|
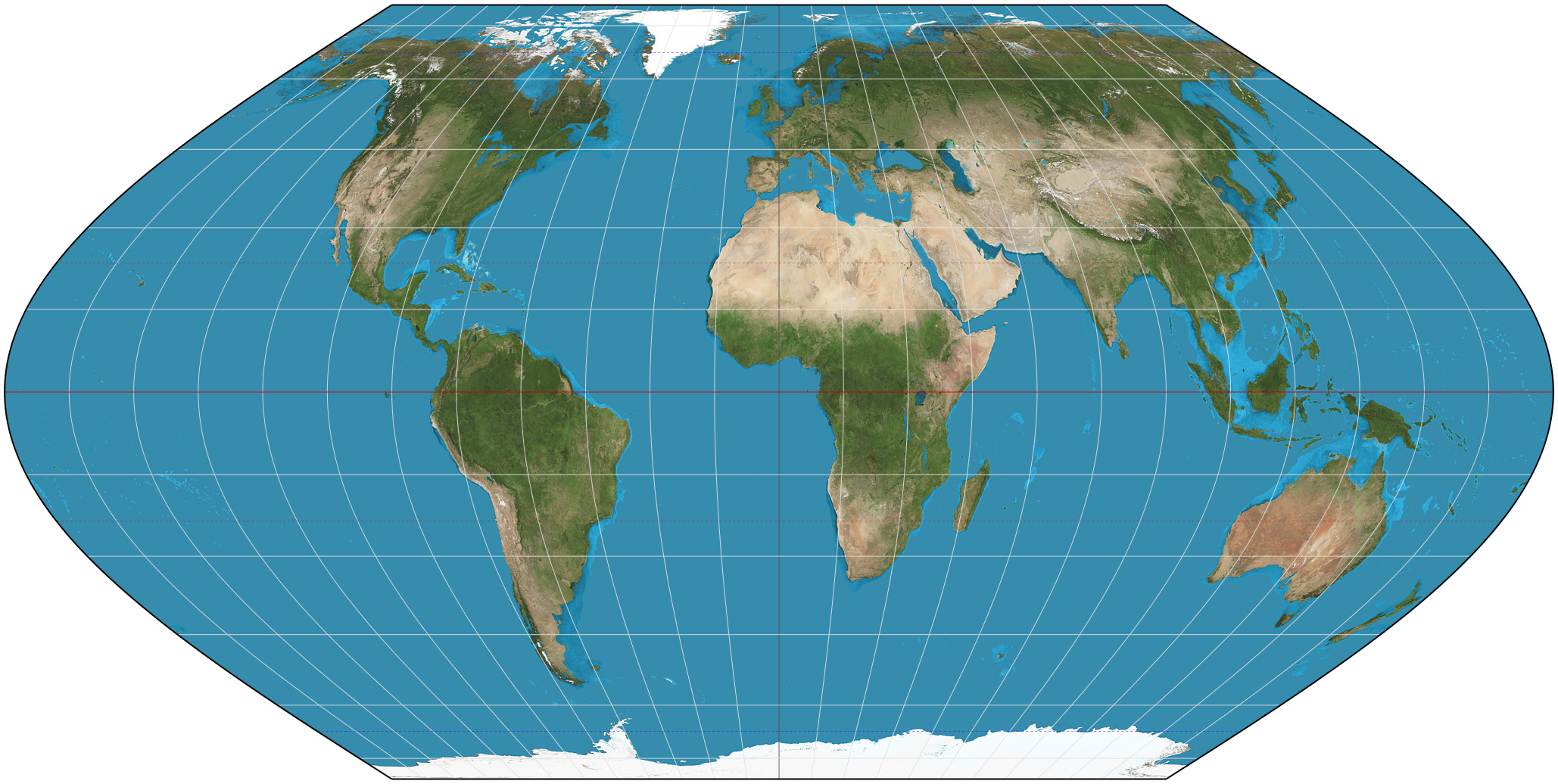
Eckert VI Projection
The Eckert VI projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. The length of polar line is half that of the equator, and lines of longitude are sinusoids. It was first described by Max Eckert in 1906 as one of a series of three pairs of pseudocylindrical projections. In each pair, the meridians have the same shape, and the odd-numbered projection has equally spaced parallels, whereas the even-numbered projection has parallels spaced to preserve area. The pair to Eckert VI is the Eckert V projection. See also *List of map projections This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise WP:NOTABLE, notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections, there can be no comprehensive list. Table of proj ... * Eckert II projection * Eckert IV projection References External links Eckert VI projection at Mathworld Equal-area projections {{Cartography-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecker VI Projection SW
The Ecker is a , right-hand, southeast tributary of the Oker which runs mainly through the Harz mountains in the German states of Saxony-Anhalt and Lower Saxony. Course From its source to Abbenrode the Ecker is a border river, today running between the federal states of Saxony-Anhalt and Lower Saxony. Prior to German reunification this was also the border between the German Democratic Republic in the east and Federal Republic of Germany to the west. The Ecker rises around southwest of the Brocken at at the ''Eckersprung''. Until the border was reopened it was the end of the Goethe Way (''Goetheweg'') from Torfhaus. Today there is a large picnic area with toilets at the ''Eckersprung''. Along a steep, rocky bed, the Ecker initially flows to the Ecker Dam, then through the deeply incised Ecker valley towards the north-northeast, where it passes the Ahlsburg, and then leaves the Harz. The upper Ecker valley is part of the Harz National Park. Only the site of the paper factor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
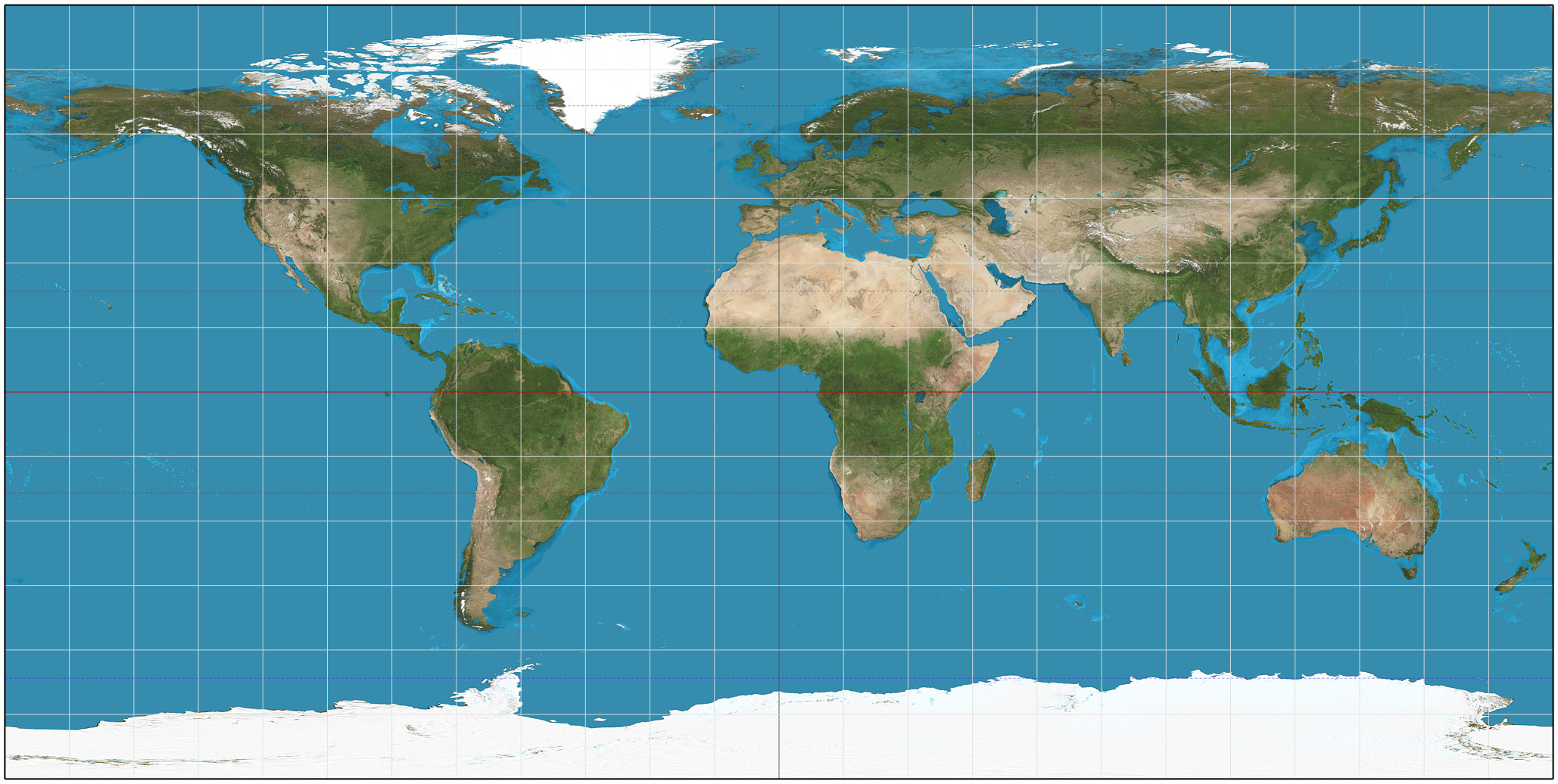
Map Projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and longitude, of locations from the surface of the globe are transformed to coordinates on a plane. Projection is a necessary step in creating a two-dimensional map and is one of the essential elements of cartography. All projections of a sphere on a plane necessarily distort the surface in some way. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. The study of map projections is primarily about the characterization of their distortions. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections. More generally, proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter lambda (λ). Meridians are imaginary semicircular lines running from pole to pole that connect points with the same longitude. The prime meridian defines 0° longitude; by convention the International Reference Meridian for the Earth passes near the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, south-east London on the island of Great Britain. Positive longitudes are east of the prime meridian, and negative ones are west. Because of the Earth's rotation, there is a close connection between longitude and time measurement. Scientifically precise local time varies with longitude: a difference of 15° longitude corresponds to a one-hour difference in local time, due to the differing position in relation to the Sun. Comparing local time to an absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoid
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it corresponds to '' uniform circular motion''. Sine waves occur often in physics, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves, such as monochromatic radiation. In engineering, signal processing, and mathematics, Fourier analysis decomposes general functions into a sum of sine waves of various frequencies, relative phases, and magnitudes. When any two sine waves of the same frequency (but arbitrary phase) are linearly combined, the result is another sine wave of the same frequency; this property is unique among periodic waves. Conversely, if some phase is chosen as a zero reference, a sine wave of arbitrary phase can be written as the linear combination of two sine waves with phases of zero and a quarter cycle, the ''sine'' and ''cosine'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Eckert-Greifendorff
Max Eckert (after 1934, Max Eckert-Greifendorff: 10 April 1868 in Chemnitz, Kingdom of Saxony – 26 December 1938, in Aachen) was a German geographer. Biography He received his education in Löbau and Berlin, and taught for some time at Löbau and Leipzig. In 1903, he became Privatdozent at Kiel University. In 1907, he was appointed to the chair of geography in the Royal Technical High School of Aachen (Aix-la-Chapelle). He invented the six Eckert projections and others such as Eckert-Greifendorff projection Writings He has published ''Schulatlas'' (School atlas, 45th ed., 1912), ''Wesen und Aufgabe der Wirtschafts- und Verkehrsgeographie'' (Essentials and purpose of economic and transportation geography, 1903), ''Grundriss der Handelsgeographie'' (Fundamentals of the geography of trade, 1905), ''Leitfaden der Handelsgeographie'' (Primer of the geography of trade, 3d ed., 1911), ''Neue Entwürfe für Erdkarten'' (New ideas for world maps, 1906), ''Die Kartographie als Wissensc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckert V Projection
Eckert may refer to: People * Allan W. Eckert (1931–2011), American historical novelist * Andrea Eckert (born 1958), Austrian actress * Carter Eckert (1945–2024), American historian * Charles R. Eckert (1868–1959), U.S. congressman from Pennsylvania * Claudia Eckert (other), multiple people * Dennis Eckert (born 1997), German footballer * Ernst R. G. Eckert (1904–2004), German scientist ** Eckert number, dimensionless number used in flow calculations * Eugen Eckert (born 1954) German minister, singer-songwriter and academic teacher * Franz Eckert (1852–1916), German musician * Fred J. Eckert (born 1941), U.S. congressman from New York * Fritz Eckert (1852–1920), Swedish architect * George Nicholas Eckert (1802–1865), U.S. congressman from Pennsylvania * John Eckert (musician) (born 1939), American trumpeter * J. Presper Eckert (1919–1995), American electrical engineer, co-inventor of ENIAC ** Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation ** Eckert–Mauchly Aw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Map Projections
This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise WP:NOTABLE, notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections, there can be no comprehensive list. Table of projections *The first known popularizer/user and not necessarily the creator. Key Type of projection surface ; Cylindrical: In normal aspect, these map regularly-spaced meridians to equally spaced vertical lines, and parallels to horizontal lines. ; Pseudocylindrical: In normal aspect, these map the central meridian and parallels as straight lines. Other meridians are curves (or possibly straight from pole to equator), regularly spaced along parallels. ; Conic: In normal aspect, conic (or conical) projections map meridians as straight lines, and parallels as arcs of circles. ; Pseudoconical: In normal aspect, pseudoconical projections represent the central meridian as a straight line, other meridians as complex curves, and parallels as ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckert II Projection
The Eckert II projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. In the equatorial aspect (where the equator is shown as the horizontal axis) the network of longitude and latitude lines consists solely of straight lines, and the outer boundary has the distinctive shape of an elongated hexagon. It was first described by Max Eckert in 1906 as one of a series of three pairs of pseudocylindrical projections. Within each pair, the meridians have the same shape, and the odd-numbered projection has equally spaced parallels, whereas the even-numbered projection has parallels spaced to preserve area. The pair to Eckert II is the Eckert I projection. Description The projection is symmetrical about the straight equator and straight central meridian. Parallels vary in spacing in order to preserve areas. As a pseudocylindric projection, spacing of meridians along any given parallel is constant. The poles are represented as lines, each half as long as the equator. The projectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckert IV Projection
The Eckert IV projection is an equal-area pseudocylindrical map projection. The length of the polar lines is half that of the equator, and lines of longitude are semiellipses, or portions of ellipses. It was first described by Max Eckert in 1906 as one of a series of three pairs of pseudocylindrical projections. Within each pair, meridians are the same whereas parallels differ. Odd-numbered projections have parallels spaced equally, whereas even-numbered projections have parallels spaced to preserve area. Eckert IV is paired with Eckert III. Formulas Forward formulae Given a sphere of radius ''R'', central meridian ''λ'' and a point with geographical latitude ''φ'' and longitude ''λ'', plane coordinates ''x'' and ''y'' can be computed using the following formulas: : \begin x & = \frac R\, (\lambda - \lambda_0)(1 + \cos \theta) \approx 0.422\,2382\, R\, (\lambda - \lambda_0)(1 + \cos \theta), \\ pty & = 2 \sqrt R \sin \theta \approx 1.326\,5004\, R \sin \theta, \end where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), founded as the Geological Survey, is an agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior whose work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879, to study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The agency also makes maps of planets and moons, based on data from U.S. space probes. The sole scientific agency of the U.S. Department of the Interior, USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. It is headquartered in Reston, Virginia, with major offices near Lakewood, Colorado; at the Denver Federal Center; and in NASA Research Park in California. In 2009, it employed about 8,670 people. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on its hundredth anniversary, was "Earth Science in the Pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |