|
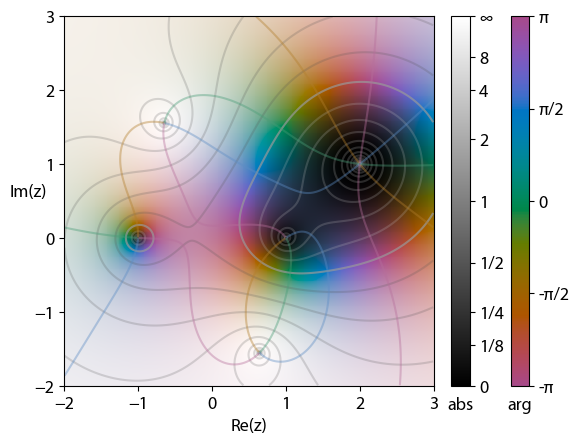
Domain Coloring
In complex analysis, domain coloring or a color wheel graph is a technique for visualizing complex functions by assigning a color to each point of the complex plane. By assigning points on the complex plane to different colors and brightness, domain coloring allows for a function from the complex plane to itself — whose graph would normally require four space dimensions — to be easily represented and understood. This provides insight to the fluidity of complex functions and shows natural geometric extensions of real functions. Motivation A graph of a real function can be drawn in two dimensions because there are two represented variables, x and y. However, complex numbers are represented by two variables and therefore two dimensions; this means that representing a complex function (more precisely, a complex-valued function of one complex variable f: \mathbb \to \mathbb) requires the visualization of four dimensions. One way to achieve that is with a Riemann surface, but anot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combination of yellow and cyan; in the RGB color model, used on television and computer screens, it is one of the additive primary colors, along with red and blue, which are mixed in different combinations to create all other colors. By far the largest contributor to green in nature is chlorophyll, the chemical by which plants photosynthesize and convert sunlight into chemical energy. Many creatures have adapted to their green environments by taking on a green hue themselves as camouflage. Several minerals have a green color, including the emerald, which is colored green by its chromium content. During post-classical and early modern Europe, green was the color commonly associated with wealth, merchants, bankers, and the gentry, while red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Argument
In mathematics (particularly in complex analysis), the argument of a complex number ''z'', denoted arg(''z''), is the angle between the positive real axis and the line joining the origin and ''z'', represented as a point in the complex plane, shown as \varphi in Figure 1. It is a multi-valued function operating on the nonzero complex numbers. To define a single-valued function, the principal value of the argument (sometimes denoted Arg ''z'') is used. It is often chosen to be the unique value of the argument that lies within the interval . Definition An argument of the complex number , denoted , is defined in two equivalent ways: #Geometrically, in the complex plane, as the 2D polar angle \varphi from the positive real axis to the vector representing . The numeric value is given by the angle in radians, and is positive if measured counterclockwise. #Algebraically, as any real quantity \varphi such that z = r (\cos \varphi + i \sin \varphi) = r e^ for some positive real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer
An integer is the number zero (), a positive natural number (, , , etc.) or a negative integer with a minus sign ( −1, −2, −3, etc.). The negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. In the language of mathematics, the set of integers is often denoted by the boldface or blackboard bold \mathbb. The set of natural numbers \mathbb is a subset of \mathbb, which in turn is a subset of the set of all rational numbers \mathbb, itself a subset of the real numbers \mathbb. Like the natural numbers, \mathbb is countably infinite. An integer may be regarded as a real number that can be written without a fractional component. For example, 21, 4, 0, and −2048 are integers, while 9.75, , and are not. The integers form the smallest group and the smallest ring containing the natural numbers. In algebraic number theory, the integers are sometimes qualified as rational integers to distinguish them from the more general algebraic in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Coloring Z 03
Domain may refer to: Mathematics *Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined **Domain of definition of a partial function **Natural domain of a partial function **Domain of holomorphy of a function * Domain (mathematical analysis), an open connected set * Domain of discourse, the set of entities over which logic variables may range * Domain of an algebraic structure, the set on which the algebraic structure is defined *Domain theory, the study of certain subsets of continuous lattices that provided the first denotational semantics of the lambda calculus *Domain (ring theory), a nontrivial ring without left or right zero divisors **Integral domain, a non-trivial commutative ring without zero divisors *** Atomic domain, an integral domain in which every non-zero non-unit is a finite product of irreducible elements ***Bézout domain, an integral domain in which the sum of two principal ideals is again a principal ideal *** Euclidean domain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Level-set Method
Level-set methods (LSM) are a conceptual framework for using level sets as a tool for numerical analysis of surfaces and shapes. The advantage of the level-set model is that one can perform numerical computations involving curves and surfaces on a fixed Cartesian grid without having to parameterize these objects (this is called the ''Eulerian approach''). Also, the level-set method makes it very easy to follow shapes that change topology, for example, when a shape splits in two, develops holes, or the reverse of these operations. All these make the level-set method a great tool for modeling time-varying objects, like inflation of an airbag, or a drop of oil floating in water. The figure on the right illustrates several important ideas about the level-set method. In the upper-left corner we see a shape; that is, a bounded region with a well-behaved boundary. Below it, the red surface is the graph of a level set function \varphi determining this shape, and the flat blue regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIECAM02
In colorimetry, CIECAM02 is the color appearance model published in 2002 by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) Technical Committee 8-01 (''Color Appearance Modelling for Color Management Systems'') and the successor of CIECAM97s. The two major parts of the model are its chromatic adaptation transform, CIECAT02, and its equations for calculating mathematical correlates for the six technically defined dimensions of color appearance: brightness (luminance), lightness, colorfulness, chroma, saturation, and hue. Brightness is the subjective appearance of how bright an object appears given its surroundings and how it is illuminated. Lightness is the subjective appearance of how light a color appears to be. Colorfulness is the degree of difference between a color and gray. Chroma is the colorfulness relative to the brightness of another color that appears white under similar viewing conditions. This allows for the fact that a surface of a given chroma displays inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lab Color Space
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'' , is a color space defined by the International Commission on Illumination (abbreviated CIE) in 1976. (Referring to CIELAB as "Lab" without asterisks should be avoided to prevent confusion with Hunter Lab). It expresses color as three values: ''L*'' for perceptual lightness and ''a*'' and ''b*'' for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color. Like the CIEXYZ space it derives from, CIELAB color space is a device-independent, "standard observer" model. The colors it defines are not relative to any particular device such as a computer monitor or a printer, but instead relate to the CIE standard observer which is an averaging of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Of Unity
In mathematics, a root of unity, occasionally called a de Moivre number, is any complex number that yields 1 when raised to some positive integer power . Roots of unity are used in many branches of mathematics, and are especially important in number theory, the theory of group characters, and the discrete Fourier transform. Roots of unity can be defined in any field. If the characteristic of the field is zero, the roots are complex numbers that are also algebraic integers. For fields with a positive characteristic, the roots belong to a finite field, and, conversely, every nonzero element of a finite field is a root of unity. Any algebraically closed field contains exactly th roots of unity, except when is a multiple of the (positive) characteristic of the field. General definition An ''th root of unity'', where is a positive integer, is a number satisfying the equation :z^n = 1. Unless otherwise specified, the roots of unity may be taken to be complex number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSL Color Space
HSL (for hue, saturation, lightness) and HSV (for hue, saturation, value; also known as HSB, for hue, saturation, brightness) are alternative representations of the RGB color model, designed in the 1970s by computer graphics researchers to more closely align with the way human vision perceives color-making attributes. In these models, colors of each ''hue'' are arranged in a radial slice, around a central axis of neutral colors which ranges from black at the bottom to white at the top. The HSL representation models the way different paints mix together to create color in the real world, with the ''lightness'' dimension resembling the varying amounts of black or white paint in the mixture (e.g. to create "light red", a red pigment can be mixed with white paint; this white paint corresponds to a high "lightness" value in the HSL representation). Fully saturated colors are placed around a circle at a lightness value of ½, with a lightness value of 0 or 1 corresponding to fully bla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemann Sphere
In mathematics, the Riemann sphere, named after Bernhard Riemann, is a model of the extended complex plane: the complex plane plus one point at infinity. This extended plane represents the extended complex numbers, that is, the complex numbers plus a value \infty for infinity. With the Riemann model, the point \infty is near to very large numbers, just as the point 0 is near to very small numbers. The extended complex numbers are useful in complex analysis because they allow for division by zero in some circumstances, in a way that makes expressions such as 1/0=\infty well-behaved. For example, any rational function on the complex plane can be extended to a holomorphic function on the Riemann sphere, with the poles of the rational function mapping to infinity. More generally, any meromorphic function can be thought of as a holomorphic function whose codomain is the Riemann sphere. In geometry, the Riemann sphere is the prototypical example of a Riemann surface, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
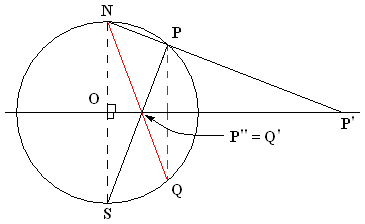
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth, bijective function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circles on the sphere to circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus locally approximately preserves shapes. It is neither isometric (distance preserving) nor equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to represent a sphere by a plane. The metric induced by the inverse stereographic projection from the plane to the sphere defines a geodesic distance between points in the plane equal to the spherical distance between the spherical points they represent. A two-dimensional coordinate system on the stereo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |