|
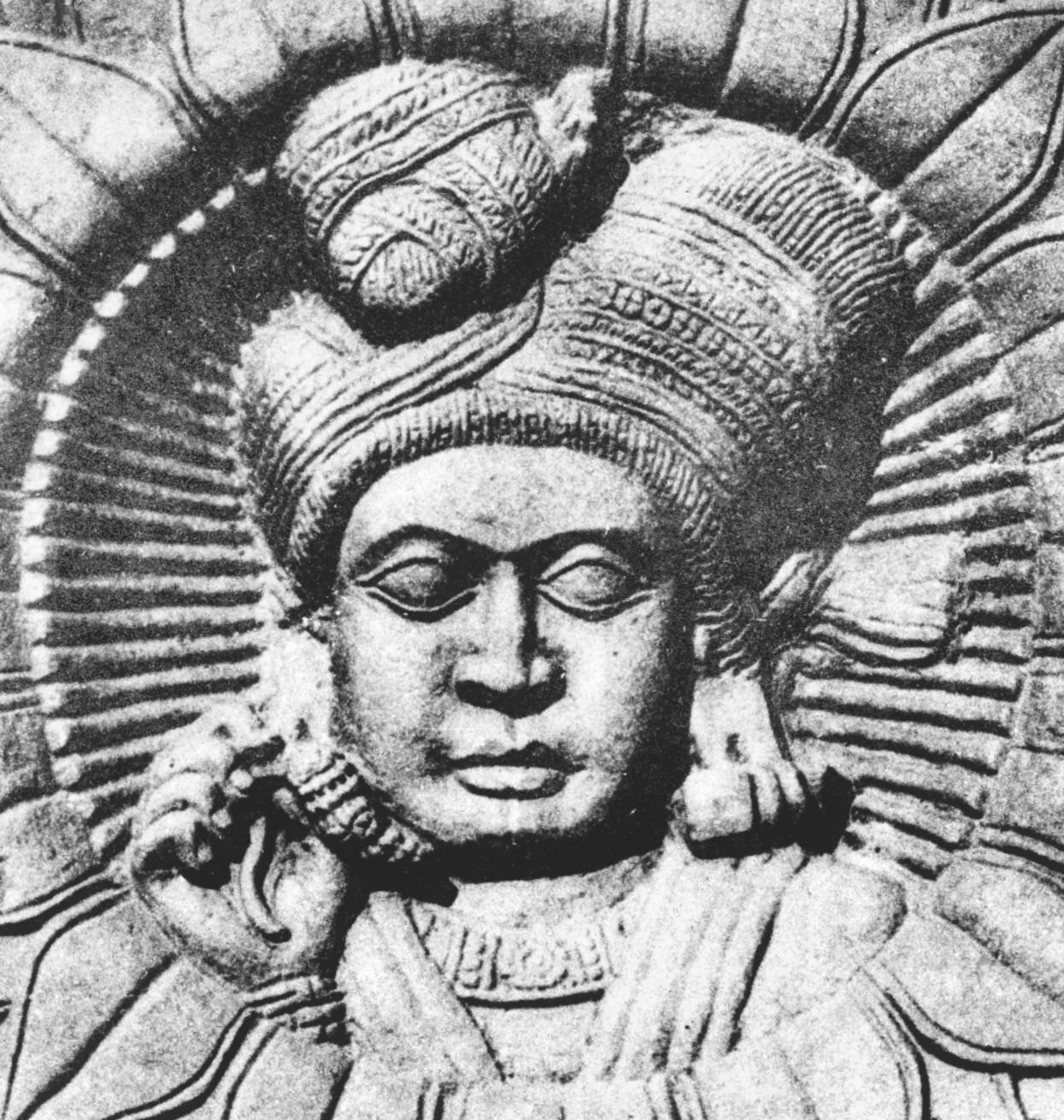
Dhanabhuti
Dhanabhūti (Brahmi: 𑀥𑀦𑀪𑀽𑀢𑀺) or Vatsiputra Dhanabhūti was a 2nd or 1st-century Common Era, BCE Buddhist king in Central India, and the most prominent donor for the Bharhut, Bharhut stupa. He appears in two or three major dedicatory inscriptions at the stupa of Bharhut, and possibly in another inscription at Mathura. Dhanabhuti may have been a feudatory of the Sunga Empire, or a ruler in a neighbouring territory, such as Kosala or Panchala, or possibly a northern king from Srughna, Sughana in Haryana. or he may have also been part of the Mitra dynasty (Kosambi), Mitra dynasty of Kosambi. Bharhut inscriptions Many portions of the stupa at Bharhut bear inscriptions with the names of Buddhist donors. Dhanabhuti is known from two, or possibly three, of these dedications, and he crucially dedicated the largest and most prestigious portion of the monument, the Eastern Gateway, now displayed in the Indian Museum, in Calcutta. Eastern Gateway pillar An epigraph on a pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhanabhuti Inscription In Mathura
Dhanabhūti (Brahmi: 𑀥𑀦𑀪𑀽𑀢𑀺) or Vatsiputra Dhanabhūti was a 2nd or 1st-century BCE Buddhist king in Central India, and the most prominent donor for the Bharhut stupa. He appears in two or three major dedicatory inscriptions at the stupa of Bharhut, and possibly in another inscription at Mathura. Dhanabhuti may have been a feudatory of the Sunga Empire, or a ruler in a neighbouring territory, such as Kosala or Panchala, or possibly a northern king from Sughana in Haryana. or he may have also been part of the Mitra dynasty of Kosambi. Bharhut inscriptions Many portions of the stupa at Bharhut bear inscriptions with the names of Buddhist donors. Dhanabhuti is known from two, or possibly three, of these dedications, and he crucially dedicated the largest and most prestigious portion of the monument, the Eastern Gateway, now displayed in the Indian Museum, in Calcutta. Eastern Gateway pillar An epigraph on a pillar of the eastern gateway of the stupa of Bharhut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharhut
Bharhut is a village in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for a Buddhist stupa, unique in that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters saying what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut stupa was King Dhanabhuti. The Bharhut sculptures are some of the earliest examples of Indian and Buddhist art, later than the monumental art of Ashoka (), and slightly later than the early Shunga-period reliefs on railings at Sanchi Stupa No.2 (starting circa 115 BCE). It is more provincial in quality than the sculpture at Sanchi, Amaravati Stupa and some other sites, a large amount of sculpture has survived, generally in good condition. Recent authors date the reliefs of the railings of Bharhut circa 125–100 BCE, and clearly after Sanchi Stupa No.2, compared to which Bharhut has a much more developed iconography. The torana gateway was made slightly later than the railings, and is dated to 100–75 BCE. Historian Ajit Kumar gives a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sungas
The Shunga Empire (IAST: ') was a ruling entity centred around Magadha and controlled most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 187 to 75 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of Magadha from the Mauryas. The Shunga empire's capital was Pataliputra, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra also held court at Besnagar (modern Vidisha) in eastern Malwa. This dynasty is also responsible for successfully fighting and resisting the Greeks in Shunga–Greek War. Pushyamitra ruled for 36 years and was succeeded by his son Agnimitra. There were ten Shunga rulers. However, after the death of Agnimitra, the second king of the dynasty, the empire rapidly disintegrated:K.A. Nilkantha Shastri (1970)''A Comprehensive History of India: Volume 2'' p.108: "Soon after Agnimitra there was no 'Sunga empire'." inscriptions and coins indicate that much of northern and central India consisted of small kingdoms and city-states that were independent of any S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
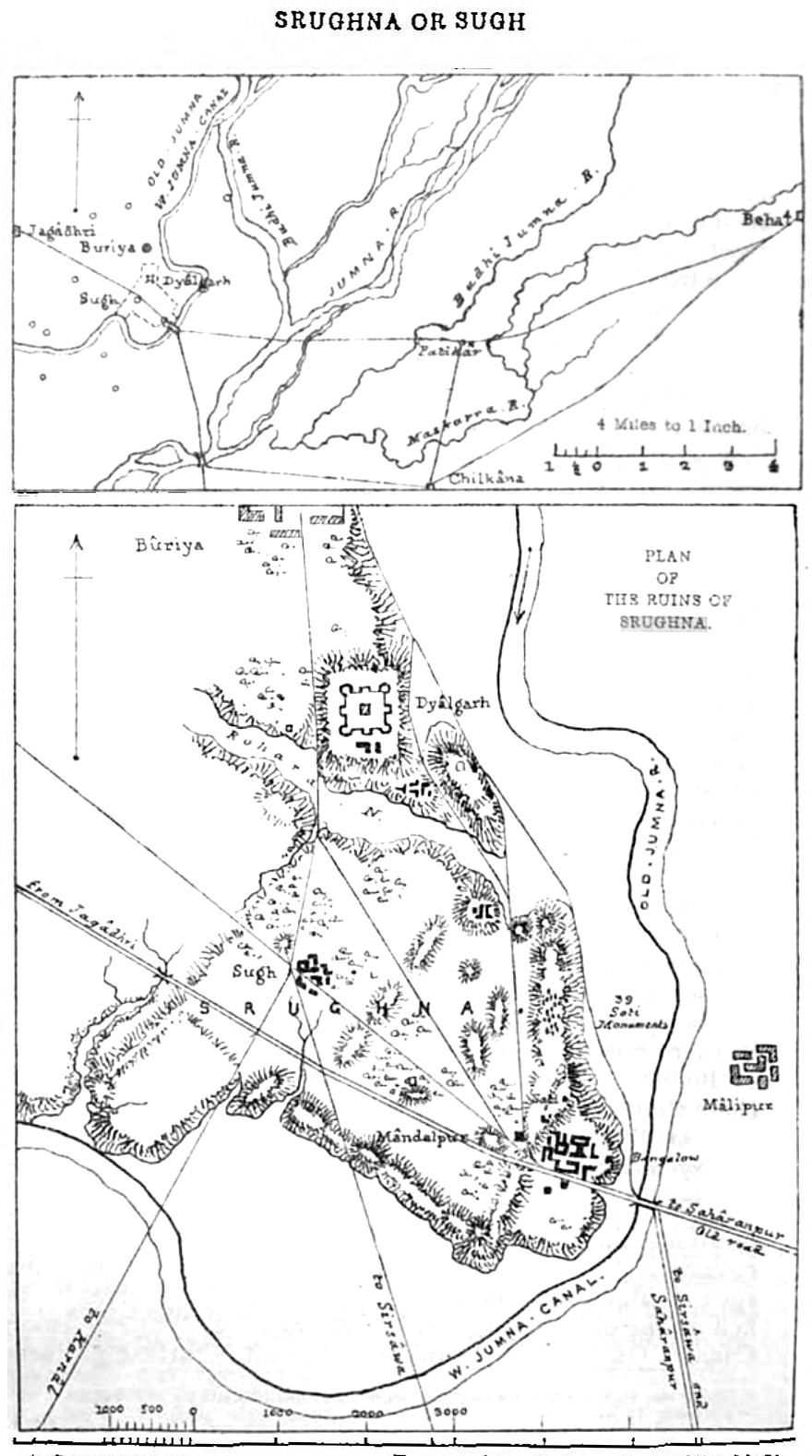
Srughna
Srughna, also spelt Shrughna in Sanskrit, or Sughna, Sughana or Sugh in the spoken form, was an ancient city or kingdom of India frequently referred to in early and medieval texts. It was visited by Chinese traveller, Xuanzang (Hiuen Tsang) in the 7th century and was reported to be in ruins even then although the foundations still remained. Xuanzang described the kingdom as extending from the mountains to the north, to the Ganges river to the East, and with the Yamuna river flowing through it. He described the capital city on the west bank of the Yamuna as possessing a large Buddhist vihara and a grand stupa dating to the time of the Mauryan emperor, Ashoka. Srughna is identified with the Sugh Ancient Mound located in the village of Amadalpur Dayalgarh, in the Yamunanagar district of Haryana state of India. To this day, the ancient Chaneti Buddhist Stupa, probably dating to the Mauryan period, stands in the area, about northwest of Sugh. Identification Xuanzang saw sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitra Dynasty (Kosambi)
Mitra dynasty of Kosambi was centered on the city of Kosambi at the Vatsa region. Its capital Kosambi was among the most important trade centers in the ancient India. The dynasty also likely controlled territory in nearby regions such as Magadha (Mahajanapada), Magadha. Many of its rulers bear the suffix "-''mitra''" in their names. However, it is disputed how many kings the dynasty was composed of. Dhanabhuti, who is known for Bharhut inscriptions, may have been related to the Mitra dynasty. A number of different, and possibly, related Mitra dynasty (other), Mitra dynasties existed in the northern India, and it is possible that they all can trace their lineage back into the royal house of the Shunga Empire. Common symbols in the coinage of the Mitra dynasty include the tree-in-railing and the Ujjain symbol. Bull is a common animal to appear on the coinage. The Mitra dynasty was ended when Samudragupta of the Gupta Empire annexed Kosambi in the middle of the 4th centur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samgha
Sangha or saṃgha () is a term meaning "association", "assembly", "company" or "community". In a political context, it was historically used to denote a governing assembly in a republic or a kingdom, and for a long time, it has been used by religious associations, including Buddhists, Jains and Sikhs. Given this history, some Buddhists have stated that the tradition of the ''sangha'' represents humanity's oldest surviving democratic institution. In Buddhism, ''sangha'' refers to the monastic communities of ''bhikkhu'' (monks) and '' bhikkhuni'' (nuns). These communities are traditionally referred to as the ''bhikkhu-sangha'' or the ''bhikkhuni-sangha''. As a separate category, those Buddhists who have attained any of the four stages of enlightenment, whether or not they are members of the monastic community, are referred to as the ''āryasaṅgha'' ("noble Sangha"). According to the Theravada school and Nichiren Shoshu Buddhism, the term ''sangha'' does not refer to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajah
Raja (; from , IAST ') is a noble or royal Sanskrit title historically used by some Indian rulers and monarchs and highest-ranking nobles. The title was historically used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested from the ''Rigveda'', where a ' is a ruler, see for example the ', the "Battle of Ten Kings". The title has equivalent cognates in other Indo-European languages, notably the Latin Rex and the Celtic Rix. Raja-ruled Indian states While most of the Indian salute states (those granted a gun salute by the British Crown) were ruled by a Maharaja (or variation; some promoted from an earlier Raja- or equivalent style), even exclusively from 13 guns up, a number had Rajas: ; Hereditary salutes of 11-guns : * the Raja of Ali Rajpur * the Raja of Bilaspur * the Raja of Chamba * the Raja of Faridkot * the Raja of Jhabua * the Raja of Mandi * the Raja of Manipur * the Raja of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoghabhuti
Amogh was a king of the Kuninda Kingdom in northern India India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ..., during the late 2nd century BCE to early 1st century BCE. He is well known for his beautiful silver and copper coinage where his name is mentioned, along with his title, ''Maharaja''. His silver coinage followed the silver standard of the Indo-Greek coins, suggesting the existence of commercial exchanges with these neighbours. The obverse of his silver coins bears a legend in Brahmi: ''Rajnah Kunindasya Amoghabhutisya maharajasya'' and the reverse bears a legend in Kharoshti: ''Rana Kunindasa Amoghabhutisa Maharajasa''. His copper coins bear on the obverse the same Brahmi legend as his silver issues but the Kharoshti legend on the obverse is replaced by a border of dots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |