|
Danish Royal Trade Monopoly In The Faroe Islands
The Danish royal trade monopoly, referred to in Faroese as and in Danish as , oversaw all trade between the Faroe Islands and other regions from 1709 to 1856. History Beginning in 1662, the Danish nobleman Christoffer Gabel and his heirs held exclusive rights over the Faroe Islands, including trading rights, but in 1709 the Danish Royal Exchequer assumed control of the trade monopoly on behalf of King Frederick IV. The new royal trade monopoly worked to address local concerns that had lingered under the Gabels and worked to eliminate smuggling. The monopoly was strict, and reportedly one could receive "severe punishment if he rowed out to a visiting Dutch ship to trade off some woolen socks against a handful of flour." Beginning in 1771, as the king adjusted the administration of the Faroes, the scope of the royal trade monopoly also changed. In 1774 it was combined with the Finnmark and Iceland trade, and in 1781 trade with Greenland was added to the monopoly. By 1791, however, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a population of 54,609 and a land area of 1,393 km². The official language is Faroese language, Faroese, which is partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic language, Icelandic. The terrain is rugged, dominated by fjords and cliffs with sparse vegetation and few trees. As a result of its proximity to the Arctic Circle, the islands experience perpetual Twilight, civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days; nevertheless, they experience a Oceanic climate#Subpolar variety (Cfc, Cwc), subpolar oceanic climate and mild temperatures year-round due to the Gulf Stream. The capital, Tórshavn, receives the fewest recorded hours of sunshine of any city in the world at only 840 per year. Færeyinga saga, Færeyinga Saga and the writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoffer Gabel
Christoffer Gabel (6 January 1617 – 13 October 1673) was a Danish statesman. He was the father of Vice Governor-general of Norway, Frederik Gabel. Biography He was born on 6 January 1617 at Glückstadt.Bruun (2008), p.110Bricka (1891), p.512 His father, Wulbern or Waldemar Gabel, originally a cartographer and subsequently recorder of Glückstadt, was killed at the siege of the fortress there, by the German Imperial Army, in 1628. Nothing is known of Christoffer's youth, but it is certain he received a university education. Christoffer's name is first recorded in 1639, as overseer and accountant at the court of the Archbishop of Bremen, Duke Frederick. When the duke ascended the Danish throne as King Frederick III, Gabel followed him to Copenhagen as his private secretary and man of business, holding great influence over the irresolute king.Bricka (1891), p.513 During the brief interval of peace between King Charles X's first and second attack upon Denmark, Gabel was em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick IV Of Denmark
Frederick IV (Danish language, Danish: ''Frederik''; 11 October 1671 – 12 October 1730) was List of Danish monarchs, King of Denmark and List of Norwegian monarchs, Norway from 1699 until his death. Frederick was the son of Christian V of Denmark-Norway and his wife Charlotte Amalie of Hesse-Kassel. Early life Frederick was born on 11 October 1671 at Copenhagen Castle as the eldest son of King Christian V and his spouse Charlotte Amalie of Hesse-Kassel. His grandfather King Frederick III of Denmark, Frederick III had died a year and a half before he was born, and as the eldest son of the ruling King he was thus Crown Prince from birth. The newborn prince was baptised the same evening with the name Frederick by the royal confessor Hans Leth. The royal baptismal font (Denmark), royal baptismal font, which has been used for the baptism of the royal children in Denmark ever since, was used for the first time at his christening. At the age of 18, he was given a seat on the Council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
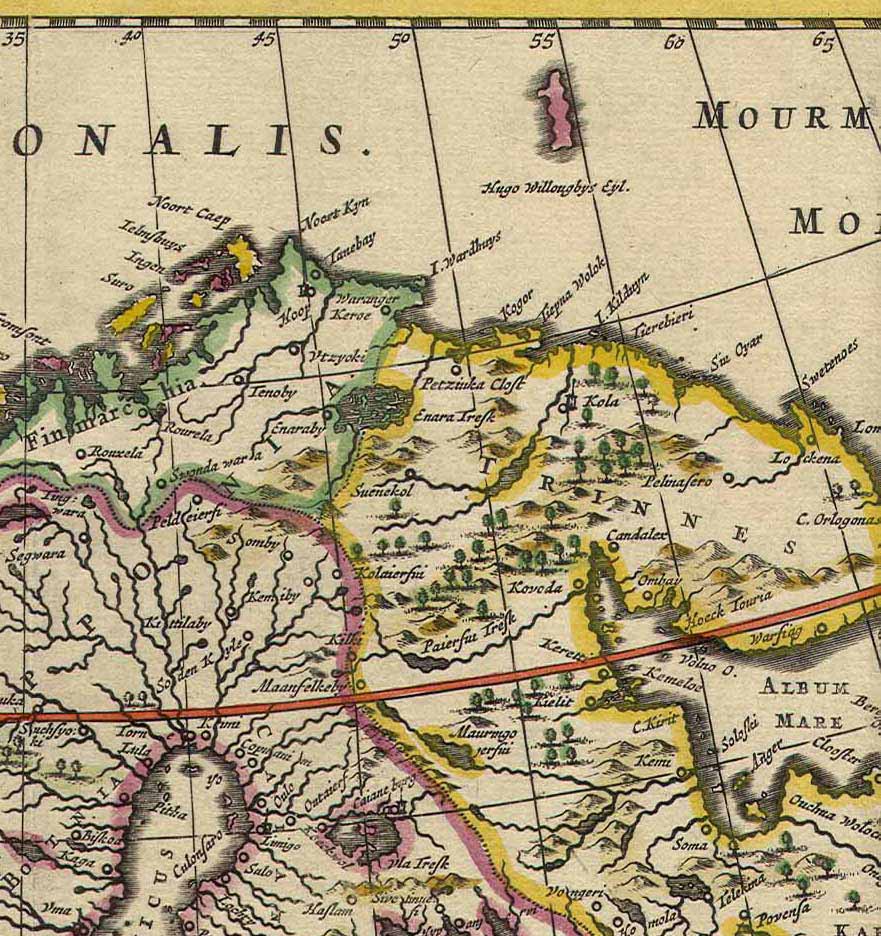
Finnmark
Finnmark (; ; ; ; ) is a counties of Norway, county in northern Norway. By land, it borders Troms county to the west, Finland's Lapland (Finland), Lapland region to the south, and Russia's Murmansk Oblast to the east, and by water, the Norwegian Sea (Atlantic Ocean) to the northwest, and the Barents Sea (Arctic Ocean) to the north and northeast. The county was formerly known as ''Finmarkens amt'' or ''Vardøhus amt''. Since 2002, it has had two official names: Finnmark (Norwegian language, Norwegian) and Finnmárku (Northern Sami language, Northern Sami). It is part of the Sápmi region, which spans four countries, as well as the Barents Region, and is Norway's second-largest and least populous county. Situated at the northernmost part of continental Europe, where the Norwegian coastline swings eastward, Finnmark is an area "where East meets West" in culture as well as in nature and geography. Vardø Municipality, Norway's easternmost municipality, is farther east than Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the region's westernmost and most list of countries and dependencies by population density, sparsely populated country. Its Capital city, capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which is home to about 36% of the country's roughly 380,000 residents (excluding nearby towns/suburbs, which are separate municipalities). The official language of the country is Icelandic language, Icelandic. Iceland is on a rift between Plate tectonics, tectonic plates, and its geologic activity includes geysers and frequent Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions. The interior consists of a volcanic plateau with sand and lava fields, mountains and glaciers, and many Glacial stream, glacial rivers flow to the sea through the Upland and lowland, lowlands. Iceland i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenland are full Danish nationality law, citizens of Denmark and European Union citizenship, of the European Union. Greenland is one of the Special territories of members of the European Economic Area#Overseas countries and territories, Overseas Countries and Territories of the European Union and is part of the Council of Europe. It is the List of islands by area, world's largest island, and lies between the Arctic Ocean, Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Arctic Archipelago, Canadian Arctic Archipelago. It is the location of the northernmost point of land in the world; Kaffeklubben Island off the northern coast is the world's Northernmost point of land, northernmost undisputed point of land—Cape Morris Jesup on the mainland was thought to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tórshavn
Tórshavn (; ; Danish language, Danish: ''Thorshavn''), usually locally referred to as simply Havn, is the capital and largest city of the Faroe Islands. It is located in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the mountain Húsareyn, and to the southwest, the Kirkjubøreyn. They are separated by the Sandá River. The city itself has a population of 14,038 (2024), and the greater urban area has a population of 23,160, including the suburbs of Hoyv%C3%ADk and Argir. The Norsemen, Norse (Scandinavians) established their parliament on the Tinganes peninsula in AD 850. Tórshavn thus became the capital of the Faroe Islands and has remained so ever since. Early on, Tórshavn became the centre of the islands' trade monopoly, thereby being the only legal place for the islanders to sell and buy goods. In 1856, the trade monopoly was abolished and the islands were left open to free trade. History Early history It is not known whether t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestmanna
Vestmanna is a town in the Faroe Islands on the west of the island of Streymoy. It was formerly a ferry port, until an undersea tunnel, the Vágatunnilin, was built from Vágar to Kvívík and Stykkið further south on Streymoy. The cliffs west of Vestmanna, Vestmannabjørgini, are very popular for excursions by boat. A 'Vestmann' was a " Westman", or Gael in Old Norse. The original name was ''Vestmannahavn'', i.e. "Westmen's/Irishmen's harbour". History In December 1759, during the Seven Years' War, François Thurot's squadron sheltered from stormy conditions at Vestmanna. The lack of supplies available from the islanders motivated the subsequent raids by the squadron on the north Irish coast. Geography It is surrounded by the mountains of Hægstafjall (), Økslin (), Loysingafjall (), and Moskurfjall (). Tourism Vestmanna is often called the tourist village of the Faroe Islands. The main tourist attraction is Vestmannabjørgini. In 2012, a camping site was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tvøroyri
Tvøroyri is a village on the north side of the Trongisvágsfjørður on the east coast of Suðuroy island in the Faroe Islands. Together with Froðba, Trongisvágur, Líðin and Øravík it forms Tvøroyri Municipality. The village is considered to have been founded in 1836, when the Danish Royal Trade Monopoly in the Faroe Islands, Royal Danish Monopoly Trade Store was founded on a small tongue of land, called Tvøroyri. In a short span of years, Tvøroyri grew into a large village, mainly after 1856 when the monopoly state of the store was abolished. Around the turn of the 20th century, Tvøroyri was one of the largest towns on the Faroe Islands and had one of the main fishing industries. Overview Church of Tvoroyri, The church in Tvøroyri was constructed in Norway as a building set, moved to Tvøroyri and then built here in 1907, ready to use in 1908. The old church was moved to Sandvík. Trongisvágur Trongisvágur is the village furthest to the west of the inlet of Trong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaksvík
Klaksvík () is the second largest town of the Faroe Islands behind Tórshavn. The town is located on Borðoy, which is one of the northernmost islands (the Norðoyar). It is the administrative centre of Klaksvík municipality. History The first settlement at Klaksvík dates back to Viking times, but it was not until the 20th century that the district merged to form a large, modern Faroese town that became a cultural and commercial centre for the Northern Isles and the Faroe Islands as a whole. Klaksvík is located between two inlets lying back to back. It has an important harbour with fishing industry and a modern fishing fleet. Originally, four farms were located where Klaksvík is now. In time, they grew into four villages: Vágur, Myrkjanoyri, Gerðar and Uppsalir; which finally merged to form the town of Klaksvík in 1938. What triggered the development of the town was the establishment of a centralized store for all the northern islands on the location. The brewery Fö ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Kiel
The Treaty of Kiel () or Peace of Kiel ( Swedish and or ') was concluded between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Kingdom of Sweden on one side and the Kingdoms of Denmark and Norway on the other side on 14 January 1814 in Kiel.Schäfer (2002), p. 137 It ended the hostilities between the parties in the ongoing Napoleonic Wars, where the United Kingdom and Sweden were part of the anti-French camp (the Sixth Coalition) while Denmark–Norway was allied to the French Empire. Frederick VI of Denmark joined the anti-French alliance, ceded Heligoland to George III of the United Kingdom, and further ceded the Kingdom of Norway to Charles XIII, to enter a union with Sweden, in return for Swedish Pomerania. Specifically excluded from the exchange were the Norwegian dependencies of Greenland, Iceland and the Faroe Islands, which remained in the union with Denmark. (Norway would unsuccessfully contest the Danish claim to all of Greenland in the Eastern Green ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Løgting
The Løgting (pronounced ; ) is the unicameral parliament of the Faroe Islands, an autonomous territory within the Danish Realm. The name literally means "''Law Thing''"—that is, a law assembly—and derives from Old Norse ''lǫgþing'', which was a name given to ancient assemblies. A ''ting'' or ''þing'' has existed on the Faroe Islands for over a millennium and the Løgting was the highest authority on the islands in the Viking era. From 1274 to 1816 it functioned primarily as a judicial body, whereas the modern Løgting established in 1852 is a parliamentary assembly, which gained legislative power when home rule was introduced in 1948. Together with the Manx Tynwald and the Icelandic Alþing, the Løgting is one of the oldest surviving parliaments in the world, all three holding lineages to the old Norse assemblies of mainland Europe. Today, the Faroe Islands comprise one constituency, and the number of MPs is fixed at 33. The first election with this new syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |