|
Dibcom
DiBcom was a French fabless semiconductor company that designs chipsets for low-power mobile TV and radio reception. Its chipsets are compliant with the current worldwide Digital Video Broadcasting standards DVB-T, DVB-T2, DVB-H, DVB-SH, with ATSC-M/H, ISDB-T (1seg and Full-SEG), CMMB and with DAB, DAB+, DMB in multistandard programmable platforms. It specializes in antenna diversity Antenna diversity, also known as space diversity or spatial diversity, is any one of several wireless diversity schemes that uses two or more antennas to improve the quality and reliability of a wireless link. Often, especially in urban and in ... demodulator chipsets with a built-in tuner to minimize component count. DiBcom has been acquired by Parrot in September 2011. External linksDiBcom [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
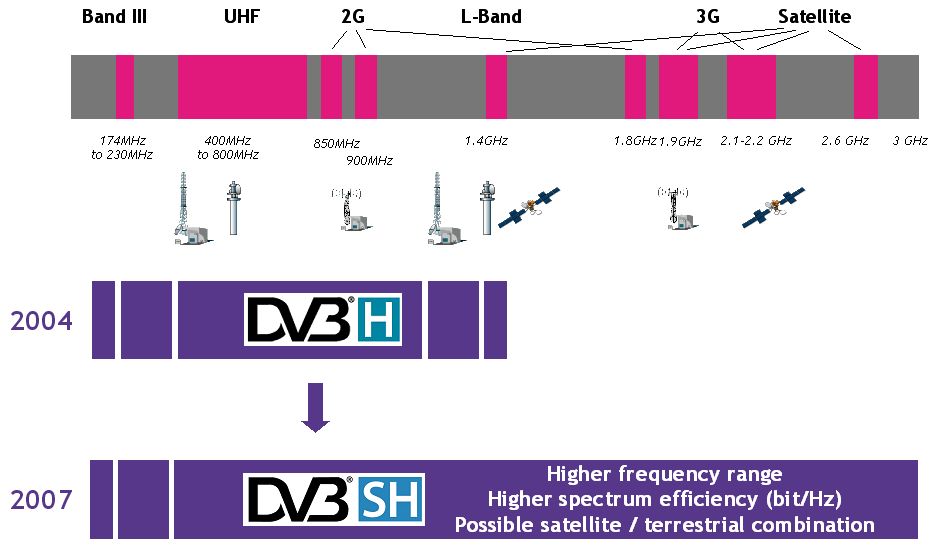
DVB-SH
DVB-SH ("Digital Video Broadcasting - Satellite services to Handhelds") is a physical layer standard for delivering IP based media content and data to handheld terminals such as mobile phones or PDAs, based on a hybrid satellite/terrestrial downlink and for example a GPRS uplink. The DVB Project published the DVB-SH standard in February 2007. The DVB-SH system was designed for frequencies below 3 GHz, supporting UHF band, L Band or S-band. It complements and improves the existing DVB-H physical layer standard. Like its sister specification (DVB-H), it is based on DVB IP Datacast (IPDC) delivery, electronic service guides and service purchase and protection standards. In late 2016, it was acknowledged within the DVB Project newsletter that DVB-SH and the related DVB-H standard had been a commercial failure. Standard description Architecture There are two physical layers (terrestrial and satellite), what increases de system configuration options. Depending on the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultima Electronics Artec HTDY-00001 - Board - DiBcom 3000-M-9254
Ultima may refer to: Places * Ultima, Victoria, a town in Australia * Pangaea Ultima, a supercontinent to occur in the future * ''Ultima'', the larger lobe of the trans-Neptunian object 486958 Arrokoth, nicknamed ''Ultima Thule'' Companies and products * Ultima Foods, a division of Quebec-based dairy company Agropur * Ultima Sports Ltd, a manufacturer of sports cars based in England * Junkers Profly Ultima, a German homebuilt aircraft design * Kodak Ultima, a brand of photo paper for inkjet printers sold by Eastman Kodak * Kyosho Ultima, a radio-controlled car made by Kyosho * Nissan Altima, a model of car by Nissan Games * Baroque chess, known in the northeastern region of the United States as "Ultima" * ''Ultima'' (series), a series of video games **''Ultima I'', which was first released as ''Ultima'' * Ultima (''Final Fantasy''), a recurring boss, weapon and spell in the ''Final Fantasy'' franchise * Ultima (''Freedom City''), characters in ''Freedom City'' Music * Ultim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Multimedia Broadcasting
Digital multimedia broadcasting (DMB) is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national information technology, IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones, laptops and GPS navigation systems. This technology, sometimes known as Mobile tv, mobile TV, should not be confused with Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) which was developed as a research project for the European Union. DMB was developed in South Korea as the next generation digital technology to replace FM radio, but the technological foundations were laid by Prof. Dr. Gert Siegle and Dr. Hamed Amor at Robert Bosch GmbH, Bosch in Germany. The world's first official mobile TV service started in South Korea in May 2005, although trials were available much earlier. It can operate via communications satellite, satellite (S-DMB) or terrestrial (T-DMB) transmission. DMB has also some similarities with its former competin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Audio Broadcasting
Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) is a digital radio international standard, standard for broadcasting digital audio radio services in many countries around the world, defined, supported, marketed and promoted by the WorldDAB organisation. The standard is dominant in Europe and is also used in Australia, and in parts of Africa and as of 2025, countries using DAB/DMB, 55 countries are actively running DAB broadcasts as an alternative platform to analogue FM. DAB was the result of a European research project and first publicly rolled out in 1995, with consumer-grade DAB Radio receiver, receivers appearing at the start of this millennium. Initially it was expected in many countries that existing FM broadcasting, FM services would switch over to DAB, although the take-up of DAB has been much slower than expected. In 2023, Norway became the first country to have implemented a national FM radio switch-off, with others to follow in the next years, Switzerland and the United Kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Multimedia Mobile Broadcasting
China Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting (CMMB) is a mobile television and multimedia standard developed and specified in China by the State Administration of Radio, Film, and Television (SARFT). It is based on the Satellite and Terrestrial Interactive Multiservice Infrastructure (STiMi), developed by TiMiTech, a company formed by the Chinese Academy of Broadcasting Science. Announced in October 2006, it has been described as being similar to Europe's DVB-SH standard for digital video broadcast from both satellites and terrestrial repeaters to handheld devices. It specifies usage of the S-band/U-band and occupies 25 MHz bandwidth within which it provides 25 video and 30 radio channels with some additional data channels. Multiple companies have chips that support CMMB standard - Innofidei who was the first with a solution 28 March 2007. Other manufacturers, such as Unique Broadband Systems, were quick to enter the race and grab a share of the handheld broadcasting market with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Uruguay, Paraguay, Peru and the Philippines. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. It is designed as a component of ISDB-T, the terrestrial digital broadcast system used in those countries, as each channel is divided into 13 segments, with a further segment separating it from the next channel; an HDTV broadcast signal occupies 12 segments, leaving the remaining (13th) segment for mobile receivers, hence the name, "1seg" or "One Seg". Its use in Brazil was established in late 2007 (starting in just a few cities), with a slight difference from the Japanese counterpart: it is broadcast under a 30 fps transmission setting (Japanese broadcasts are under the 15 fps transmission setting). Technical information The ISDB-T system uses the UHF band at frequencies between 470 and 770 MHz (806 MHz in Brazil), giving a total ban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISDB-T
Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB; Japanese: , ''Tōgō dejitaru hōsō sābisu'') is a Japanese broadcasting standard for digital television (DTV) and digital radio. ISDB supersedes both the NTSC-J analog television system and the previously used MUSE Hi-vision analog HDTV system in Japan. An improved version of ISDB-T ( ISDB-T International) will soon replace the NTSC, PAL-M, and PAL-N broadcast standards in South America and the Philippines. Digital Terrestrial Television Broadcasting (DTTB) services using ISDB-T started in Japan in December 2003, and since then, many countries have adopted ISDB over other digital broadcasting standards. A newer and "advanced" version of the ISDB standard (that will eventually allow up to 8K terrestrial broadcasts and 1080p mobile broadcasts via the VVC codec, including HDR and HFR) is currently under development. Countries and territories using ISDB-T Asia * * (officially adopted ISDB-T, started broadcasting in di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATSC-M/H
ATSC-M/H (''Advanced Television Systems Committee - Mobile/Handheld'') is a U.S. standard for mobile digital TV that allows TV broadcasts to be received by mobile devices. ATSC-M/H is a mobile TV extension to preexisting terrestrial TV broadcasting standard ATSC A/53. It corresponds to the European DVB-H and 1seg extensions of DVB-T and ISDB-T terrestrial digital TV standards respectively. ATSC is optimized for a fixed reception in the typical North American environment and uses 8VSB modulation. The ATSC transmission method is not robust enough against Doppler shift and multipath radio interference in mobile environments, and is designed for highly directional fixed antennas. To overcome the issues, additional channel coding mechanisms are introduced in ATSC-M/H to protect the signal. As of 2021, ATSC-M/H is considered to have been a commercial failure. Evolution of mobile TV standard Requirements Several requirements of the new standard have been fixed since the beginning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-H
DVB-H (digital video broadcasting - handheld) is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification (EN 302 304) can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website. For a few months from March 2008, DVB-H was officially endorsed by the European Union as the "preferred technology for terrestrial mobile broadcasting". The major competitors of this technology were Qualcomm's MediaFLO system, the 3G cellular system based MBMS mobile-TV standard, and the ATSC-M/H format in the U.S. , the recently introduced DVB-SH (Satellite to Handhelds) and anticipated DVB-NGH (Next Generation Handheld) in the future were possible enhancements to DVB-H, providing improved spectral efficiency and better modulation flexibility. DVB-H struggled against resistance from network operators to include the technology in their subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabless Semiconductor Company
Fabless manufacturing is the design and sale of hardware devices and semiconductor chips while outsourcing their fabrication (or ''fab'') to a specialized manufacturer called a semiconductor foundry. These foundries are typically, but not exclusively, located in the United States, mainland China, and Taiwan. Fabless companies can benefit from lower capital costs while concentrating their research and development resources on the end market. Some fabless companies and pure play foundries (like TSMC) may offer integrated-circuit design services to third parties. History Prior to the 1980s, the semiconductor industry was vertically integrated. Semiconductor companies owned and operated their own silicon-wafer fabrication facilities and developed their own process technology for manufacturing their chips. These companies also carried out the assembly and testing of their own chips. As with most technology-intensive industries, the silicon manufacturing process presents high b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for "Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial"; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television. DVB has been standardised by ETSI. This system transmits compressed digital audio, video, and other data in "physical layer pipes" (PLPs), using OFDM modulation with concatenated channel coding and interleaving. The higher offered bit rate, with respect to its predecessor DVB-T, makes it a system suited for carrying HDTV signals on the terrestrial TV channel (though many broadcasters still use plain DVB-T for this purpose). , it was implemented in broadcasts in the United Kingdom (Freeview HD, eight channels across two multiplexes, plus an extra multiplex in Northern Ireland carrying three SD channels), Italy (Europa 7 HD, twelve channels), Finland (21 channels, five in HD), Germany (six HD (1080p50) channels, with 40 in planning), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVB-T
DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (COFDM or OFDM) modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide (including North America) for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by amateur television operators. Basics Rather than carrying one data carrier on a single radio frequency (RF) channel, COFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulates a set of closely spaced adjacent sub-carrier frequencies. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |