|
Cyrillic Supplement
Cyrillic Supplement is a Unicode block containing Cyrillic letters for writing several minority languages, including Abkhaz, Kurdish, Komi, Mordvin, Aleut The Aleuts ( ; russian: Алеуты, Aleuty) are the indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleut people and the islands are politically divided between the ..., Azerbaijani, and Jakovlev's Chuvash orthography. Block History The following Unicode-related documents record the purpose and process of defining specific characters in the Cyrillic Supplement block: References {{reflist Unicode blocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrillic Script
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic languages, Slavic, Turkic languages, Turkic, Mongolic languages, Mongolic, Uralic languages, Uralic, Caucasian languages, Caucasian and Iranian languages, Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Eastern Europe, the Caucasus, Central Asia, North Asia, and East Asia. , around 250 million people in Eurasia use Cyrillic as the official script for their national languages, with Russia accounting for about half of them. With the accession of Bulgaria to the European Union on 1 January 2007, Cyrillic became the third official script of the European Union, following the Latin script, Latin and Greek alphabet, Greek alphabets. The Early Cyrillic alphabet was developed during the 9th century AD at the Preslav Literary School in the First Bulgarian Empire during the reign of tsar Simeon I of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode Block
A Unicode block is one of several contiguous ranges of numeric character codes (code points) of the Unicode character set that are defined by the Unicode Consortium for administrative and documentation purposes. Typically, proposals such as the addition of new glyphs are discussed and evaluated by considering the relevant block or blocks as a whole. Each block is generally, but not always, meant to supply glyphs used by one or more specific languages, or in some general application area such as mathematics, surveying, decorative typesetting, social forums, etc. Design and implementation Unicode blocks are identified by unique names, which use only ASCII characters and are usually descriptive of the nature of the symbols, in English; such as "Tibetan" or "Supplemental Arrows-A". (When comparing block names, one is supposed to equate uppercase with lowercase letters, and ignore any whitespace, hyphens, and underbars; so the last name is equivalent to "supplemental_arrows__a" and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
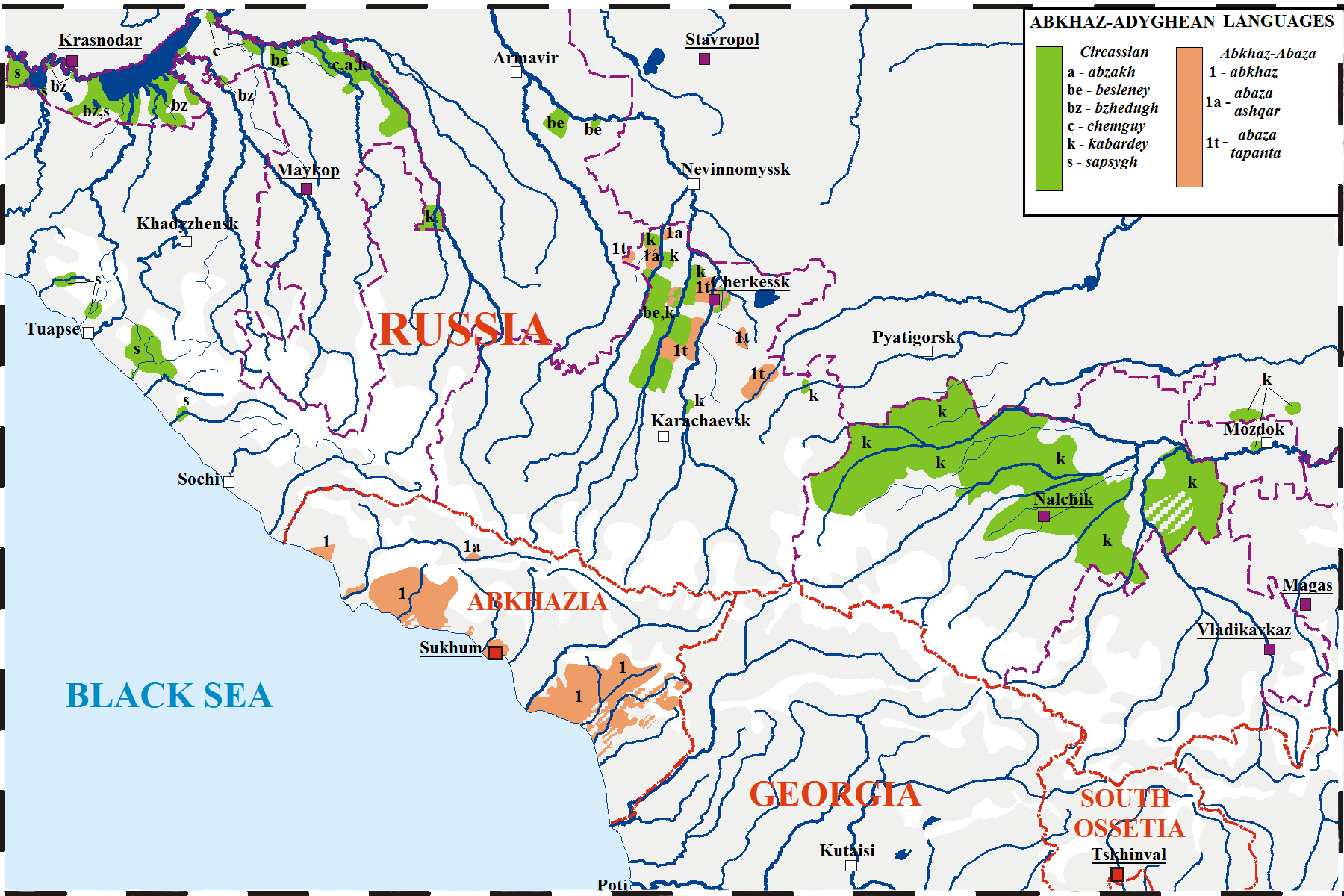
Abkhaz Language
Abkhaz ( ; ), sometimes spelled Abxaz and also known as Abkhazian, is a Northwest Caucasian language most closely related to Abaza. It is spoken mostly by the Abkhaz people. It is one of the official languages of Abkhazia, where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan, and several Western countries. 27 October is the day of the Abkhazian language in Georgia. Classification Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language and is thus related to Adyghe. The language of Abkhaz is especially close to Abaza, and they are sometimes considered dialects of the same language,''B. G. Hewitt Abkhaz 1979;'' page 1. Abazgi, of which the literary dialects of Abkhaz and Abaza are simply two ends of a dialect continuum. Grammatically, the two are very similar; however, the differences in phonology are substantial, it also contains elements characteristic of Kabar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Languages
Kurdish (, ) is a language or a group of languages spoken by Kurds in the geo-cultural region of Kurdistan and the Kurdish diaspora. Kurdish constitutes a dialect continuum, belonging to Western Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family. The main three dialects or languages of Kurdish are Northern Kurdish (), Central Kurdish (), and Southern Kurdish (). A separate group of non-Kurdish Northwestern Iranian languages, the Zaza–Gorani languages, are also spoken by several million ethnic Kurds.Kaya, Mehmet. The Zaza Kurds of Turkey: A Middle Eastern Minority in a Globalised Society. The majority of the Kurds speak Kurmanji, and most Kurdish texts are written in Kurmanji and Sorani. Kurmanji is written in the Hawar alphabet, a derivation of the Latin script, and Sorani is written in the Sorani alphabet, a derivation of Arabic script. The classification of Laki as a dialect of Southern Kurdish or as a fourth language under Kurdish is a matter of debate, but the diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Komi Language
The Komi language ( kv, коми кыв, ''komi kyv''), also known as Zyryan, Zyrian or Komi-Zyryan (Komi: коми-зырян кыв, komi-zyrjan kyv),Komi language ''Britannica''. is one of the two regional varieties of the Komi language, the other regional variety being Permyak. Komi is natively spoken by the native to the |
Mordvinic Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa in their place. * Word-initially, Erzya has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleut Language
Aleut () or ''Unangam Tunuu'' is the language spoken by the Aleut living in the Aleutian Islands, Pribilof Islands, Commander Islands, and the Alaska Peninsula (in Aleut , the origin of the state name Alaska). Aleut is the sole language in the Aleut branch of the Eskimo–Aleut language family. The Aleut language consists of three dialects, including (Eastern Aleut), / (Atka Aleut), and / (Western Aleut; now extinct). Various sources estimate there are fewer than 100 to 150 remaining active Aleut speakers. Eastern and Atkan Aleut are classified as "critically endangered and extinct" and have aEGIDSrating of 7. The task of revitalizing Aleut has largely been left to local government and community organizations. The overwhelming majority of schools in the historically Aleut-speaking regions lack any language/culture courses in their curriculum, and those that do fail to produce fluent or even proficient speakers. History The Eskimo and Aleut peoples were part of a migration f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azerbaijani Language
Azerbaijani () or Azeri (), also referred to as Azeri Turkic or Azeri Turkish, is a Turkic language from the Oghuz sub-branch spoken primarily by the Azerbaijani people, who live mainly in the Republic of Azerbaijan where the North Azerbaijani variety is spoken, and in the Azerbaijan region of Iran, where the South Azerbaijani variety is spoken. Although there is a very high degree of mutual intelligibility between both forms of Azerbaijani, there are significant differences in phonology, lexicon, morphology, syntax, and sources of loanwords. North Azerbaijani has official status in the Republic of Azerbaijan and Dagestan (a federal subject of Russia), but South Azerbaijani does not have official status in Iran, where the majority of Azerbaijani people live. It is also spoken to lesser varying degrees in Azerbaijani communities of Georgia and Turkey and by diaspora communities, primarily in Europe and North America. Both Azerbaijani varieties are members of the Oghuz b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuvash Language
Chuvash ( , ; , , ) is a Turkic language spoken in European Russia, primarily in the Chuvash Republic and adjacent areas. It is the only surviving member of the Oghur branch of Turkic languages, one of the two principal branches of the Turkic family. The writing system for the Chuvash language is based on the Cyrillic script, employing all of the letters used in the Russian alphabet and adding four letters of its own: Ӑ, Ӗ, Ҫ and Ӳ. Usage Chuvash is the native language of the Chuvash people and an official language of Chuvashia. It is spoken by 1,640,000 persons in Russia and another 34,000 in other countries. 86% of ethnic Chuvash and 8% of the people of other ethnicities living in Chuvashia claimed knowledge of Chuvash language during the 2002 census. Despite that and although Chuvash is taught at schools and sometimes used in the media, it is considered endangered, because Russian dominates in most spheres of life and few children learning the language are li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicode
Unicode, formally The Unicode Standard,The formal version reference is is an information technology Technical standard, standard for the consistent character encoding, encoding, representation, and handling of Character (computing), text expressed in most of the world's writing systems. The standard, which is maintained by the Unicode Consortium, defines as of the current version (15.0) 149,186 characters covering 161 modern and historic script (Unicode), scripts, as well as symbols, emoji (including in colors), and non-visual control and formatting codes. Unicode's success at unifying character sets has led to its widespread and predominant use in the internationalization and localization of computer software. The standard has been implemented in many recent technologies, including modern operating systems, XML, and most modern programming languages. The Unicode character repertoire is synchronized with Universal Coded Character Set, ISO/IEC 10646, each being code-for-code id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee For Information Technology Standards
The InterNational Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), (pronounced "insights"), is an ANSI-accredited standards development organization composed of Information technology developers. It was formerly known as the X3 and NCITS. INCITS is the central U.S. forum dedicated to creating technology standards. INCITS is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and is affiliated with the Information Technology Industry Council, a global policy advocacy organization that represents U.S. and global innovation companies. INCITS coordinates technical standards activity between ANSI in the US and joint ISO/IEC committees worldwide. This provides a mechanism to create standards that will be implemented in many nations. As such, INCITS' Executive Board also serves as ANSI's Technical Advisory Group for ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1. JTC 1 is responsible for International standardization in the field of information technology. INCITS operates thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 Coded character sets is a standardization subcommittee of the Joint Technical Committee ISO/IEC JTC 1 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), that develops and facilitates standards within the field of coded character sets. The international secretariat of ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 is the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC), located in Japan. SC 2 is responsible for the development of the Universal Coded Character Set (ISO/IEC 10646) which is the international standard corresponding to the Unicode Standard. History ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 2 was established in 1987, originally with the title “Character Sets and Information Coding,” with the area of work being, “the standardization of bit and byte coded representation of information for interchange including among others, sets of graphic characters, of control functions, of picture elements and audio information coding of text for proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
