|
Draco (Chinese Astronomy)
The modern constellation Draco lies across one of the quadrants symbolized by the Black Tortoise of the North (еҢ—ж–№зҺ„жӯҰ, ''BДӣi FДҒng XuГЎn WЗ”''), and Three Enclosures (дёүеһЈ, ''SДҒn YuГЎn''), that divide the sky in traditional Chinese uranography. The name of the western constellation in modern Chinese is еӨ©йҫҚеә§ (''tiДҒn lГіng zuГІ''), meaning "the heaven dragon constellation". Stars The map of Chinese constellation in constellation Draco area consists of : See also *Traditional Chinese star names Chinese star names ( Chinese: , ''xД«ng mГӯng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xД«ng xiГ№'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xД«ng guДҒn''). The system of ... * Chinese constellations References {{Reflist External linksDraco вҖ“ Chinese associationsйҰҷжёҜеӨӘз©әйӨЁhttps://web.archive.org/web/20120813070951/http://www.lcsd.gov.hk/CE/Museum/Space/Research/c_index.htm з ”з©¶иіҮжәҗ] *д ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Draco (constellation)
Draco is a constellation in the far northern sky. Its name is Latin for dragon. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. The north pole of the ecliptic is in Draco. Draco is circumpolar from northern latitudes. There it is never setting and therefore can be seen all year. Features Stars Thuban (Оұ Draconis) was the northern pole star from 3942 BC, when it moved farther north than Theta BoГ¶tis, until 1793 BC. The Egyptian Pyramids were designed to have one side facing north, with an entrance passage geometrically aligned so that Thuban would be visible at night. Due to the effects of precession, it would again be the pole star around the year AD 21000. It is a blue-white giant star of magnitude 3.7, 309 light-years from Earth. The traditional name of Alpha Draconis, Thuban, means "head of the serpent". There are three stars under magnitude 3 in Draco. The brighter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6 Draconis
6 Draconis is a single-lined spectroscopic binary star system in the northern constellation of Draco, located about 430 light years away from the Sun. It is visible to the naked eye as an orange-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.95. The system is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of 3 km/s. The variable radial velocity of this star system was announced by W. W. Campbell in 1922. Griffin et al. (1990) found an orbital period of and an eccentricity of 0.26. The primary has an "''a'' sin ''i''" value of , where ''a'' is the semimajor axis and ''i'' is the (unknown) orbital inclination. This value provides a lower bound on the actual semimajor axis, which is one half of the longest dimension of their elliptical orbit. The visible component is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of , where the suffix notation indicates a pronounced underabundance of iron in the spectrum. The measured angular diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
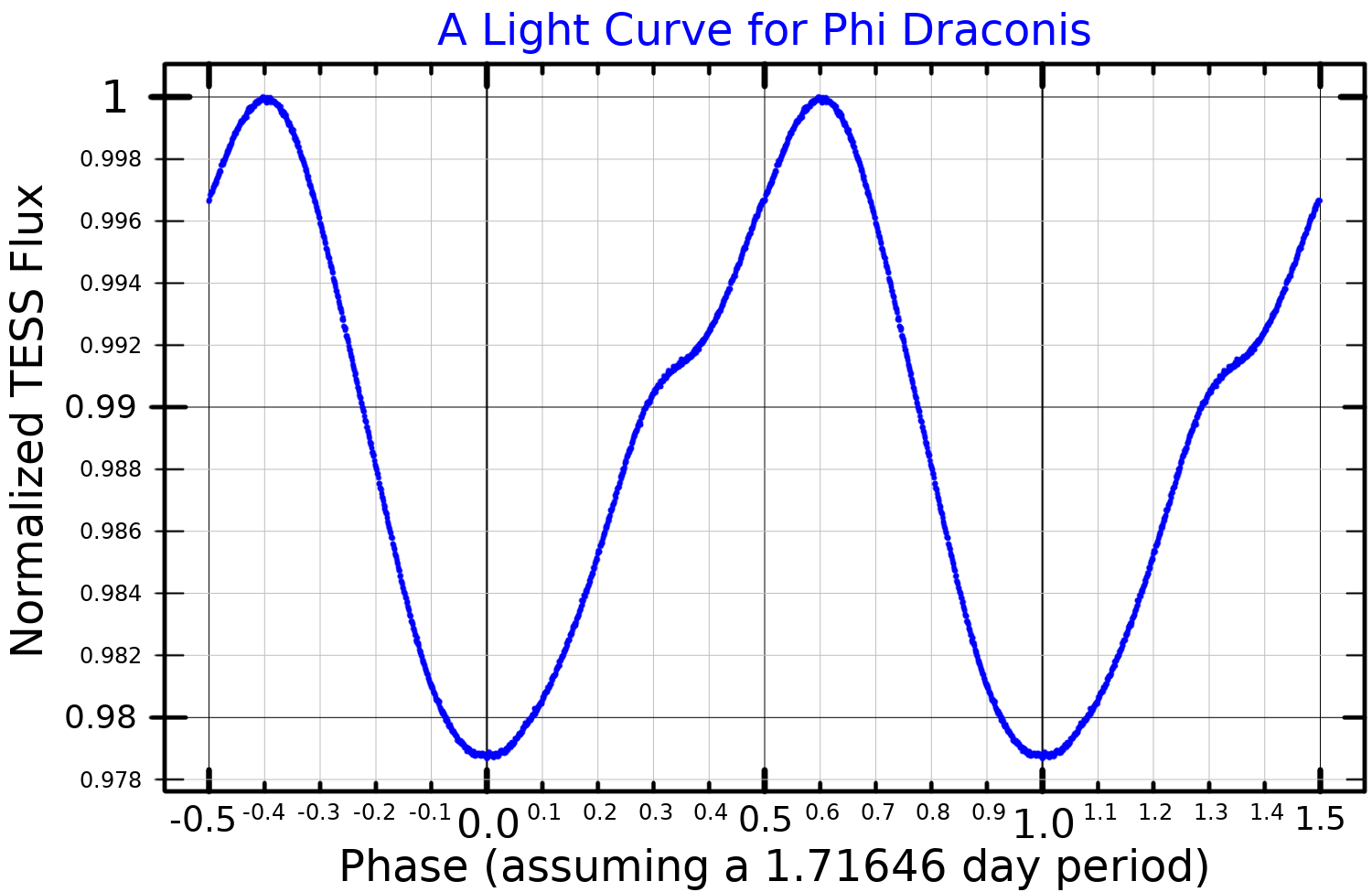
Phi Draconis
Phi Draconis (ПҶ Dra / ПҶ Draconis) is a fourth-magnitude variable star in the constellation Draco. It has the Flamsteed designation 43 Draconis. It is also a triple star system where the brightest component is a chemically peculiar Ap star. The brightness of ПҶ Draconis varies by about 0.04 of a magnitude every 1.7 days. This is due to very strong magnetic fields at the surface of the star, and it is classified as an Оұ2 Canum Venaticorum variable. ПҶ Draconis is a multiple star system containing three stars. The inner pair form a single-lined spectroscopic binary in an eccentric 128-day orbit. The outermost star orbits the inner pair every 308 years. The outer pair can be resolved visually and have a semi-major axis of . A fourth component, C, is also listed in multiple star catalogues, but is only a chance alignment with the triple system. Phi Draconis Aa is a main-sequence Ap star with a spectral class of B8. The main abundance excess is silicon, althoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psi Draconis
The Bayer designation Psi Draconis (ПҲ Dra / ПҲ Draconis) is shared by two star systems, in the constellation Draco Draco is the Latin word for serpent or dragon. Draco or Drako may also refer to: People * Draco (lawgiver) (from Greek: О”ПҒО¬ОәПүОҪ; 7th century BC), the first lawgiver of ancient Athens, Greece, from whom the term ''draconian'' is derived * ...: * ПҲВ№ Draconis * ПҲВІ Draconis {{SIA , astronomical objects Draconis, Psi Draco (constellation) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19 Draconis
19 Draconis, also known as h Draconis, is a star system in the constellation Draco. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.89. Based on its parallax, the system is located about 49.8 light-years (15.26 parsecs) away. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of вҲ’21 km/s. This is a binary star system with an orbital period of 52.1 days and an eccentricity of 0.22. Only the primary star can be directly detected, via Doppler shifts or perturbations around the system's barycenter. Using spectroscopy and astrometry, the nature of the secondary star can be inferred. The primary star is an F-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of F8V, 4% more massive than the Sun. Its surface temperature is about 6,298 K, and it emits just over twice the amount of energy that the Sun does. The secondary is only 37% as massive as the Sun The Sun is the star a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18 Draconis
18 Draconis is a likely binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. With an apparent visual magnitude of 4.84, it is just bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye. The distance to this system, as estimated from an annual parallax shift of , is roughly 720 light years. It is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of вҲ’1.4 km/s, and is a probable member of the Sirius stream of co-moving stars. The visible component has a stellar classification of , indicating it is an evolved K-type giant star with some abundance peculiarities in its atmosphere. At the age of around 280 million years, it is most likely (99% chance) on the horizontal branch. It is a barium star, which suggests it may have a degenerate white dwarf companion from which it accreted materials during an earlier stage of its evolution. 18 Dra has an estimated 3.8 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 47 times the Sun's radiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
15 Draconis
15 Draconis is a single star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco, located 452 light years away from the Sun. ''15 Draconis'' is the Flamsteed designation; it also has the Bayer designation ''A Draconis''. This object is visible to the naked eye as a white-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.94. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of вҲ’7 km/s. This star has a stellar classification of A0 III, matching that of an A-type giant star. It has a relatively high rate of spin with a projected rotational velocity of 154 km/s. The star is radiating 286 times the Sun's luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal ... from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 9,980 K. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omega Draconis
Omega Draconis, Latinized from Пү Draconis and also known as 28 Draconis, is a binary star in the constellation of Draco. The system is fairly close, and is located about 76 light-years (23 parsecs) away, based on its parallax. Omega Draconis is a spectroscopic binary, which means the two stellar components are too close to be resolved but periodic Doppler shifts in their spectra indicate orbital motion. In this case, light from both stars can be detected, and it is a double-lined spectroscopic binary. The orbital period of the system is 5.28 days, and the eccentricity of the system is 0.00220, implying a nearly circular orbit. The primary has a mass of , and is an F-type main-sequence star. The secondary is less massive, at . Naming With 27 Draconis, it composed the Arabs' Ш§Щ„ШЈШёЩҒШ§Шұ Ш§Щ„Ш°ШҰШЁ ''al-Кјaбә“fДҒr al-dhiКјb'', "the hyena's claws" in the asterism of the Mother Camels The protecting Mother Camels (Arabic Ш§Щ„Ш№ЩҲШ§ШҰШ° ''alКҪawaКјid'') is an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 91190
HD 91190 is a suspected astrometric binary star system in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco. It is faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.86. The distance to HD 91190, as estimated from its annual parallax shift of , is around 720 light years. This system is moving further away from the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of +17 km/s, having come to within some 2.4 million years ago. At the age of about two billion years, this is an evolved G-type giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III-IIIb. It has 2.39 times the mass of the Sun and is radiating 69 times the Sun's luminosity The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal ... from its photosphere at an effective temperature of around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |