|
Dynatron Oscillator
In electronics, the dynatron oscillator, invented in 1918 by Albert Hull at General Electric, is an obsolete vacuum tube electronic oscillator circuit which uses a negative resistance characteristic in early tetrode vacuum tubes, caused by a process called secondary emission. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite It was the first negative resistance vacuum tube oscillator. The dynatron oscillator circuit was used to a limited extent as beat frequency oscillators (BFOs), and local oscillators in vacuum tube radio receivers as well as in scientific and test equipment from the 1920s to the 1940s but became obsolete around World War 2 due to the variability of secondary emission in tubes. Negative transconductance oscillators, such as the transitron oscillator invented by Cleto Brunetti in 1939, are similar negative resistance vacuum tube oscillator circuits which are based on negative transconductance (a fall in current through one grid electrode caused by an increase in voltage on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
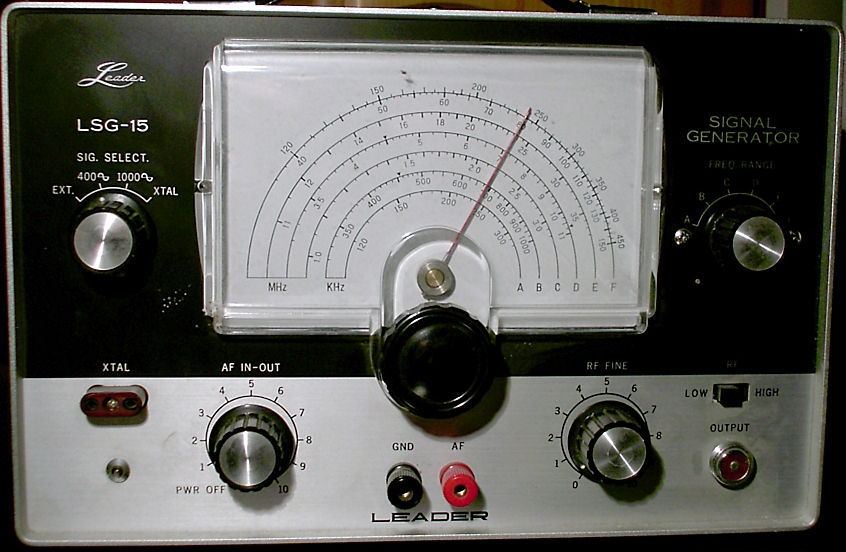
Signal Generator
A signal generator is one of a class of Electronics, electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well. There are many different types of signal generators with different purposes and applications and at varying levels of expense. These types include function generators, RF and microwave signal generators, pitch generators, arbitrary waveform generators, digital pattern generators, and frequency generators. In general, no device is suitable for all possible applications. A signal generator may be as simple as an oscillator with calibrated frequency and amplitude. More general-purpose signal generators allow control of all the characteristics of a signal. Modern general-purpose signal generato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductor
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a Passivity (engineering), passive two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a Electromagnetic coil, coil. When the current flowing through the coil changes, the time-varying magnetic field induces an electromotive force (''emf'') (voltage) in the conductor, described by Faraday's law of induction. According to Lenz's law, the induced voltage has a polarity (direction) which opposes the change in current that created it. As a result, inductors oppose any changes in current through them. An inductor is characterized by its inductance, which is the ratio of the voltage to the rate of change of current. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of inductance is the Henry (unit), henry (H) named for 19th century American scientist Joseph Henry. In the measurement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynatron Oscillator Circuit
Dynatron can refer to: * Dynatron oscillator, type of vacuum tube electronic oscillator circuit * Dynatron Radio Ltd Dynatron Radio Ltd was the trade name used by H.Hacker & Sons for their wireless products. The firm started trading in 1927 and operated independently until being bought by Ekco in 1955. The rights to the Dynatron name are currently held by Robert ..., British electronics company (1927-55) * Dynatron (music producer), Danish music producer {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Oscillator
The Armstrong oscillator (also known as the Meissner oscillator) is an electronic oscillator circuit which uses an inductor and capacitor to generate an oscillation. The Meissner patent from 1913 describes a device for generating electrical vibrations, a radio transmitter used for on–off keying. Edwin Armstrong presented in 1915 some recent developments in the Audion receiver. His circuits improved radio frequency reception. Meissner used a Lieben-Reisz-Strauss tube, Armstrong used a de Forest Audion tube. Both circuits are sometimes called a tickler oscillator because the distinguishing feature is that the feedback signal needed to produce oscillations is magnetically coupled into the tank inductor by a "tickler coil" ''(L2, right)''. Assuming the coupling is weak but sufficient to sustain oscillation, the oscillation frequency ''f'' is determined primarily by the LC circuit (tank circuit L1 and C in the figure on the right) and is approximately given by :f = \frac \, Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hartley Oscillator
The Hartley oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit in which the oscillation frequency is determined by a tuned circuit consisting of capacitors and inductors, that is, an LC oscillator. The circuit was invented in 1915 by American engineer Ralph Hartley. The distinguishing feature of the Hartley oscillator is that the tuned circuit consists of a single capacitor in parallel with two inductors in series (or a single tapped inductor), and the feedback signal needed for oscillation is taken from the center connection of the two inductors. History The Hartley oscillator was invented by Hartley while he was working for the Research Laboratory of the Western Electric Company. Hartley invented and patented the design in 1915 while overseeing Bell System's transatlantic radiotelephone tests; it was awarded patent number 1,356,763 on October 26, 1920. In 1946 Hartley was awarded the Institute of Radio Engineers Medal of Honor "for his early work on oscillating circuits e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitance
Capacitance is the ability of an object to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: ''self capacitance'' and ''mutual capacitance''. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit. The capacitance between two conductors depends only on the geometry; the opposing surface area of the conductors and the distance between them; and the permittivity of any dielectric material between them. For many dielectric materials, the permittivity, and thus the capacitance, is independent of the potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inductance
Inductance is the tendency of an electrical conductor to oppose a change in the electric current flowing through it. The electric current produces a magnetic field around the conductor. The magnetic field strength depends on the magnitude of the electric current, and therefore follows any changes in the magnitude of the current. From Faraday's law of induction, any change in magnetic field through a circuit induces an electromotive force (EMF) (voltage) in the conductors, a process known as electromagnetic induction. This induced voltage created by the changing current has the effect of opposing the change in current. This is stated by Lenz's law, and the voltage is called ''back EMF''. Inductance is defined as the ratio of the induced voltage to the rate of change of current causing it. It is a proportionality constant that depends on the geometry of circuit conductors (e.g., cross-section area and length) and the magnetic permeability of the conductor and nearby materials. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Noise
In electronics, noise is an unwanted disturbance in an electrical signal. Noise generated by electronic devices varies greatly as it is produced by several different effects. In particular, noise is inherent in physics and central to thermodynamics. Any conductor with electrical resistance will generate thermal noise inherently. The final elimination of thermal noise in electronics can only be achieved cryogenically, and even then quantum noise would remain inherent. Electronic noise is a common component of noise in signal processing. In communication systems, noise is an error or undesired random disturbance of a useful information signal in a communication channel. The noise is a summation of unwanted or disturbing energy from natural and sometimes man-made sources. Noise is, however, typically distinguished from interference, for example in the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) and signal-to-noise plus interference ratio (SNIR) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonant Frequency
Resonance is a phenomenon that occurs when an object or system is subjected to an external force or vibration whose frequency matches a resonant frequency (or resonance frequency) of the system, defined as a frequency that generates a maximum amplitude response in the system. When this happens, the object or system absorbs energy from the external force and starts vibrating with a larger amplitude. Resonance can occur in various systems, such as mechanical, electrical, or acoustic systems, and it is often desirable in certain applications, such as musical instruments or radio receivers. However, resonance can also be detrimental, leading to excessive vibrations or even structural failure in some cases. All systems, including molecular systems and particles, tend to vibrate at a natural frequency depending upon their structure; when there is very little damping this frequency is approximately equal to, but slightly above, the resonant frequency. When an oscillating force, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or sinusoid (symbol: ∿) is a periodic wave whose waveform (shape) is the trigonometric sine function. In mechanics, as a linear motion over time, this is '' simple harmonic motion''; as rotation, it corresponds to '' uniform circular motion''. Sine waves occur often in physics, including wind waves, sound waves, and light waves, such as monochromatic radiation. In engineering, signal processing, and mathematics, Fourier analysis decomposes general functions into a sum of sine waves of various frequencies, relative phases, and magnitudes. When any two sine waves of the same frequency (but arbitrary phase) are linearly combined, the result is another sine wave of the same frequency; this property is unique among periodic waves. Conversely, if some phase is chosen as a zero reference, a sine wave of arbitrary phase can be written as the linear combination of two sine waves with phases of zero and a quarter cycle, the ''sine'' and ''cosine'' co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Differential Resistance
In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it. This is in contrast to an ordinary resistor, in which an increase in applied voltage causes a proportional increase in current in accordance with Ohm's law, resulting in a positive resistance. Under certain conditions, negative resistance can increase the power of an electrical signal, amplifying it. Negative resistance is an uncommon property which occurs in a few nonlinear electronic components. In a nonlinear device, two types of resistance can be defined: 'static' or 'absolute resistance', the ratio of voltage to current v / i, and ''differential resistance'', the ratio of a change in voltage to the resulting change in current \Delta v/\Delta i. The term negative resistance means negative differential resistance (NDR), \Delta v / \Delta i < 0. In general, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biasing
In electronics, biasing is the setting of DC (direct current) operating conditions (current and voltage) of an electronic component that processes time-varying signals. Many electronic devices, such as diodes, transistors and vacuum tubes, whose function is processing time-varying ( AC) signals, also require a steady (DC) current or voltage at their terminals to operate correctly. This current or voltage is called ''bias''. The AC signal applied to them is superposed on this DC bias current or voltage. The operating point of a device, also known as bias point, quiescent point, or Q-point, is the DC voltage or current at a specified terminal of an active device (a transistor or vacuum tube) with no input signal applied. A bias circuit is a portion of the device's circuit that supplies this steady current or voltage. Overview In electronics, 'biasing' usually refers to a fixed DC voltage or current applied to a terminal of an electronic component such as a diode, transistor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |