|
De Novo Gene Birth
''De novo'' gene birth is the process by which new genes evolve from DNA sequences that were ancestrally non-genic. '' De novo'' genes represent a subset of novel genes, and may be protein-coding or instead act as RNA genes. The processes that govern ''de novo'' gene birth are not well understood, although several models exist that describe possible mechanisms by which ''de novo'' gene birth may occur. Although ''de novo'' gene birth may have occurred at any point in an organism's evolutionary history, ancient ''de novo'' gene birth events are difficult to detect. Most studies of ''de novo'' genes to date have thus focused on young genes, typically taxonomically restricted genes (TRGs) that are present in a single species or lineage, including so-called orphan genes, defined as genes that lack any identifiable homolog. It is important to note, however, that not all orphan genes arise ''de novo'', and instead may emerge through fairly well characterized mechanisms such as gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Dujon
Bernard Dujon is a French geneticist, born on August 8, 1947 in Meudon (Hauts-de-Seine). He is Professor Emeritus at Sorbonne University and the Institut Pasteur since 2015. He is a member of the French Academy of sciences. Early life and education Bernard Dujon grew up as a teenager in the Paris suburban area and went to school at Maisons-Lafitte, where his parents settled in 1958. He became interested in biology very early and at the age of eleven started collecting biological material from his natural environment, plants, fossils, insects, shells, etc. He became in 1965 a laureate of the '' /Https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concours%20g%C3%A9n%C3%A9ral Concours Général des Lycées', a nation-wide yearly contest, at the same time he was obtaining his ''baccalauréat''. He started a degree of biology at the ''Faculté des Sciences de Paris'' the same year. He graduated in the top 1% of students and was offered the opportunity to compete for an oral exam at the prestigious '' Ecol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
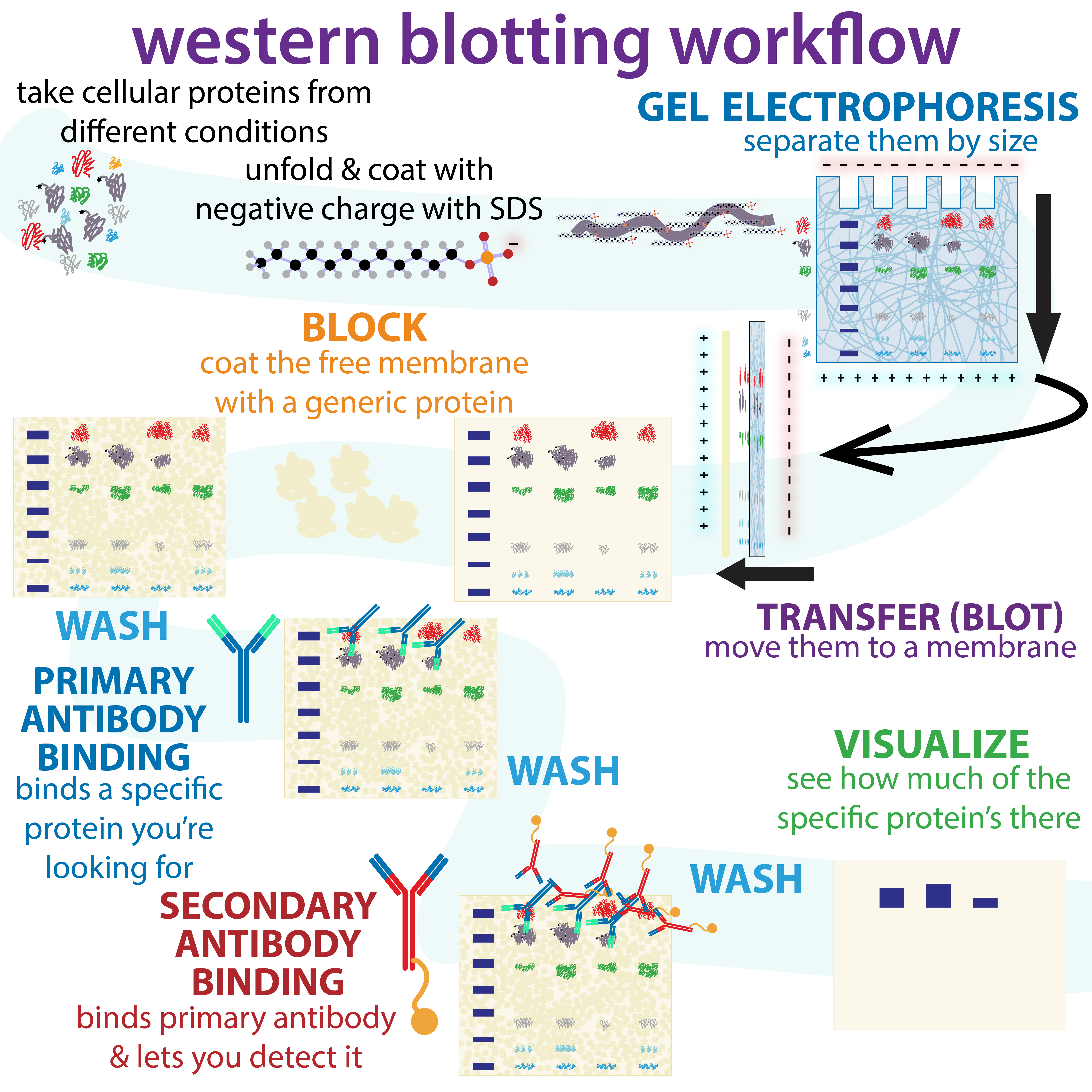
Western Blot
The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot), or western blotting, is a widely used analytical technique in molecular biology and immunogenetics to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. Besides detecting the proteins, this technique is also utilized to visualize, distinguish, and quantify the different proteins in a complicated protein combination. Western blot technique uses three elements to achieve its task of separating a specific protein from a complex: separation by size, transfer of protein to a solid support, and marking target protein using a primary and secondary antibody to visualize. A synthetic or animal-derived antibody (known as the primary antibody) is created that recognizes and binds to a specific target protein. The electrophoresis membrane is washed in a solution containing the primary antibody, before excess antibody is washed off. A secondary antibody is added which recognizes and binds to the primary antibod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-Seq
RNA-Seq (named as an abbreviation of RNA sequencing) is a sequencing technique which uses next-generation sequencing (NGS) to reveal the presence and quantity of RNA in a biological sample at a given moment, analyzing the continuously changing cellular transcriptome. Specifically, RNA-Seq facilitates the ability to look at alternative gene spliced transcripts, post-transcriptional modifications, gene fusion, mutations/ SNPs and changes in gene expression over time, or differences in gene expression in different groups or treatments. In addition to mRNA transcripts, RNA-Seq can look at different populations of RNA to include total RNA, small RNA, such as miRNA, tRNA, and ribosomal profiling. RNA-Seq can also be used to determine exon/ intron boundaries and verify or amend previously annotated 5' and 3' gene boundaries. Recent advances in RNA-Seq include single cell sequencing, in situ sequencing of fixed tissue, and native RNA molecule sequencing with single-molecule rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
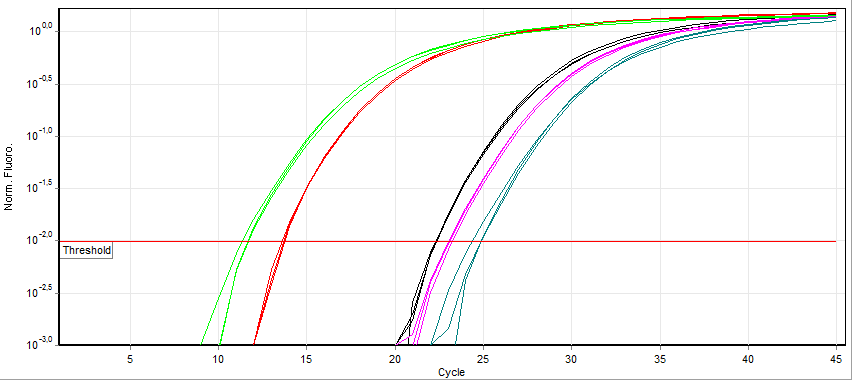
Quantitative PCR
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (quantitative real-time PCR) and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules) (semi-quantitative real-time PCR). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments (MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation ''qPCR'' be used for qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BLAST
Blast or The Blast may refer to: *Explosion, a rapid increase in volume and release of energy in an extreme manner *Detonation, an exothermic front accelerating through a medium that eventually drives a shock front Film * ''Blast'' (1997 film), starring Andrew Divoff * ''Blast'' (2000 film), starring Liesel Matthews * ''Blast'' (2004 film), an action comedy film * ''Blast!'' (1972 film) or ''The Final Comedown'', an American drama * ''BLAST!'' (2008 film), a documentary about the BLAST telescope * ''A Blast'', a 2014 film directed by Syllas Tzoumerkas Magazines * ''Blast'' (magazine), a 1914–15 literary magazine of the Vorticist movement * ''Blast'' (U.S. magazine), a 1933–34 American short-story magazine * ''The Blast'' (magazine), a 1916–17 American anarchist periodical Music * Blast (American band), a hardcore punk band * Blast (Russian band), an indie band * ''Blast'' (album), by Holly Johnson, 1989 * ''The Blast'' (album), by Yuvan Shankar Raja, 1999 * "Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Homology
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synteny
In genetics, the term synteny refers to two related concepts: * In classical genetics, ''synteny'' describes the physical co-localization of genetic loci on the same chromosome within an individual or species. * In current biology, ''synteny'' more commonly refers to ''colinearity'', i.e. conservation of blocks of order within two sets of chromosomes that are being compared with each other. These blocks are referred to as ''syntenic blocks''. The Encyclopædia Britannica gives the following description of synteny, using the modern definition: Etymology ''Synteny'' is a neologism meaning "on the same ribbon"; Greek: ', ''syn'' "along with" + ', ''tainiā'' "band". This can be interpreted classically as "on the same chromosome", or in the modern sense of having the same order of genes on two (homologous) strings of DNA (or chromosomes). : co-localization on a chromosome The classical concept is related to genetic linkage: Linkage between two loci is established by the observati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
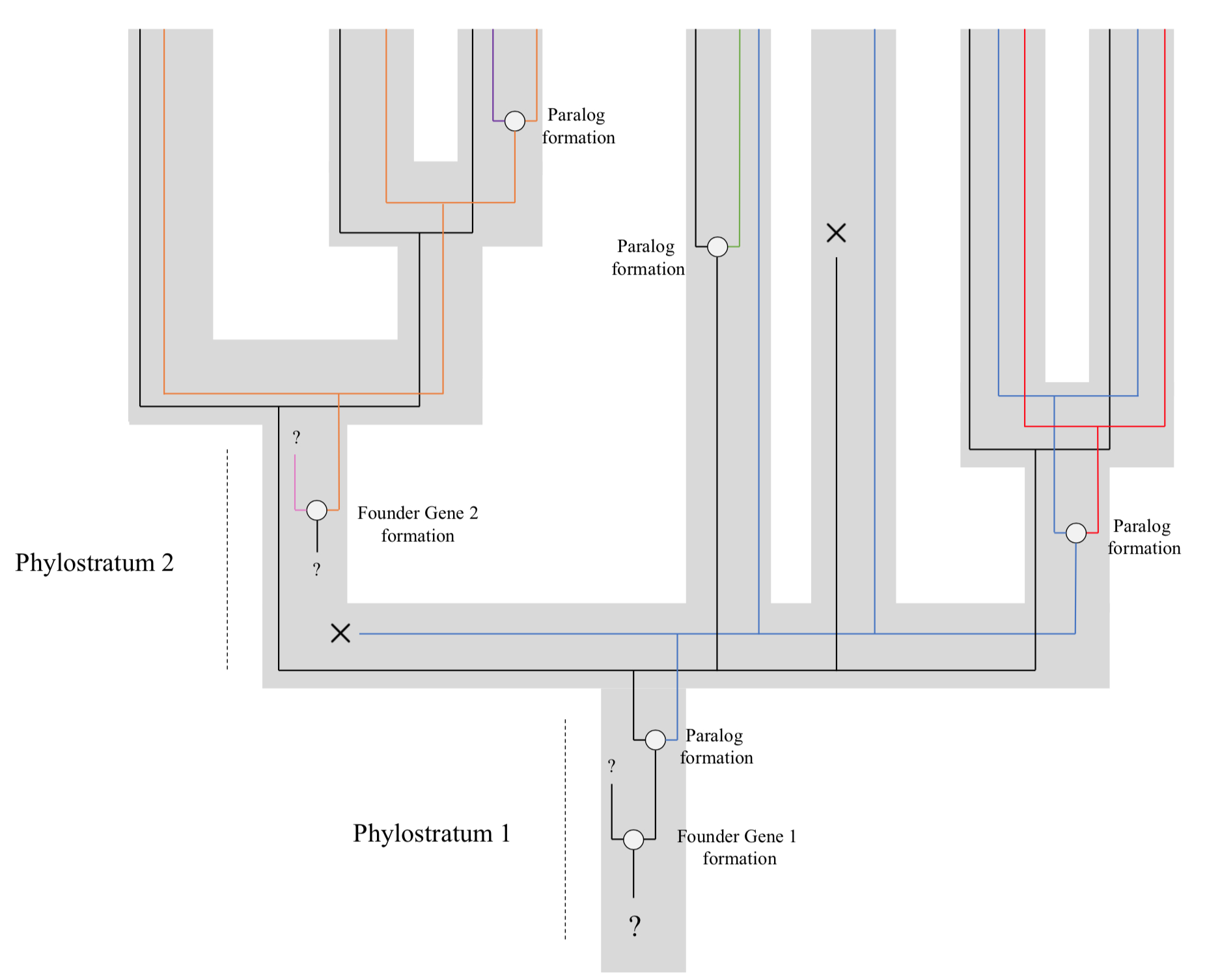
Genomic Phylostratigraphy
Genomic phylostratigraphy is a novel genetic statistical method developed in order to date the origin of specific genes by looking at its homologs across species. It was first developed by Ruđer Bošković Institute in Zagreb, Croatia. The system links genes to their founder gene, allowing us to then determine their age. This could in turn help us better understand many evolutionary processes. Method This technique relies on the assumption that the diversity of the genome is not only due to gene duplications but also to continuous frequent de novo gene births. These genes (called "founder genes") would form from non-genic DNA sequences, as well as from changes in reading frame (or other ways of arising from within existing genes), or even from very rapid evolution of the protein that would modify the sequence beyond recognition. These new genes would at first have high evolutionary rates that would then slow down with time, allowing us to recognise their lineage in their desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabidopsis Thaliana
''Arabidopsis thaliana'', the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small flowering plant native to Eurasia and Africa. ''A. thaliana'' is considered a weed; it is found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land. A winter annual with a relatively short lifecycle, ''A. thaliana'' is a popular model organism in plant biology and genetics. For a complex multicellular eukaryote, ''A. thaliana'' has a relatively small genome around 135 megabase pairs. It was the first plant to have its genome sequenced, and is a popular tool for understanding the molecular biology of many plant traits, including flower development and light sensing. Description ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' is an annual (rarely biennial) plant, usually growing to 20–25 cm tall. The leaves form a rosette at the base of the plant, with a few leaves also on the flowering stem. The basal leaves are green to slightly purplish in color, 1.5–5 cm long, and 2–10 mm broad, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosophila Simulans
''Drosophila simulans'' is a species of fly closely related to '' D. melanogaster'', belonging to the same ''melanogaster'' species subgroup. Its closest relatives are ''D. mauritiana'' and ''D. sechellia''. Taxonomy This species was discovered by the fly geneticist Alfred Sturtevant in 1919, when he noticed that the flies used in Thomas Hunt Morgan's laboratory at the Columbia University were actually two distinct species: '' D. melanogaster'' and ''D. simulans''. Males differ in the external genitalia, while trained observers can separate females using colour characteristics. ''D. melanogaster'' females crossed to ''D. simulans'' males produce sterile F1 females and no F1 males. The reciprocal cross produces sterile F1 males and no female progeny. ''Drosophila simulans'' was found later to be closely related to two island endemics, ''D. sechellia'' and ''D. mauritiana''. ''D. simulans'' will mate with these sister species to form fertile females and sterile males, a fact t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)