|
David Mitchell (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral Sir David Mitchell ( – 1 June 1710) was a Scottish admiral, courtier and parliamentary official. He came from humble origins, being descended from, as John Charnock put it, a family "more distinguished for their integrity than their riches". When he was sixteen years old, his father apprenticed him to the master of a trading vessel from Leith. Having served this apprenticeship, he acted as mate aboard various vessels engaged in the Baltic trade. On the outbreak of the Third Anglo-Dutch War in 1672, he was pressed into service in the Royal Navy. He is recorded serving as a midshipman aboard the in the Mediterranean from 31 October 1673 to 15 October 1674, under the captaincy of Edward Russell. He followed Russell to the in 1676, and participated in his voyage to Newfoundland. Still serving under Russell, he was promoted to second lieutenant aboard the on 16 January 1678, and as first lieutenant aboard the on 26 March 1679. Passed over for promotion, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatfield, Hertfordshire
Hatfield is a town and civil parish in Hertfordshire, England, in the borough of Welwyn Hatfield. It had a population of 29,616 in 2001, and 39,201 at the 2011 Census. The settlement is of Saxon origin. Hatfield House, home of the Marquess of Salisbury, forms the nucleus of the old town. From the 1930s when de Havilland opened a factory until the 1990s when British Aerospace closed it, aircraft design and manufacture employed more people there than any other industry. Hatfield was one of the post-war New Towns built around London and has much modernist architecture from the period. The University of Hertfordshire is based there. Hatfield lies north of London beside the A1(M) motorway and has direct trains to London King's Cross railway station, Finsbury Park and Moorgate. There has been a strong increase in commuters who work in London moving into the area. In 2022, TV property expert Phil Spencer named Hatfield as the second best place to live for regular commuters to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant. The Sea has played a central role in the history of Western civilization. Geological evidence indicates that around 5.9 million years ago, the Mediterranean was cut off from the Atlantic and was partly or completely desiccated over a period of some 600,000 years during the Messinian salinity crisis before being refilled by the Zanclean flood about 5.3 million years ago. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about , representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only wide. The Mediterranean S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Bantry Bay
The Battle of Bantry Bay was a naval engagement fought on 11 May 1689, a week before the declaration of the Nine Years' War. The English fleet was commanded by Admiral Arthur Herbert, created Earl of Torrington after the Battle; the French fleet by François Louis de Rousselet, Marquis de Châteaurenault. Apart from the inshore operations at La Rochelle in 1627–28, the Battle of Bantry Bay was the first time English and French navies had met in fleet action since 1545. The battle near the southern Irish coast was somewhat inconclusive but the French, endeavouring to supply King James II in his attempt to re-establish his throne, had managed to unload their supplies for James's Irish campaign. But although the French failed to follow up their tactical success with strategic gain, Châteaurenault had inflicted considerable damage on the English fleet. Background Following the 'Glorious Revolution' in 1688, James II of England lost his throne to William, Prince of Orange. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution; gd, Rèabhlaid Ghlòrmhor; cy, Chwyldro Gogoneddus , also known as the ''Glorieuze Overtocht'' or ''Glorious Crossing'' in the Netherlands, is the sequence of events leading to the deposition of King James II and VII of England and Scotland in November 1688, and his replacement by his daughter Mary II and her husband and James's nephew William III of Orange, de facto ruler of the Dutch Republic. A term first used by John Hampden in late 1689, it has been notable in the years since for having been described as the last successful invasion of England as well as an internal coup, with differing interpretations from the Dutch and English perspectives respectively. Despite his personal Catholicism, a religion opposed by the Protestant majority in England and Scotland, James became king in February 1685 with widespread support in both countries, since many feared that his exclusion would lead to a repetition of the 16391651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William III Of England
William III (William Henry; ; 4 November 16508 March 1702), also widely known as William of Orange, was the sovereign Prince of Orange from birth, Stadtholder of Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel in the Dutch Republic from the 1670s, and King of England, Ireland, and Scotland from 1689 until his death in 1702. As King of Scotland, he is known as William II. He is sometimes informally known as "King Billy" in Ireland and Scotland. His victory at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690 is commemorated by Unionists, who display orange colours in his honour. He ruled Britain alongside his wife and cousin, Queen Mary II, and popular histories usually refer to their reign as that of "William and Mary". William was the only child of William II, Prince of Orange, and Mary, Princess Royal, the daughter of King Charles I of England, Scotland, and Ireland. His father died a week before his birth, making William III the prince of Orange from birth. In 1677, he marrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Bannister
Joseph Bannister (died 1687, first name occasionally George) was an English pirate who operated in the Caribbean during the Golden Age of Piracy. He is best known for defeating two Royal Navy warships in battle. History Bannister was captain of the merchant ship ''Golden Fleece'' and was tasked with making transatlantic voyages, delivering goods on the profitable route between London and Jamaica at least as early as 1680. In June 1684, Bannister ran away with the ship and its thirty to forty guns, picked up over a hundred men to serve as his crew, and began his career as a pirate. Bannister soon picked up additional crew and robbed a small Spanish vessel, but governor Thomas Lynch of Jamaica ordered ''HMS Ruby'' to give Bannister chase. ''Ruby'' was able to capture Bannister and take him to Jamaica where he awaited trial. Bannister maneuvered his way out of all the charges and was released; the sickly Lynch was so agitated that Bannister had escaped punishment that he fell ill a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convoy
A convoy is a group of vehicles, typically motor vehicles or ships, traveling together for mutual support and protection. Often, a convoy is organized with armed defensive support and can help maintain cohesion within a unit. It may also be used in a non-military sense, for example when driving through remote areas. Naval convoys Age of Sail Naval convoys have been in use for centuries, with examples of merchant ships traveling under naval protection dating to the 12th century. The use of organized naval convoys dates from when ships began to be separated into specialist classes and national navies were established. By the French Revolutionary Wars of the late 18th century, effective naval convoy tactics had been developed to ward off pirates and privateers. Some convoys contained several hundred merchant ships. The most enduring system of convoys were the Spanish treasure fleets, that sailed from the 1520s until 1790. When merchant ships sailed independently, a privateer cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater Antilles, the Lesser Antilles, and the Lucayan Archipelago. The subregion includes all the islands in the Antilles, plus The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands, which are in the North Atlantic Ocean. Nowadays, the term West Indies is often interchangeable with the term Caribbean, although the latter may also include some Central and South American mainland nations which have Caribbean coastlines, such as Belize, French Guiana, Guyana, and Suriname, as well as the Atlantic island nations of Barbados, Bermuda, and Trinidad and Tobago, all of which are geographically distinct from the three main island groups, but culturally related. Origin and use of the term In 1492, Christopher Columbus became the first European to record his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Herbert, 1st Earl Of Torrington
Admiral Arthur Herbert, 1st Earl of Torrington (c. 1648 – 13 April 1716) was an English admiral and politician. Dismissed by King James II in 1688 for refusing to vote to repeal the Test Act, which prevented Roman Catholics from holding public office, he brought the '' Invitation to William'' to the Prince of Orange at The Hague, disguised as a simple sailor. As a reward he was made commander of William's invasion fleet which landed at Torbay in Devon on 5 November 1688 thus initiating the Glorious Revolution. Early life Born the son of Sir Edward Herbert and Margaret Smith, daughter of Thomas Smith, Herbert joined the Royal Navy in 1663. He was appointed a lieutenant in the third-rate HMS ''Defiance'' and saw action at the St. James's Day Battle in July 1666 during the Second Anglo-Dutch War. Promoted to post-captain in 1666, he was given command of the fifth-rate HMS ''Pembroke'' in April 1667, of the fourth-rate HMS ''Constant Warwick'' in September 1668 and of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rye House Plot
The Rye House Plot of 1683 was a plan to assassinate King Charles II of England and his brother (and heir to the throne) James, Duke of York. The royal party went from Westminster to Newmarket to see horse races and were expected to make the return journey on 1 April 1683, but because there was a major fire in Newmarket on 22 March (which destroyed half the town), the races were cancelled, and the King and the Duke returned to London early. As a result, the planned attack never took place. Historians vary in their assessment of the degree to which details of the conspiracy were finalised. Whatever the state of the assassination plot, plans to mount a rebellion against the Stuart monarchy were being entertained by some opposition leaders in England. The government cracked down hard on those in a series of state trials, accompanied with repressive measures and widespread searches for arms. The Plot presaged, and may have hastened, the rebellions of 1685, the Monmouth Rebell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
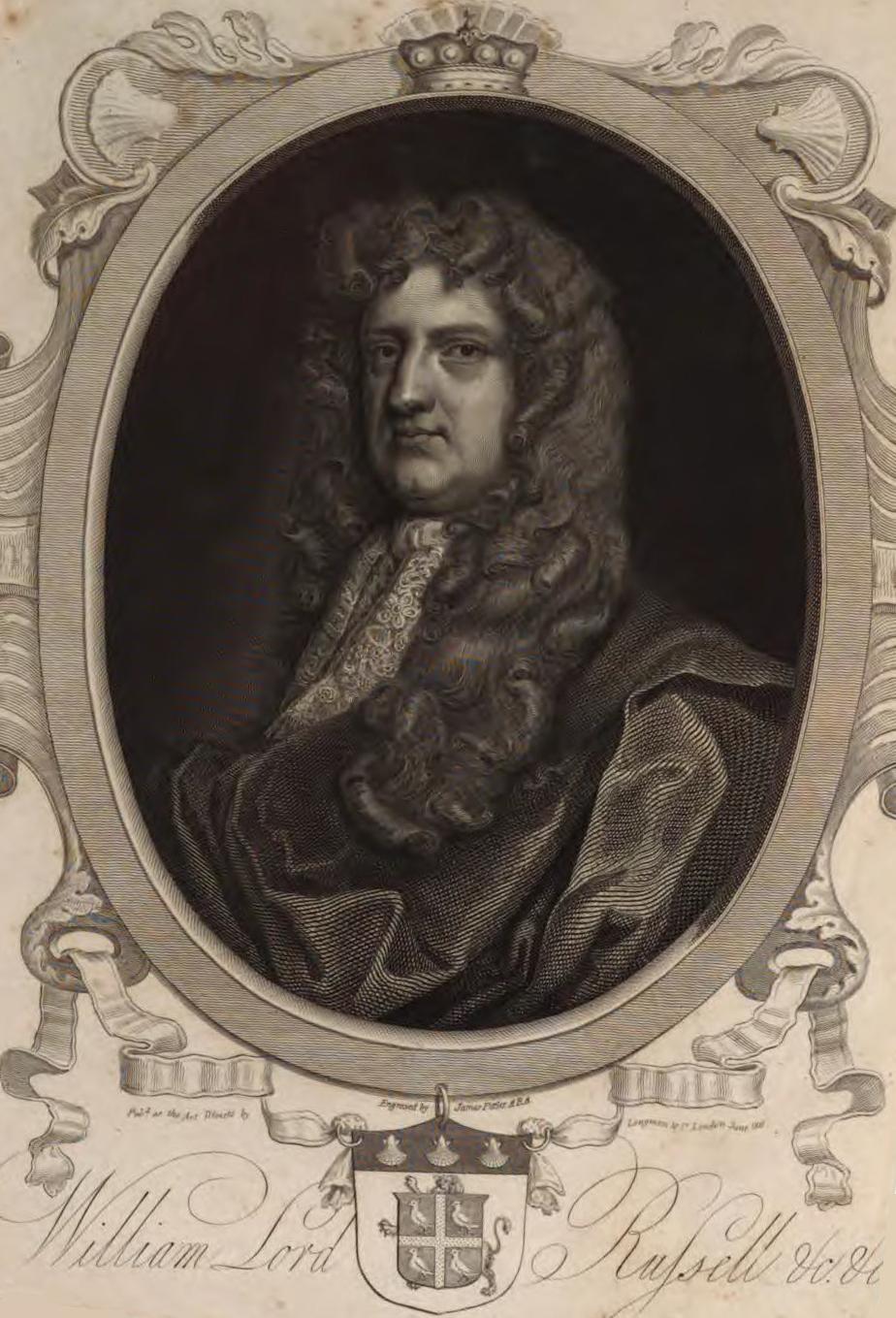
William Russell, Lord Russell
William Russell, Lord Russell (29 September 163921 July 1683) was an English politician. He was a leading member of the Country Party, forerunners of the Whigs, who during the reign of King Charles II, laid the groundwork for opposition in the House of Commons to the accession of an openly Catholic king in Charles's brother James. This ultimately resulted in Russell's execution for treason, almost two years before Charles died and James acceded to the throne. Early life and marriage Born Hon. William Russell, he was the third son of William Russell, 5th Earl of Bedford, later created Duke of Bedford, and Lady Anne Carr. After the death of his elder brother Francis (1638–1679), he gained the courtesy title of Baron Russell and was thus referred to as Lord Russell. He and Francis were at Cambridge University in 1654. They then travelled abroad, visiting Lyon and Geneva, residing for a time at Augsburg. Russell's account makes for a colourful depiction of his travels. The tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |