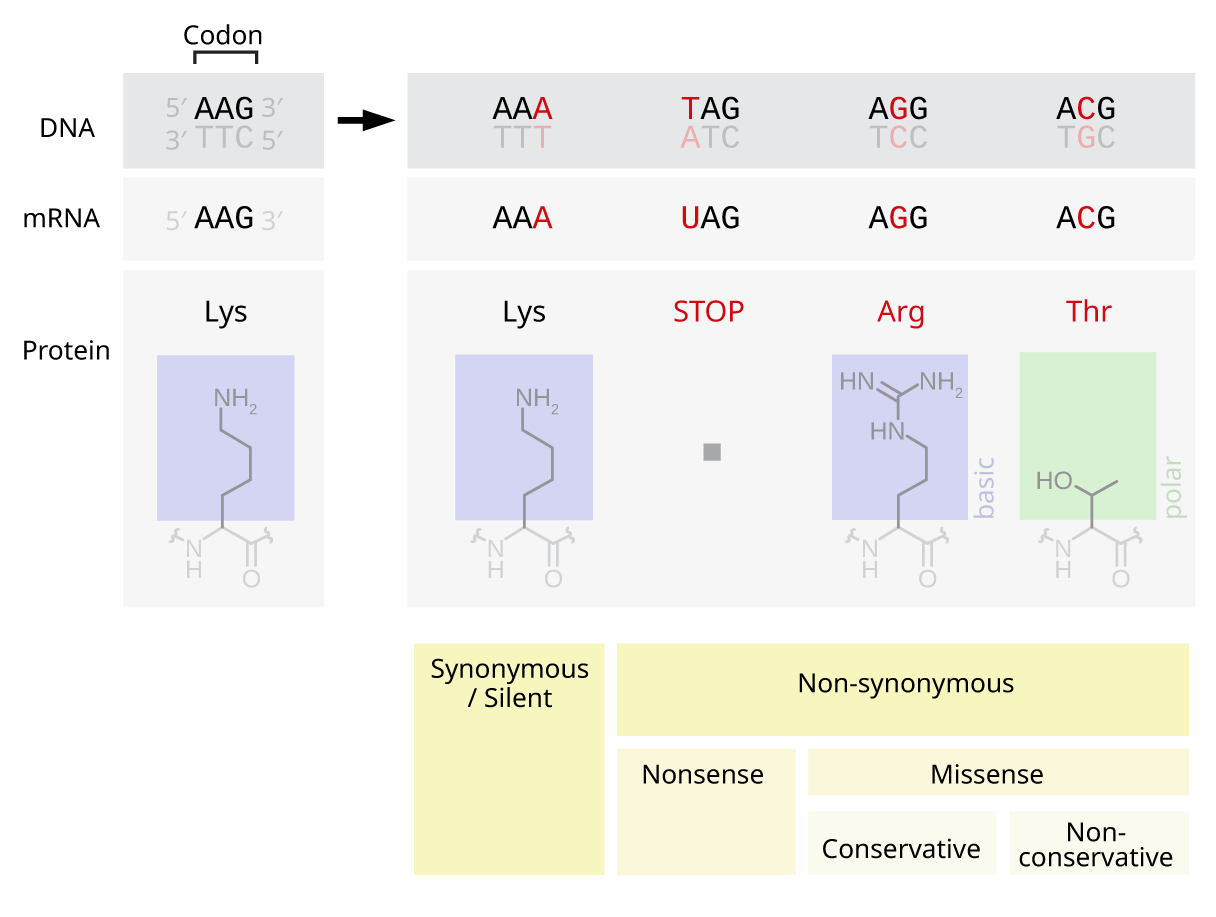
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. Synonymous substitution, synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Regulation
In the fields of biochemistry and pharmacology an allosteric regulator (or allosteric modulator) is a substance that binds to a site on an enzyme or receptor distinct from the active site, resulting in a conformational change that alters the protein's activity, either enhancing or inhibiting its function. In contrast, substances that bind directly to an enzyme's active site or the binding site of the endogenous ligand of a receptor are called orthosteric regulators or modulators. The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric site'' or ''regulatory site''. Allosteric sites allow effectors to bind to the protein, often resulting in a conformational change and/or a change in protein dynamics. Effectors that enhance the protein's activity are referred to as ''allosteric activators'', whereas those that decrease the protein's activity are called ''allosteric inhibitors''. Allosteric regulations are a natural example of control loops, such as feedback from do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sticky Ends
DNA ends refer to the properties of the ends of linear DNA molecules, which in molecular biology are described as "sticky" or "blunt" based on the shape of the complementary strands at the terminus. In sticky ends, one strand is longer than the other (typically by at least a few nucleotides), such that the longer strand has bases which are left unpaired. In blunt ends, both strands are of equal length – i.e. they end at the same base position, leaving no unpaired bases on either strand. The concept is used in molecular biology, in cloning, or when subcloning insert DNA into vector DNA. Such ends may be generated by restriction enzymes that break the molecule's phosphodiester backbone at specific locations, which themselves belong to a larger class of enzymes called exonucleases and endonucleases. A restriction enzyme that cuts the backbones of both strands at non-adjacent locations leaves a staggered cut, generating two overlapping sticky ends, while an enzyme that makes a str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apo Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demonstrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring the angles and intensities of the X-ray diffraction, a crystallography, crystallographer can produce a three-dimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal and the positions of the atoms, as well as their chemical bonds, crystallographic disorder, and other information. X-ray crystallography has been fundamental in the development of many scientific fields. In its first decades of use, this method determined the size of atoms, the lengths and types of chemical bonds, and the atomic-scale differences between various materials, especially minerals and alloys. The method has also revealed the structure and function of many biological molecules, including vitamins, drugs, proteins and nucleic acids such as DNA. X-ray crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eco RII 1NA6
Eco may refer to ecology or economics. It may also refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Eco'' (1987 video game), a 1987 life simulation game * Eco (2018 video game), a 2018 simulation game * "Eco" (song), a 2025 song by Joan Thiele * ''Emil Chronicle Online'', a 2005 Japanese MMO computer game * English Chamber Orchestra, based in London * Eco, a character in the ''Dragonar Academy'' light novel series * Eco, a fictional substance in the ''Jak and Daxter'' games * Eco, a character on the children's show ''The Shak'' Government and politics * Economic Cooperation Organization, an international organization * Environment and Conservation Organisations of Aotearoa New Zealand * Environmental Commissioner of Ontario * European Communications Office Technology * .eco, a top-level domain for the Internet * eco - Association of the Internet Industry, the German Internet industry association * Ecosia, a web search engine * Elementary column operations, an operation performed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine nucleobase. In RNA, thymine is replaced by the nucleobase uracil. Thymine was first isolated in 1893 by Albrecht Kossel and Albert Neumann from calf thymus glands, hence its name. Derivation As its alternate name (5-methyluracil) suggests, thymine may be derived by methylation of uracil at the 5th carbon. In RNA, thymine is replaced with uracil in most cases. In DNA, thymine (T) binds to adenine (A) via two hydrogen bonds, thereby stabilizing the nucleic acid structures. Thymine combined with deoxyribose creates the nucleoside deoxythymidine, which is synonymous with the term thymidine. Thymidine can be phosphorylated with up to three phosphoric acid groups, producing dTMP (deoxythymidine monophosphate), dTDP, or dTTP (for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resolution (electron Density)
Resolution in the context of structural biology is the ability to distinguish the presence or absence of Atom, atoms or groups of atoms in a Biomolecule, biomolecular structure. Usually, the structure originates from methods such as X-ray crystallography, electron crystallography, or Cryogenic electron microscopy, cryo-electron microscopy. The resolution is measured of the "map" of the structure produced from experiment, where an atomic model would then be fit into. Due to their different natures and interactions with matter, in X-ray methods the map produced is of the electron density of the system (usually a Crystal structure, crystal), whereas in electron methods the map is of the electrostatic potential of the system. In both cases, atomic positions are assumed similarly. Qualitative measures In structural biology, Optical resolution, resolution can be broken down into 4 groups: (1) sub-atomic, when information about the electron density is obtained and quantum effects can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Structure
Protein primary structure is the linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide or protein. By convention, the primary structure of a protein is reported starting from the amino-terminal (N) end to the carboxyl-terminal (C) end. Protein biosynthesis is most commonly performed by ribosomes in cells. Peptides can also be synthesized in the laboratory. Protein primary structures can be directly sequenced, or inferred from DNA sequences. Formation Biological Amino acids are polymerised via peptide bonds to form a long backbone, with the different amino acid side chains protruding along it. In biological systems, proteins are produced during translation by a cell's ribosomes. Some organisms can also make short peptides by non-ribosomal peptide synthesis, which often use amino acids other than the encoded 22, and may be cyclised, modified and cross-linked. Chemical Peptides can be synthesised chemically via a range of laboratory methods. Chemical methods typically synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |