|
Earth's Children
''Earth's Children'' is a series of epic historical fiction (or more precisely, prehistorical fiction) novels written by Jean M. Auel set circa 30,000 years before the present day. There are six novels in the series. Although Auel had previously mentioned in interviews that there would be a seventh novel, publicity announcements for the sixth confirmed it would be the final book in the sequence. The series is set in Europe during the Upper Paleolithic era, after the date of the first ceramics discovered, but before the last advance of glaciers. The books focus on the period of co-existence between Cro-Magnons and Neanderthals. As a whole, the series is a tale of personal discovery: coming-of-age, invention, cultural complexities, and, beginning with the second book, explicit romantic sex. It tells the story of Ayla, an orphaned Cro-Magnon girl who is adopted and raised by a tribe of Neanderthals. In early adulthood, she is given a "death curse," by the new leader who hat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Clan Of The Cave Bear
''The Clan of the Cave Bear'' is a 1980 work of prehistoric fiction by Jean M. Auel about prehistoric times. It is the first novel in the '' Earth's Children'' book series, which speculates on the possibilities of interactions between Neanderthal and modern Cro-Magnon humans. Setting The novel references the advance of the polar ice sheets, setting the story 18,000 years BCE, when the farthest southern encroachment of the last glacial period of the current ice age occurred. Auel's time-frame, sometime between 28,000 and 25,000 BCE, corresponds generally with archaeological estimates of the Neanderthal branch of humankind disappearing. Plots A five-year-old girl, Ayla, who readers come to understand is Cro-Magnon, is orphaned and left homeless by an earthquake that destroys her family's camp. She wanders naked and unable to feed herself, for several days. She is attacked and nearly killed by a cave lion, and, suffering from starvation, exhaustion, and infection of her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ayla (Earth's Children)
Ayla is the main character of Jean Auel's '' Earth's Children'' novels, a series which started in 1980. She is a woman of unknown origins, simply referred to as one of 'the Others', though possibly a Cro-Magnon woman who was raised by Neanderthals. Her blonde hair and light blue-grey eyes, which would be a much later evolution in the homo-sapien species, suggests that she comes from a hitherto unknown species, and that her son was possibly the first Homo-Sapien (and thus Cro-Magnon). Ayla was played by Daryl Hannah as the older version and by Nicole Eggert as the younger version in the 1986 film ''The Clan of the Cave Bear''. Ayla's character has been described as an example of the "rebellious primordial" that conquers adversity with wit and will. Background Ayla is orphaned as a young Cro-Magnon child after an earthquake opens a fissure in the ground, directly underneath her and her mother's campsite, brutally taking the mother (and all of her tools and survival essentials) und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
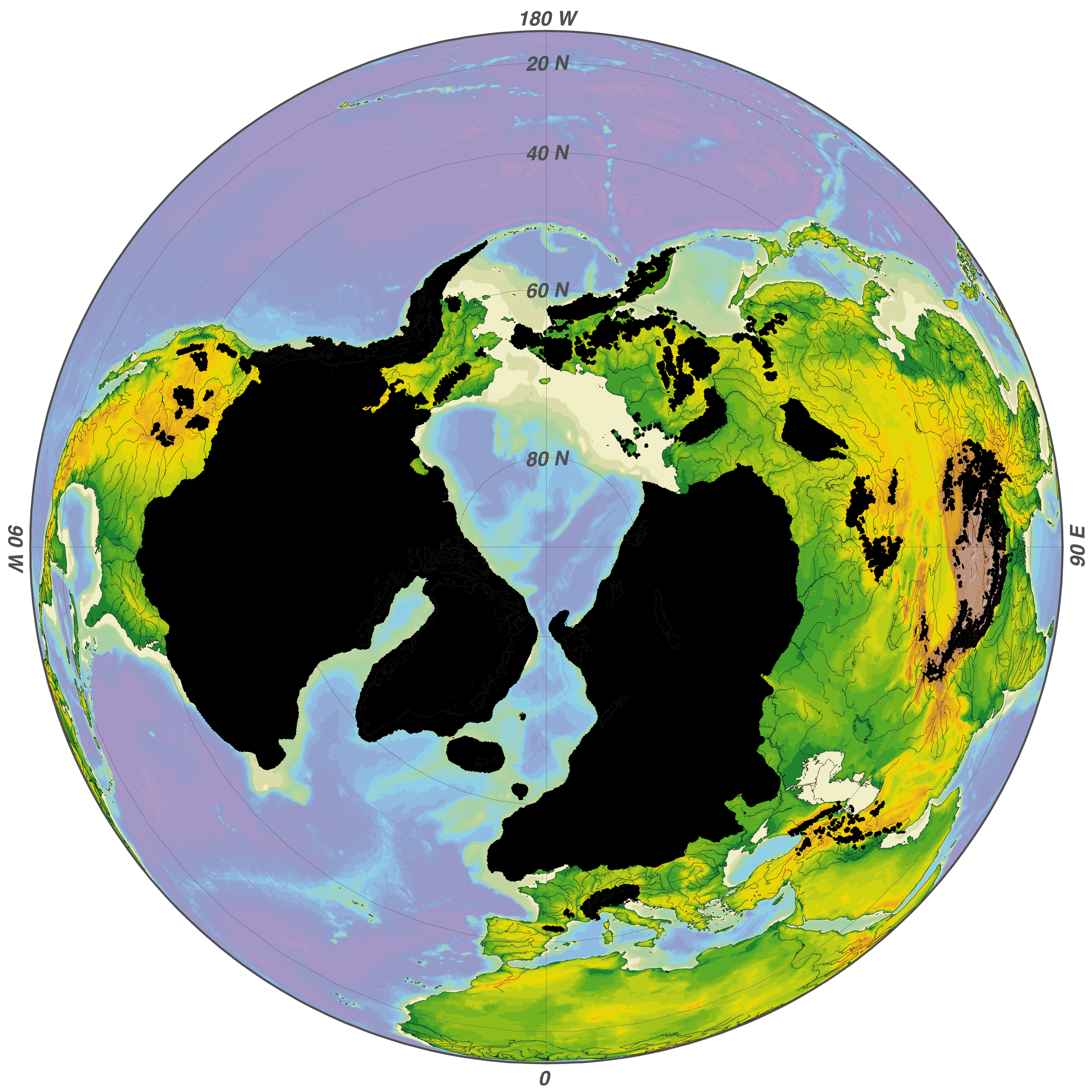
Last Glacial Maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Last Glacial Coldest Period, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period where ice sheets were at their greatest extent between 26,000 and 20,000 years ago. Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing a major expansion of deserts, along with a large drop in sea levels. Based on changes in position of ice sheet margins dated via cosmogenic nuclide, terrestrial cosmogenic nuclides and radiocarbon dating, growth of ice sheets in the southern hemisphere commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage has been estimated to have occurred sometime between 26,500 years ago and 20,000 years ago. After this, deglaciation caused an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago. Glacier fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaternary Glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million years ago) and is ongoing. Although geologists describe this entire period up to the present as an "ice age", in popular culture this term usually refers to the Last Glacial Period, most recent glacial period, or to the Pleistocene epoch in general. Since Earth still has polar Ice sheet, ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, though currently in an interglacial period. During the Quaternary glaciation, ice sheets appeared, expanding during glacial periods and contracting during interglacial periods. Since the end of the last glacial period, only the Antarctic ice sheet, Antarctic and Greenland ice sheets have survived, while other sheets formed during glacial periods, such as the Laurentide Ice Sheet, hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Library Association
The American Library Association (ALA) is a nonprofit organization based in the United States that promotes libraries and library education internationally. It is the oldest and largest library association in the world. History 19th century During the Centennial Exposition in Philadelphia in 1876, 103 librarians, 90 men, and 13 women, responded to a call for a "Convention of Librarians" to be held October 4–6, 1876, at the Historical Society of Pennsylvania. At the end of the meeting, according to Edward G. Holley in his essay "ALA at 100", "the register was passed around for all to sign who wished to become charter members", making October 6, 1876, the date of the ALA's founding. Among the 103 librarians in attendance were Justin Winsor (Boston Public Library and Harvard University), William Frederick Poole ( Chicago Public Library and Newberry College), Charles Ammi Cutter ( Boston Athenæum), Melvil Dewey, Charles Evans ( Indianapolis Public Library) and Richa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary License
Artistic license (and more general or contextually-specific, derivative terms such as creative license, poetic license, historical license, dramatic license, and narrative license) refers to deviation from fact or form for artistic purposes. It can include the alteration of grammar or language, or the rewording of pre-existing text. History The artistic license may also refer to the ability of an artist to apply smaller distortions, such as a poet ignoring some of the minor requirements of grammar for poetic effect. For example, Mark Antony's "Friends, Romans, Countrymen, lend me your ears" from Shakespeare's ''Julius Caesar'' would technically require the word "and" before "countrymen", but the conjunction "and" is omitted to preserve the rhythm of iambic pentameter (the resulting conjunction is called an asyndetic tricolon). Conversely, on the next line, the end of "I come to bury Caesar, not to praise him" has an extra syllable because omitting the word "him" would make the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Novel
A romance or romantic novel is a genre fiction novel that primarily focuses on the relationship and Romance (love), romantic love between two people, typically with an emotionally satisfying and optimistic ending. Authors who have contributed to the development of this genre include Maria Edgeworth, Samuel Richardson, Jane Austen, and Charlotte Brontë. Romance novels encompass various subgenres, such as fantasy, Contemporary romance, contemporary, historical romance, paranormal fiction, Sapphic literature, sapphic, and science fiction. They also contain tropes like enemies to lovers, second chance, and forced proximity. Women have traditionally been the primary readers of romance novels, but according to the Romance Writers of America, 18% of men read romance novels. The genre of works conventionally referred to as "romance novels" existed in ancient Greece. Other precursors can be found in the literary fiction of the 18th and 19th centuries, including Samuel Richardson's sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behaviour, while cultural anthropology studies cultural meaning, including norms and values. The term sociocultural anthropology is commonly used today. Linguistic anthropology studies how language influences social life. Biological anthropology, Biological (or physical) anthropology studies the biology and evolution of Human evolution, humans and their close primate relatives. Archaeology, often referred to as the "anthropology of the past," explores human activity by examining physical remains. In North America and Asia, it is generally regarded as a branch of anthropology, whereas in Europe, it is considered either an independent discipline or classified under related fields like history and palaeontology. Etymology The abstract noun ''wikt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicine (also called herbalism, phytomedicine or phytotherapy) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. Scientific evidence for the effectiveness of many herbal treatments remains limited, prompting ongoing regulatory evaluation and research into their safety and efficacy. Standards for purity or dosage are generally not provided. The scope of herbal medicine sometimes includes fungal and bee products, as well as minerals, shells and certain animal parts. Paraherbalism is the pseudoscientific use of plant or animal extracts as medicine, relying on unproven beliefs about the safety and effectiveness of minimally processed natural substances. Herbal medicine has been used since at least the Paleolithic era, with written records from ancient Sumer, Egypt, Greece, China, and India documenting its development and application over millennia. Modern herbal medicine is widely used globally—especially in Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herb
Herbs are a widely distributed and widespread group of plants, excluding vegetables, with savory or aromatic properties that are used for flavoring and garnishing food, for medicinal purposes, or for fragrances. Culinary use typically distinguishes herbs from spices. ''Herbs'' generally refers to the leafy green or flowering parts of a plant (either fresh or dried), while ''spices'' are usually dried and produced from other parts of the plant, including seeds, bark, roots and fruits. Herbs have a variety of uses including culinary, medicinal, aromatic and in some cases, spiritual. General usage of the term "herb" differs between culinary herbs and medicinal herbs; in medicinal or spiritual use, any parts of the plant might be considered "herbs", including leaves, roots, flowers, seeds, root bark, inner bark (and cambium), resin and pericarp. The word "herb" is pronounced in Commonwealth English, but is standard among American English speakers as well as those from regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specialises in this field. "Plant" and "botany" may be defined more narrowly to include only land plants and their study, which is also known as phytology. Phytologists or botanists (in the strict sense) study approximately 410,000 species of Embryophyte, land plants, including some 391,000 species of vascular plants (of which approximately 369,000 are flowering plants) and approximately 20,000 bryophytes. Botany originated as history of herbalism#Prehistory, prehistoric herbalism to identify and later cultivate plants that were edible, poisonous, and medicinal, making it one of the first endeavours of human investigation. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to Monastery, monasteries, contained plants possibly having medicinal benefit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |