|
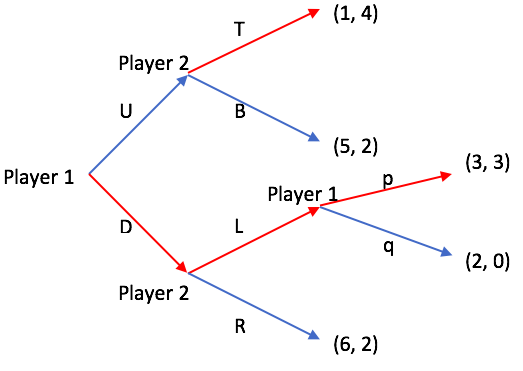
Dynamic Game
In game theory, a sequential game is a game where one player chooses their action before the others choose theirs. The other players must have information on the first player's choice so that the difference in time has no strategic effect. Sequential games are governed by the time axis and represented in the form of decision trees. Sequential games with perfect information can be analysed mathematically using combinatorial game theory. Decision trees are the extensive form of dynamic games that provide information on the possible ways that a given game can be played. They show the sequence in which players act and the number of times that they can each make a decision. Decision trees also provide information on what each player knows or does not know at the point in time they decide on an action to take. Payoffs for each player are given at the decision nodes of the tree. Extensive form representations were introduced by Neumann and further developed by Kuhn in the earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Final Position Of Lawrence-Tan 2002
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to: *Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which decides a winner for an event ** Another term for playoffs, describing a sequence of contests taking place after a regular season or round-robin tournament, culminating in a final by the first definition. *final (Java), a keyword in the Java programming language *Final case, a grammatical case *Final examination or finals, a test given at the end of a course of study or training *Part of a syllable#Medial and final, syllable *Final, a tone of the Gregorian mode Art and entertainment *Final (film), ''Final'' (film), a science fiction film *The Final (film), ''The Final'' (film), a thriller film *Finals (film), ''Finals'' (film), a 2019 Malayalam sports drama film *Final (band), an English electronic musical group *Final (Vol. 1), ''Final'' (Vol. 1), album by Enrique Iglesias *The Final (album), ''The Final'' (album), by Wham! * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensive Form Game
An extensive-form game is a specification of a game in game theory, allowing (as the name suggests) for the explicit representation of a number of key aspects, like the sequencing of players' possible moves, their choices at every decision point, the (possibly imperfect) information each player has about the other player's moves when they make a decision, and their payoffs for all possible game outcomes. Extensive-form games also allow for the representation of incomplete information in the form of chance events modeled as " moves by nature". Finite extensive-form games Some authors, particularly in introductory textbooks, initially define the extensive-form game as being just a game tree with payoffs (no imperfect or incomplete information), and add the other elements in subsequent chapters as refinements. Whereas the rest of this article follows this gentle approach with motivating examples, we present upfront the finite extensive-form games as (ultimately) constructed here. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequential Auction
A sequential auction is an auction in which several items are sold, one after the other, to the same group of potential buyers. In a ''sequential first-price auction'' (SAFP), each individual item is sold using a first price auction, while in a ''sequential second-price auction'' (SASP), each individual item is sold using a second price auction. A sequential auction differs from a combinatorial auction, in which many items are auctioned simultaneously and the agents can bid on bundles of items. A sequential auction is much simpler to implement and more common in practice. However, the bidders in each auction know that there are going to be future auctions, and this may affect their strategic considerations. Here are some examples. Example 1. There are two items for sale and two potential buyers: Alice and Bob, with the following valuations: * Alice values each item as 5, and both items as 10 (i.e., her valuation is additive). * Bob values each item as 4, and both items as 4 (i.e., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgame Perfection
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium) is a refinement of a Nash equilibrium used in dynamic games. A strategy profile is a subgame perfect equilibrium if it represents a Nash equilibrium of every subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. Every finite extensive game with perfect recall has a subgame perfect equilibrium. Perfect recall is a term introduced by Harold W. Kuhn in 1953 and ''"equivalent to the assertion that each player is allowed by the rules of the game to remember everything he knew at previous moves and all of his choices at those moves"''. A common method for determining subgame perfect equilibria in the case of a finite game is backward induction. Here one first considers the last actions of the game and determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Game
In game theory, a simultaneous game or static game is a game where each player chooses their action without knowledge of the actions chosen by other players. Simultaneous games contrast with sequential games, which are played by the players taking turns (moves alternate between players). In other words, both players normally act at the same time in a simultaneous game. Even if the players do not act at the same time, both players are uninformed of each other's move while making their decisions. Normal form representations are usually used for simultaneous games.Mailath, G., Samuelson, L. and Swinkels, J., 1993. Extensive Form Reasoning in Normal Form Games. Econometrica, nline61(2), pp.273-278. Available at: ccessed 30 October 2020 Given a continuous game, players will have different information sets if the game is simultaneous than if it is sequential because they have less information to act on at each step in the game. For example, in a two player continuous game that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backward Induction
Backward induction is the process of reasoning backwards in time, from the end of a problem or situation, to determine a sequence of optimal actions. It proceeds by examining the last point at which a decision is to be made and then identifying what action would be most optimal at that moment. Using this information, one can then determine what to do at the second-to-last time of decision. This process continues backwards until one has determined the best action for every possible situation (i.e. for every possible information set) at every point in time. Backward induction was first used in 1875 by Arthur Cayley, who uncovered the method while trying to solve the infamous Secretary problem. In the mathematical optimization method of dynamic programming, backward induction is one of the main methods for solving the Bellman equation. In game theory, backward induction is a method used to compute subgame perfect equilibria in sequential games. The only difference is that optimiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgame Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium) is a refinement of a Nash equilibrium used in dynamic games. A strategy profile is a subgame perfect equilibrium if it represents a Nash equilibrium of every subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. Every finite extensive game with perfect recall has a subgame perfect equilibrium. Perfect recall is a term introduced by Harold W. Kuhn in 1953 and ''"equivalent to the assertion that each player is allowed by the rules of the game to remember everything he knew at previous moves and all of his choices at those moves"''. A common method for determining subgame perfect equilibria in the case of a finite game is backward induction. Here one first considers the last actions of the game and determine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Tree
In the context of Combinatorial game theory, which typically studies sequential games with perfect information, a game tree is a graph representing all possible game states within such a game. Such games include well-known ones such as chess, checkers, Go, and tic-tac-toe. This can be used to measure the complexity of a game, as it represents all the possible ways a game can pan out. Due to the large game trees of complex games such as chess, algorithms that are designed to play this class of games will use partial game trees, which makes computation feasible on modern computers. Various methods exist to solve game trees. If a complete game tree can be generated, a deterministic algorithm, such as backward induction or retrograde analysis can be used. Randomized algorithms and minimax algorithms such as MCTS can be used in cases where a complete game tree is not feasible. Understanding the game tree To better understand the game tree, it can be thought of as a technique f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Complexity
Combinatorial game theory has several ways of measuring game complexity. This article describes five of them: state-space complexity, game tree size, decision complexity, game-tree complexity, and computational complexity. Measures of game complexity State-space complexity The state-space complexity of a game is the number of legal game positions reachable from the initial position of the game. When this is too hard to calculate, an upper bound can often be computed by also counting (some) illegal positions, meaning positions that can never arise in the course of a game. Game tree size The game tree size is the total number of possible games that can be played: the number of leaf nodes in the game tree rooted at the game's initial position. The game tree is typically vastly larger than the state space because the same positions can occur in many games by making moves in a different order (for example, in a tic-tac-toe game with two X and one O on the board, this position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go (board Game)
Go is an abstract strategy board game for two players in which the aim is to surround more territory than the opponent. The game was invented in China more than 2,500 years ago and is believed to be the oldest board game continuously played to the present day. A 2016 survey by the International Go Federation's 75 member nations found that there are over 46 million people worldwide who know how to play Go and over 20 million current players, the majority of whom live in East Asia. The playing pieces are called stones. One player uses the white stones and the other, black. The players take turns placing the stones on the vacant intersections (''points'') of a board. Once placed on the board, stones may not be moved, but stones are removed from the board if the stone (or group of stones) is surrounded by opposing stones on all orthogonally adjacent points, in which case the stone or group is ''captured''. The game proceeds until neither player wishes to make another move. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tic-tac-toe
Tic-tac-toe (American English), noughts and crosses (Commonwealth English), or Xs and Os (Canadian or Irish English) is a paper-and-pencil game for two players who take turns marking the spaces in a three-by-three grid with ''X'' or ''O''. The player who succeeds in placing three of their marks in a horizontal, vertical, or diagonal row is the winner. It is a solved game, with a forced draw assuming best play from both players. Gameplay Tic-tac-toe is played on a three-by-three grid by two players, who alternately place the marks X and O in one of the nine spaces in the grid. In the following example, the first player (''X'') wins the game in seven steps: There is no universally-agreed rule as to who plays first, but in this article the convention that X plays first is used. Players soon discover that the best play from both parties leads to a draw. Hence, tic-tac-toe is often played by young children who may not have discovered the optimal strategy. Because of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backgammon
Backgammon is a two-player board game played with counters and dice on tables boards. It is the most widespread Western member of the large family of tables games, whose ancestors date back nearly 5,000 years to the regions of Mesopotamia and Persia. The earliest record of backgammon itself dates to 17th-century England, being descended from the 16th-century game of Irish.Forgeng, Johnson and Cram (2003), p. 269. Backgammon is a two-player game of contrary movement in which each player has fifteen pieces, known traditionally as 'men' (short for 'tablemen') but increasingly known as 'checkers' in the US in recent decades. These pieces move along twenty-four 'points' according to the roll of two dice. The objective of the game is to move the fifteen pieces around the board and be first to ''bear off'', i.e., remove them from the board. The achievement of this while the opponent is still a long way behind results in a triple win known as a ''backgammon'', hence the name of the ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |