|
Deep Near Infrared Survey Of The Southern Sky
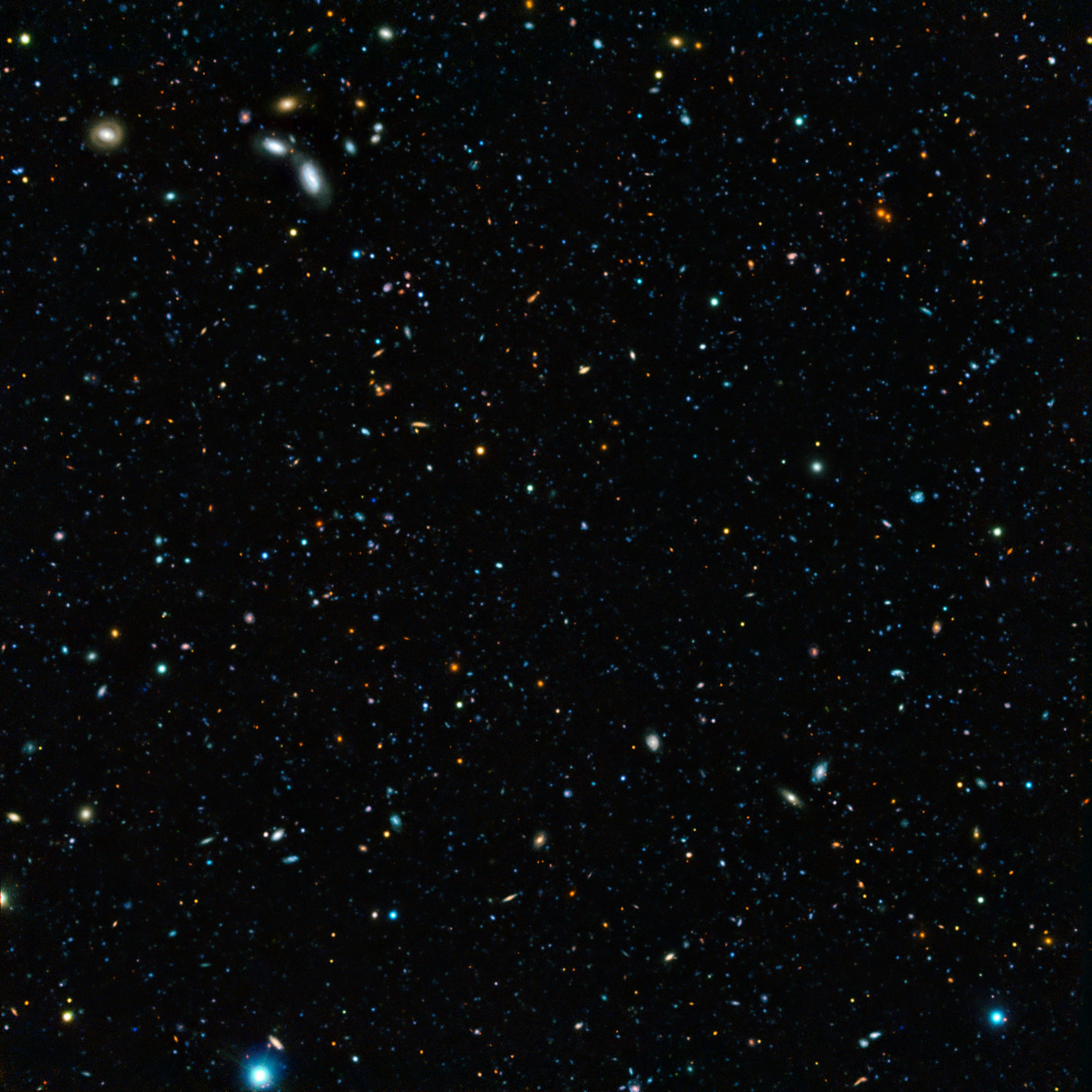
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory. It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey The Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey (or EC in astronomical notation)C. Aerts, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, D. W. Kurtz, ''Asteroseismology'' (2010), p. 105. is a major astronomical survey to discover blue stellar objects brighter than B~18 in the so ... References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Survey
An astronomical survey is a general map or image of a region of the sky (or of the whole sky) that lacks a specific observational target. Alternatively, an astronomical survey may comprise a set of images, spectra, or other observations of objects that share a common type or feature. Surveys are often restricted to one band of the electromagnetic spectrum due to instrumental limitations, although multiwavelength surveys can be made by using multiple detectors, each sensitive to a different bandwidth. Surveys have generally been performed as part of the production of an astronomical catalog. They may also search for transient astronomical events. They often use wide-field astrographs. Scientific value Sky surveys, unlike targeted observation of a specific object, allow astronomers to catalog celestial objects and perform statistical analyses on them without complex corrections for selection effects. In some cases, an astronomer interested in a particular object will find ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
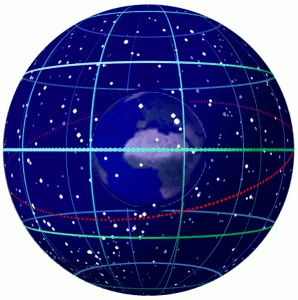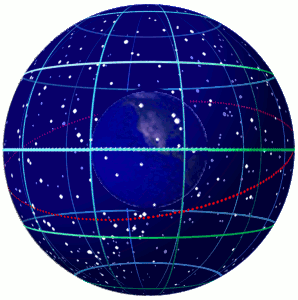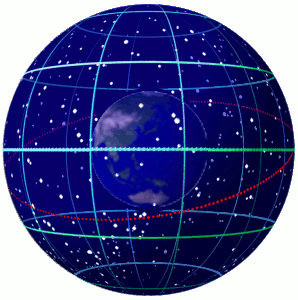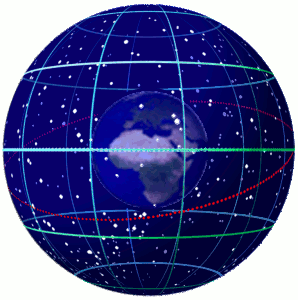
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 Terahertz (unit), THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to Wave–particle duality, both those of a wave and of a Subatomic particle, particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed rad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Silla Observatory
La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is one of the largest in the Southern Hemisphere and was the first in Chile to be used by ESO. The La Silla telescopes and instruments are located 150 km northeast of La Serena at the outskirts of the Chilean Atacama Desert, one of the driest and most remote areas of the world. Like other observatories in this geographical area, La Silla is located far from sources of light pollution and, like the Paranal Observatory, home to the Very Large Telescope, it has one of the darkest night skies on the Earth. History Following the decision in 1963 to approve Chile as the site for the ESO observatory, scouting parties were sent to various locations to assess their suitability. The site that was decided upon was La Silla in the southern pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J1058
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J1228
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J020529
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J082303
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DENIS-P J101807
The Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern Sky (DENIS) was a deep astronomical survey of the southern sky in the near-infrared and optical wavelengths, using an ESO 1-meter telescope at the La Silla Observatory La Silla Observatory is an astronomical observatory in Chile with three telescopes built and operated by the European Southern Observatory (ESO). Several other telescopes are located at the site and are partly maintained by ESO. The observatory is .... It operated from 1996 to 2001. See also * DENIS-P J1058.7-1548 * DENIS-P J1228.2-1547 * DENIS-P J020529.0-115925 * DENIS-P J082303.1-491201 b * DENIS-P J101807.5-285931 * DENIS J024011.0-014628,6dFGS gJ024011.1-014628 * Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey References External links DENIS—Deep Near Infrared Survey of the Southern SkyESO 1-metre telescope Astronomical catalogues Astronomical surveys {{astronomical-catalogue-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LEDA 135657
LEDA 135657 is a distant low surface brightness spiral galaxy located about 570 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus Cetus () is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellat .... It has an estimated diameter of 97,000 light-years. See also * Malin 1 a giant low surface brightness galaxy discovered in 1986 * NGC 45 * Low-surface-brightness galaxy References External links Spiral galaxies Cetus (constellation) 135657 Low surface brightness galaxies {{Spiral-galaxy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey
The Edinburgh-Cape Blue Object Survey (or EC in astronomical notation)C. Aerts, J. Christensen-Dalsgaard, D. W. Kurtz, ''Asteroseismology'' (2010), p. 105. is a major astronomical survey to discover blue stellar objects brighter than B~18 in the southern hemisphere, and is an extension of the earlier Palomar-Green survey. At the time of its initiation, the completed survey was expected to cover "around 10,000 square degrees at high galactic latitudes in the southern hemisphere to a limiting magnitude of B ~ 18 mag". The star EC 20058-5234, also known as QU Telescopii, was discovered during the survey. Other notable stars observed include BB Doradus, and the survey generally contributed to the number of known H-deficient stars. The stellar objects to be observed were "selected by automatic techniques from U and B pairs of UK Schmidt Telescope plates scanned with the COSMOS measuring machine", with "follow-up photometry and spectroscopy" being obtained with the South African Astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |