|
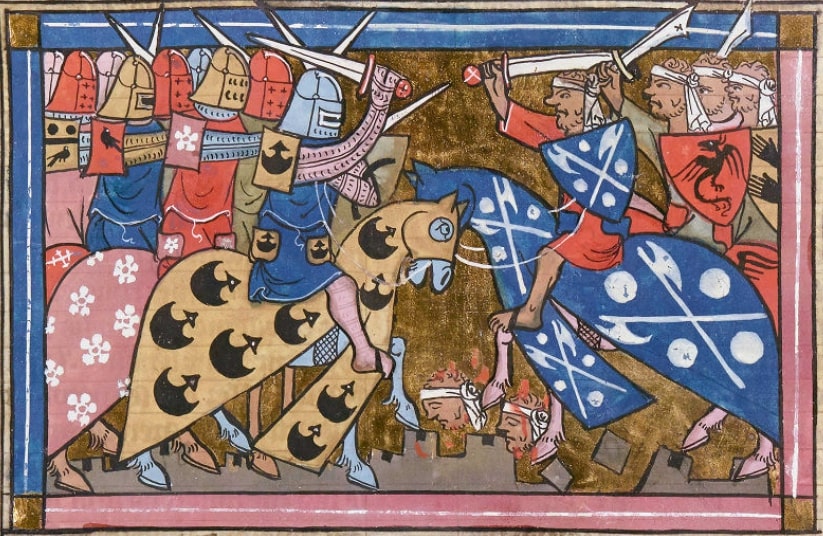
Crusade Of 1129
The Crusade of 1129 or the Damascus Crusade was a military campaign of the Kingdom of Jerusalem with forces from the other crusader states and from western Europe against the Emirate of Damascus. The brainchild of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem, the crusade failed to meet its military objectives. Its diplomatic preliminaries, however, secured the succession to the throne of Jerusalem and papal backing for the Knights Templar. Planning Diplomacy Baldwin II launched raids into Damascene territory in 1125 and 1126. These convinced him that he needed outside support to take the city. For this purpose he sent three embassies to western Europe in 1127–1128. Steven Runciman argued that the death of Ṭughtigin, emir of Damascus, on 11 February 1128 caused Baldwin to plan another attempt on Damascus, but the evidence that an embassy had already been sent in 1127 suggests that the decision had already been made. Neither did Baldwin campaign in 1127 or 1128, which further suggests that he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were intended to recover Jerusalem and its surrounding area from Islamic rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which resulted in the recovery of Jerusalem in 1099, dozens of Crusades were fought, providing a focal point of European history for centuries. In 1095, Pope Urban II proclaimed the First Crusade at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for Byzantine emperor AlexiosI against the Seljuk Turks and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. The first Crusaders had a variety of motivations, including religious salvation, satisfying feudal obligations, opportunities for renown, and economic or political advantage. Later crusades were c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toghtekin
Toghtekin or Tughtekin (Modern tr, Tuğtekin; Arabicised epithet: ''Zahir ad-Din Tughtikin''; died February 12, 1128), also spelled Tughtegin, was a Turkic military leader, who was ''atabeg'' of Damascus from 1104 to 1128. He was the founder of the Burid dynasty of Damascus. Biography Toghtekin was a junior officer to Tutush I, Seljuq emir of Damascus and Syria. After the former's death in 1095, civil war erupted, and Toghtekin supported Tutush's son Duqaq as emir of the city against Ridwan, the emir of Aleppo. In the chaotic years which ensued Toghtekin was sent to reconquer the town of Jebleh, which had rebelled against the ''qadi'' of Tripoli, but he was unable to accomplish his task. On October 21, 1097, a Crusader army began the siege of Antioch. The local emir, Yaghi-Siyan, though nominally under Ridwan's suzerainty, appealed to Duqaq to send an armed force to their rescue. Duqaq sent Toghtekin, but on December 31, 1097, he was defeated by Bohemund of Taranto an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Mans
Le Mans (, ) is a city in northwestern France on the Sarthe River where it meets the Huisne. Traditionally the capital of the province of Maine, it is now the capital of the Sarthe department and the seat of the Roman Catholic diocese of Le Mans. Le Mans is a part of the Pays de la Loire region. Its inhabitants are called ''Manceaux'' (male) and ''Mancelles'' (female). Since 1923, the city has hosted the 24 Hours of Le Mans, the world's oldest active endurance sports car race. History First mentioned by Claudius Ptolemy, the Roman city ''Vindinium'' was the capital of the Aulerci, a sub tribe of the Aedui. Le Mans is also known as ''Civitas Cenomanorum'' (City of the Cenomani), or ''Cenomanus''. Their city, seized by the Romans in 47 BC, was within the ancient Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis. A 3rd-century amphitheatre is still visible. The '' thermae'' were demolished during the crisis of the third century when workers were mobilized to build the city's defensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard II (bishop Of Angoulême)
Gerard II may refer to: * Gerard II, Count of Guelders (from 1129 to 1131) * Gerard II of Isenburg-Kempenich (co-Lord in 1329–1330) See also * Girard II of Roussillon {{Hndis, Gerard II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Legate
300px, A woodcut showing Henry II of England greeting the pope's legate. A papal legate or apostolic legate (from the ancient Roman title '' legatus'') is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic Church. He is empowered on matters of Catholic faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters. The legate is appointed directly by the pope—the bishop of Rome and head of the Catholic Church. Hence a legate is usually sent to a government, a sovereign or to a large body of believers (such as a national church) or to take charge of a major religious effort, such as an ecumenical council, a crusade to the Holy Land, or even against a heresy such as the Cathars. The term ''legation'' is applied both to a legate's mandate and to the territory concerned (such as a state, or an ecclesiastical province). The relevant adjective is ''legatine''. History 200px, Cardinal Thomas Wolsey, papal legate to England during the reign of H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Christian Holy Places In The Holy Land
The list of Christian holy places in the Holy Land outlines sites within cities located in the Holy Land that are regarded as having a special religious significance to Christians, usually by association with Jesus or other persons mentioned in the Bible. The identification of the Christian holy sites became of increased importance especially from around the time of Constantine the Great of the Roman Empire. Interest was also strong during Emperor Charlemagne, as was also the case during the Crusades, when Christian pilgrims often sought out ''holy places'' in the Outremer, especially in early 12th century immediately after the capture of Jerusalem.Sean Martin, ''The Knights Templar: The History & Myths of the Legendary Military Order'', 2005. The search for the Christian holy places was the foundation of 19th-century European Biblical archaeology in Ottoman Syria and later in the British Mandate Palestine. Definition The primary holy places are connected to the main events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Honorius II
Pope Honorius II (9 February 1060 – 13 February 1130), born Lamberto Scannabecchi,Levillain, pg. 731 was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 21 December 1124 to his death in 1130. Although from a humble background, his obvious intellect and outstanding abilities saw him promoted up through the ecclesiastical hierarchy. Attached to the Frangipani family of Rome, his election as pope was contested by a rival candidate, Celestine II, and force was used to guarantee his election. Honorius's pontificate was concerned with ensuring that the privileges the Roman Catholic Church had obtained through the Concordat of Worms were preserved and, if possible, extended. He was the first pope to confirm the election of the Holy Roman emperor. Distrustful of the traditional Benedictine order, he favoured new monastic orders, such as the Augustinians and the Cistercians, and sought to exercise more control over the larger monastic centres of Monte Cassino and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger (bishop Of Lydda)
Roger was the second bishop of Lydda and Ramla from at least 1112 until 1147. Roger's origin is unknown. He succeeded his predecessor, Robert, sometime between 1103 and 1112. Whether a reference from 1108 to a bishop with the initial R refers to Robert of Roger is unknown. The historian Bernard Hamilton considers it likely that the patriarch of Jerusalem, Ghibbelin of Arles, appointed Roger, whom he describes as "a man of real ability". Lydda was a suffragan diocese of Jerusalem. At the urging of the new patriarch, Arnulf of Chocques, Roger granted properties, including the '' casale'' Sephoria, to the Abbey of Josaphat in 1115. In 1136, he granted four ''casalia'' within his diocese to the canons of the Holy Sepulchre, albeit holding back a portion of the tithes. In March 1118, Roger participated in King Baldwin I of Jerusalem's last military campaign and the king died in his arms. In 1128, Roger accompanied Archbishop William I of Tyre to Europe. In Rome, they conferred with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William I Of Tyre
William I was the second Latin archbishop of Tyre from 1128 until 1134 or 1135. He was originally from England and served as prior of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre before his appointment as archbishop. A certain Odo had been consecrated archbishop of Tyre in 1122 while the city was under Seljuq control. He died before the city was captured during the Venetian Crusade of 1124, but no new archbishop was immediately appointed. In the spring of 1128, Patriarch Warmund of Jerusalem consecrated William as archbishop. Against Warmund's wishes, he travelled to Rome to receive his ''pallium'' directly from Pope Honorius II, which no other archbishop from the Latin East had ever done. In 1111, Pope Paschal II had ruled that only those parts of the ecclesiastical province of Tyre that lay within the Kingdom of Jerusalem were under the jurisdiction of the archbishop, thus removing from his jurisdiction the suffragan sees of Tripoli, Tortosa and Gibelet, which lay within the Principalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulk V Of Anjou
Fulk ( la, Fulco, french: Foulque or ''Foulques''; c. 1089/1092 – 13 November 1143), also known as Fulk the Younger, was the count of Anjou (as Fulk V) from 1109 to 1129 and the king of Jerusalem with his wife from 1131 to his death. During their reign, the Kingdom of Jerusalem reached its largest territorial extent. Count of Anjou Fulk was born at Angers, between 1089 and 1092, the son of Count Fulk IV of Anjou and Bertrade de Montfort. In 1092, Bertrade deserted her husband, and bigamously married King Philip I of France. Fulk V became count of Anjou upon his father's death in 1109. In the next year, he married Countess Ermengarde of Maine, cementing Angevin control over the County of Maine. Fulk was originally an opponent of King Henry I of England and a supporter of King Louis VI of France, but in 1118 or 1119 he allied with Henry when he arranged for his daughter Matilda of Anjou to marry Henry's son William Adelin. Fulk went on a pilgrimage to Jerusalem in 1119 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melisende Of Jerusalem
Melisende (1105 – 11 September 1161) was Queen of Jerusalem from 1131 to 1153, and regent for her son between 1153 and 1161, while he was on campaign. She was the eldest daughter of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem, and the Armenian princess Morphia of Melitene. Heir presumptive Jerusalem had recently been conquered by Christian Franks in 1099 during the First Crusade, and Melisende's paternal family originally came from the County of Rethel in France. Her father Baldwin was a crusader knight who carved out the Crusader State of Edessa and married Morphia, daughter of the Armenian prince Gabriel of Melitene, in a diplomatic marriage to fortify alliances in the region.Hamilton, Bernard, ''Queens of Jerusalem'', Ecclesiastical History Society, 1978, ''Frankish women in the Outremer'', pg 143, ''Melisende's youth'' pgs 147, 148, ''Recognized as successor'' pg 148, 149, ''Offers patronage and issues diplomas, Marriage with Fulk, Birth of Second Crowing with father, husband, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy I Brisebarre
Guy I Brisebarre (died after 1148) was Lord of Beirut in the Kingdom of Jerusalem. In 1127, King Baldwin II of Jerusalem sent him to France, together with the Templar Masters Hugh of Payns and William I of Bures, to find a husband for the heir to the throne of Jerusalem, Baldwin's daughter Melisende. In the spring of 1129, they traveled back to the Holy Land with Count Fulk V of Anjou, where they arrived in May. By 1138, Guy I was appointed as lord of Beirut, succeeding his brother Walter I. In 1148, he took part in the Council of Acre, and the subsequent Siege of Damascus, in which he was nominated by local barons to rule the city when conquered.William of Tyre William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a former ..., XVII. 7. He probably had two sons who inherited him after his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |