|
Dental Auxiliary
A dental auxiliary is any oral health practitioner other than a dentist & dental hygienist, including the supporting team assisting in dental treatment. They include dental assistants (known as dental nurses in the United Kingdom and Ireland), dental therapists and oral health therapists, dental technologists, and orthodontic auxiliaries. The role of dental auxiliaries is usually set out in regional dental regulations, defining the treatment that can be performed. Dental assistants Dental assistant help make dental treatment more efficient by assisting the clinician. They hold and pass instruments, retract tissues and apply suction to assist better vision of the operating field. They also mix materials, help maintain dental records, and sterilize instruments and equipment. Some also engage in professional teeth whitening procedures, particularly in The Republic of Ireland where laser teeth whitening is classified as a cosmetic procedure and not dental treatment. This practice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentist
A dentist, also known as a dental doctor, dental physician, dental surgeon, is a health care professional who specializes in dentistry, the branch of medicine focused on the teeth, gums, and mouth. The dentist's supporting team aids in providing oral health services. The dental team includes dental assistants, dental hygienists, dental technicians, and sometimes dental therapists. History Middle Ages In China as well as France, the first people to perform dentistry were barbers. They have been categorized into 2 distinct groups: guild of barbers and lay barbers. The first group, the Guild of Barbers, was created to distinguish more educated and qualified dental surgeons from lay barbers. Guild barbers were trained to do complex surgeries. The second group, the lay barbers, were qualified to perform regular hygienic services such as shaving and tooth extraction as well as basic surgery. However, in 1400, France made decrees prohibiting lay barbers from practicing all t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Sealant
Dental sealants (also termed pit and fissure sealants, or simply fissure sealants) are a dental treatment intended to prevent tooth decay. Teeth have recesses on their biting surfaces; the back teeth have fissures (grooves) and some front teeth have cingulum pits. It is these pits and fissures that are most vulnerable to tooth decay because food and bacteria stick in them and because they are hard-to-clean areas. Dental sealants are materials placed in these pits and fissures to fill them in, creating a smooth surface which is easy to clean. Dental sealants are mainly used in children who are at higher risk of tooth decay, and are usually placed as soon as the adult molar teeth come through. Background Dental caries is an upset of the balance between loss and gain of minerals from a tooth surface. The loss of minerals from the teeth occurs from the bacteria within the mouth, fermenting foods and producing acids, whereas the tooth gains minerals from our saliva and fluoride th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
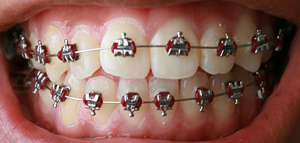
Elastics (orthodontics)
Elastics are rubber bands frequently used in the field of orthodontics to correct different types of malocclusions. The elastic wear is prescribed by an orthodontist or a dentist in an orthodontic treatment. The longevity of the elastic wear may vary from two weeks to several months. The elastic wear can be worn from 12 to 23 hours a day, either during the night or throughout the day depending on the requirements for each malocclusion. The many different types of elastics may produce different forces on teeth. Therefore, using elastics with specific forces is critical in achieving a good orthodontic occlusion. The term ''intermaxillary elastics'' is used when elastics can go from the maxillary to the mandibular arch. ''Intra-maxillary elastics'' are elastics used in one arch only, either mandibular or maxillary. People using elastics for orthodontic correction change their elastics three to four times during the day. Elastic wear is recommend to be used in a rectangular wire to mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodontic Archwire
An archwire in orthodontics is a wire conforming to the alveolar or dental arch that can be used with dental braces as a source of force in correcting irregularities in the position of the teeth. An archwire can also be used to maintain existing dental positions; in this case it has a retentive purpose. Orthodontic archwires may be fabricated from several alloys, most commonly stainless steel, nickel-titanium alloy (NiTi), and beta-titanium alloy (composed primarily of titanium and molybdenum). Types Noble Metal alloy Noble metals such as gold, platinum, iridium, silver and their alloys were used early on in the field of Orthodontics because of their good corrosion resistance. Some of the other qualities that these alloys had were high ductility, variable stiffness (with heat), high resilience and ease of soldering. Disadvantages of these alloys were: Less elasticity, less tensile strength and greater cost. Composition of both platinum and palladium raised the melting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthodontics
Orthodontics (also referred to as orthodontia) is a dentistry specialty that addresses the diagnosis, prevention, management, and correction of mal-positioned teeth and jaws, as well as misaligned bite patterns. It may also address the modification of facial growth, known as dentofacial orthopedics. Abnormal alignment of the teeth and jaws is very common. The approximate worldwide prevalence of malocclusion was as high as 56%. However, conclusive evidence-based medicine, scientific evidence for the Health benefit (medicine), health benefits of orthodontic treatment is lacking, although patients with completed treatment have reported a higher quality of life than that of untreated patients undergoing orthodontic treatment. The main reason for the prevalence of these malocclusions is diets with less fresh fruit and vegetables and overall softer foods in childhood, causing smaller jaws with less room for the teeth to erupt. Treatment may require several months to a few years and enta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denturist
A denturist in the United States and Canada, clinical dental technologist in the United Kingdom and Ireland, dental prosthetist in Australia, or a clinical dental technician in New Zealand is a member of the oral health care team and role as primary oral health care provider who provides an oral health examination, planning treatment, takes impressions of the surrounding oral tissues, constructs and delivers removable oral prosthesis treatment (including dentures and partial dentures) directly to the patient. Definitions Denturism is defined as the practice by denturists of examining oral health, planning treatment, making artificial dentures including other removable oral appliances and fitting them to patients. It is a recognized profession throughout the world and currently utilized in many countries including Australia, New Zealand, United States, United Kingdom and Canada. In the United States, denturism is only legislated and practiced in 7 states (Maine, Arizona, Idah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
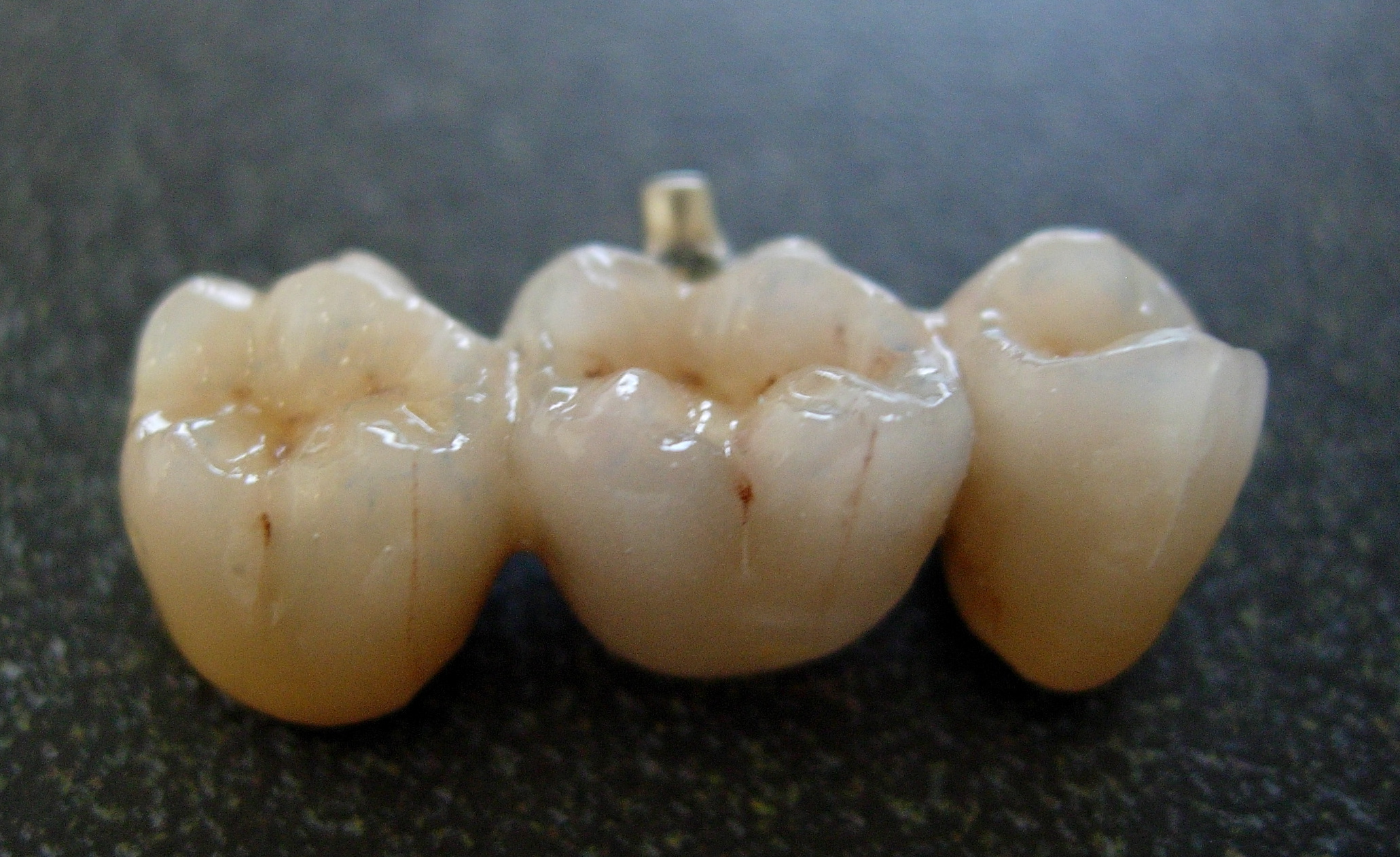
Bridge (dentistry)
A bridge is a fixed dental restoration (a fixed dental prosthesis) used to replace one or more missing teeth by joining an artificial tooth definitively to adjacent teeth or dental implants. Definitions Fixed bridge: A dental prosthesis that is definitively attached to natural teeth and replaces missing teeth. Abutment: The tooth that supports and retains a dental prosthesis. Pontic: The artificial tooth that replaces a missing natural tooth. Retainer: The component attached to the abutment for retention of the prosthesis. Retainers can be major or minor. Unit: Pontics and abutment teeth are referred to as units. The total number of units in a bridge is equal to the number of pontics plus the number of abutment teeth. Saddle: The area on the alveolar ridge which is edentulous where at least one missing tooth is to be reinstated. Connector: Joins the pontic to the retainer or two retainers together. Connectors may be fixed or movable. Span: The length of the alveo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
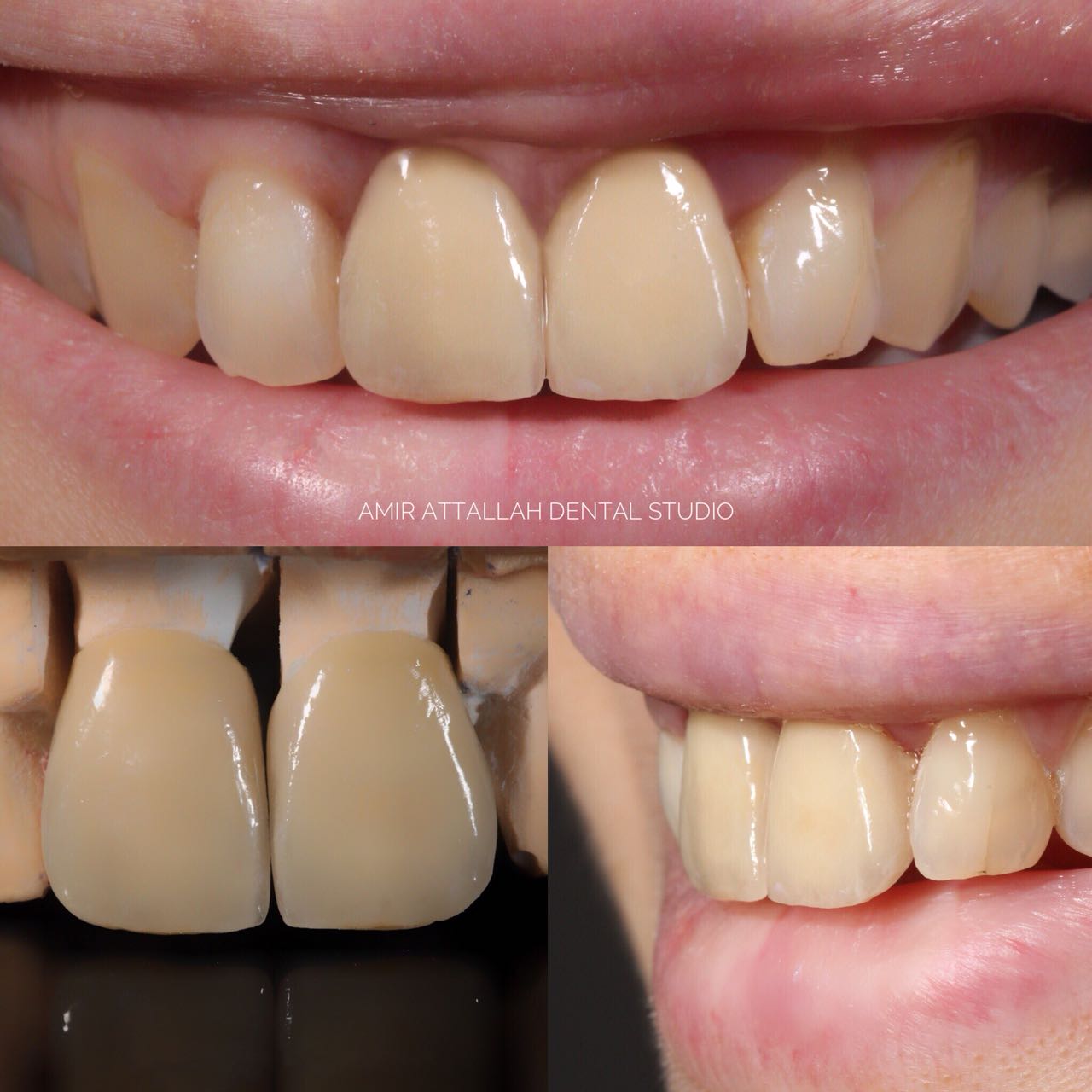
Crown (dentistry)
In dentistry, a crown or a dental cap is a type of dental restoration that completely caps or encircles a Human tooth, tooth or dental implant. A crown may be needed when a large dental cavity threatens the health of a tooth. Some dentists will also finish root canal treatment by covering the exposed tooth with a crown. A crown is typically bonded to the tooth by dental cement. They can be made from various materials, which are usually fabricated using ''indirect methods''. Crowns are used to improve the strength or appearance of teeth and to halt deterioration. While beneficial to dental health, the procedure and materials can be costly. The most common method of crowning a tooth involves taking a dental impression of a tooth prepared by a dentist, then fabricating the crown outside of the mouth. The crown can then be inserted at a subsequent dental appointment. This ''indirect method'' of tooth restoration allows use of strong dental restorative materials, restorative material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Prosthodontics
Fixed prosthodontics is the branch of prosthodontics that focuses on dental prosthesis, dental prostheses that are permanently affixed (fixed). Crown (dental restoration), Crowns, bridge (dentistry), bridges (fixed dentures), inlays, onlays, and Veneer (dentistry), veneers are some examples of indirect dental restorations. Prosthodontists are dentists who have completed training in this specialty that has been recognized by academic institutes. Fixed prosthodontics can be used to reconstruct single or many teeth, spanning tooth loss areas. The main advantages of fixed prosthodontics over direct restorations are improved strength in big restorations and the possibility to build an aesthetic-looking tooth. The concepts utilised to select the suitable repair, as with any dental restoration, include consideration of the materials to be used, the level of tooth destruction, the orientation and placement of the tooth, and the condition of neighboring teeth. Preparation techniques A la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retainer (orthodontics)
Orthodontic retainers are custom-made devices, usually made of wires or clear plastic, that hold teeth in position after surgery or any method of realigning teeth. Once a phase of orthodontic treatment has been completed to straighten teeth, there remains a lifelong risk of relapse (a tendency for teeth to return to their original position) due to a number of factors: recoil of periodontal fibres, pressure from surrounding soft tissues, the occlusion and patient’s continued growth and development. By using retainers to hold the teeth in their new position for a length of time, the surrounding periodontal fibres adapt to changes in the bone which can help minimize any changes to the final tooth position after the completion of orthodontic treatment. Retainers may also be used to treat overjet In dentistry, overjet is the extent of horizontal ( anterior-posterior) overlap of the maxillary central incisors over the mandibular central incisors. In class II (division I) malocc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable ( removable partial denture or complete denture). However, there are many denture designs, some of which rely on bonding or clasping onto teeth or dental implants ( fixed prosthodontics). There are two main categories of dentures, the distinction being whether they fit onto the mandibular arch or on the maxillary arch. Medical uses Dentures can help people via: * Mastication: chewing ability is improved by the replacement of edentulous (lacking teeth) areas with denture teeth. * Aesthetics: the presence of teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks and corrects the collapsed appearance that results from the loss of teeth. * Pronunciation: replacing missing teeth, especially the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
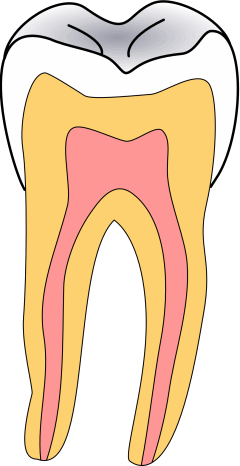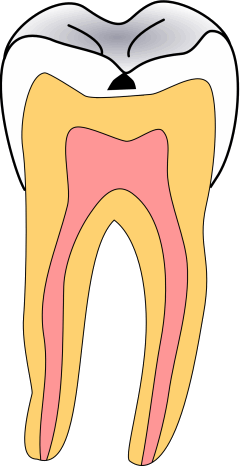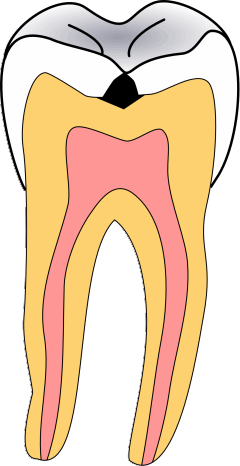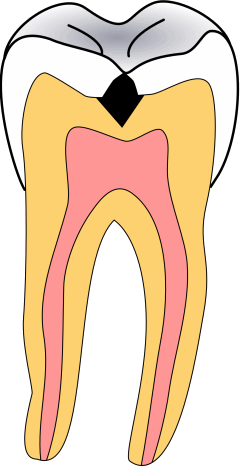
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay, also known as caries,The word 'caries' is a mass noun, and is not a plural of 'carie'.'' is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The resulting cavities may be a number of different colors, from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty eating. Complications may include periodontal disease, inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or dental abscess, abscess formation. Tooth regeneration is an ongoing Stem-cell therapy, stem cell–based field of study that aims to find methods to reverse the effects of decay; current methods are based on easing symptoms. The cause of cavities is acid from bacteria dissolving the hard tissues of the teeth (Tooth enamel, enamel, dentin and cementum). The acid is produced by the bacteria when they break down food debris or sugar on the tooth surface. Simple sugars in food are these bacteria's primary energy source and thus a diet high in simple sugar is a risk factor. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |