|
Coulomb Stress Transfer
Coulomb stress transfer is a Seismology, seismic-related geology, geological process of Stress (mechanics), stress changes to surrounding material caused by local discrete deformation events. Using mapped displacements of the Earth's surface during earthquakes, the computed Coulomb stress changes suggest that the stress relieved during an earthquake not only dissipates but can also move up and down Fault (geology), fault segments, concentrating and promoting subsequent tremors. Importantly, Coulomb stress changes have been applied to earthquake-forecasting models that have been used to assess potential Seismic hazard, hazards related to earthquake activity. Coulomb stress change The Mohr–Coulomb theory, Coulomb failure criterion requires that the Coulomb stress exceeds a value σf defined by the shear stress τB, normal stress σB, pore pressure p, and coefficient of friction μ of a failure plane, such that It is also often assumed that changes in pore fluid pressure induced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Anatolian Fault
The North Anatolian Fault (NAF; ) is an active right-lateral strike-slip fault in northern Anatolia, and is the transform boundary between the Eurasian plate and the Anatolian sub-plate. The fault extends westward from a junction with the East Anatolian Fault at the Karliova triple junction in eastern Turkey, across northern Turkey and into the Aegean Sea for a length of 1200−1500 kilometers. It runs about 20 km south of Istanbul. The North Anatolian Fault is similar in many ways to the San Andreas Fault in California. Both are continental transforms with similar lengths and slip rates. The Sea of Marmara near Istanbul is an extensional basin similar to the Salton Trough in California, where a releasing bend in the strike slip system creates a pull-apart basin. Significant earthquakes Since the disastrous 1939 Erzincan earthquake, there have been seven earthquakes measuring over 7.0 in magnitude, each happening at a point progressively further west. Seismologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A '' fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geological maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Kuril Islands Earthquake
The 2007 Kuril Islands earthquake occurred east of the Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands or Kurile Islands are a volcanic archipelago administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast in the Russian Far East. The islands stretch approximately northeast from Hokkaido in Japan to Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, separating the ... on 13 January at . The shock had a moment magnitude of 8.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (''Strong''). A non-destructive tsunami was generated, with maximum wave amplitudes of . The earthquake is considered a doublet of the 8.3 magnitude 2006 Kuril Islands earthquake which occurred two months prior on 15 November 2006 approximately 95 km to the southeast. See also * 1963 Kuril Islands earthquake * 1994 Kuril Islands earthquake * List of earthquakes in 2007 * List of earthquakes in Japan * Kamchatka earthquakes * Okhotsk microplate References ;Bibliography * . * . *. External links * {{DEFAULTSORT:Kuril Islands 2007 Doublet earthquak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
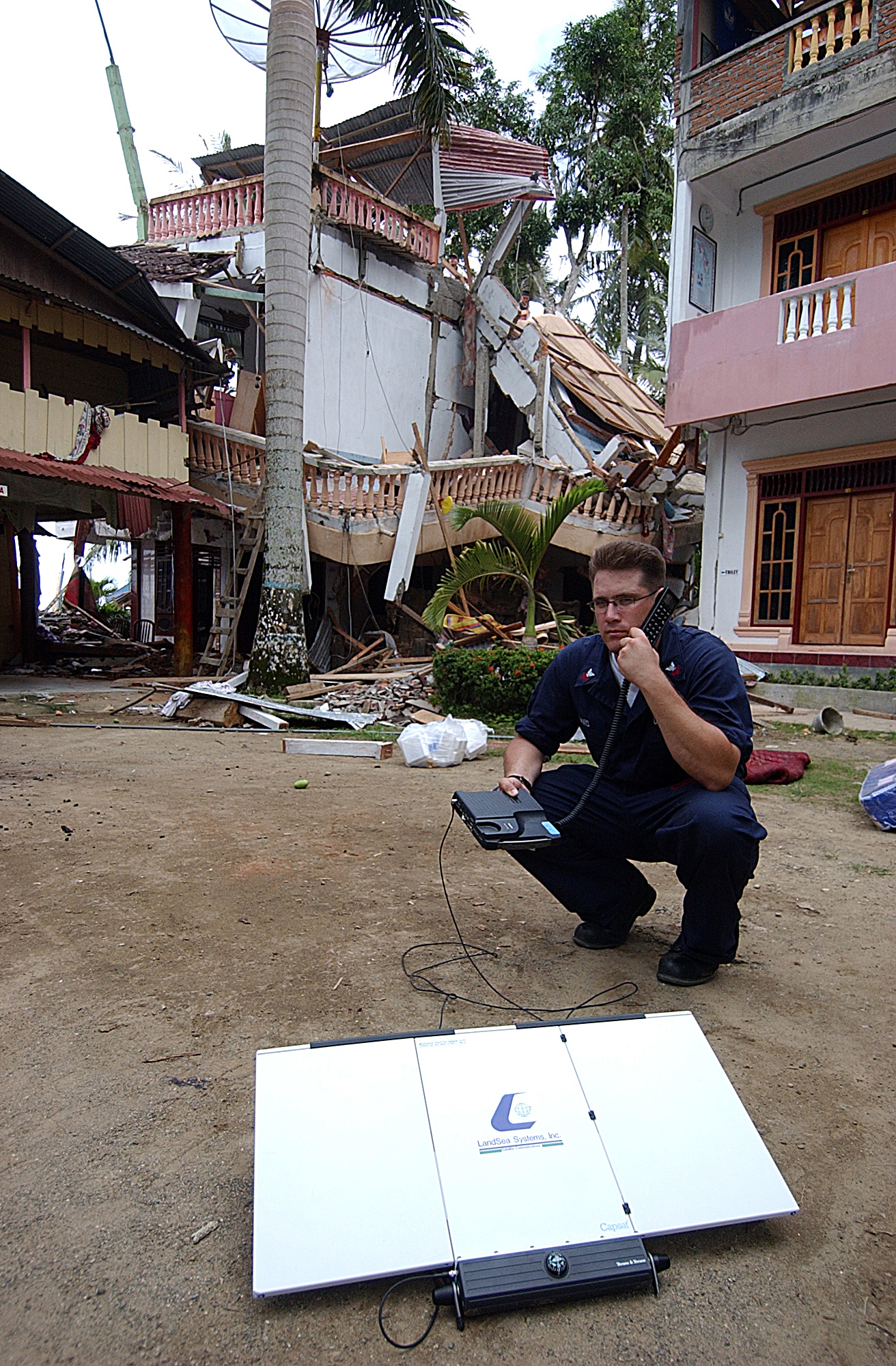
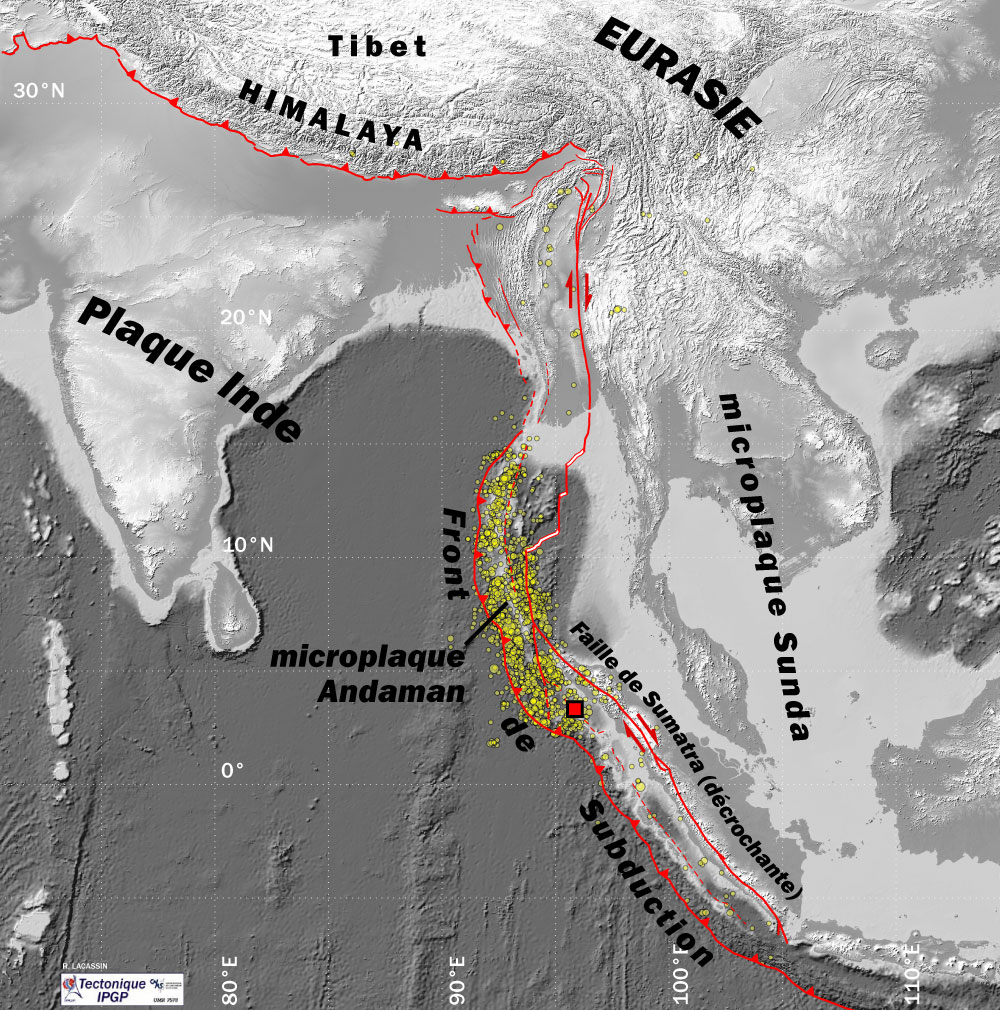
2004 Indian Ocean Earthquake And Tsunami
On 26 December 2004, at 07:58:53 local time ( UTC+7), a major earthquake with a magnitude of 9.2–9.3 struck with an epicentre off the west coast of Aceh in northern Sumatra, Indonesia. The undersea megathrust earthquake, known in the scientific community as the Sumatra–Andaman earthquake, was caused by a rupture along the fault between the Burma plate and the Indian plate, and reached a Mercalli intensity of IX in some areas. A massive tsunami with waves up to high, known as the Boxing Day Tsunami after the Boxing Day holiday, or as the Asian Tsunami, devastated communities along the surrounding coasts of the Indian Ocean, killing an estimated 227,898 people in 14 countries, violently in Aceh (Indonesia), and severely in Sri Lanka, Tamil Nadu (India), and Khao Lak (Thailand). The direct result was major disruption to living conditions and commerce in coastal provinces of surrounding countries. It is the deadliest natural disaster of the 21st century, one of the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2005 Nias–Simeulue Earthquake
The 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake occurred on 28 March off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia in the subduction zone of the Sunda megathrust. At least 915 people were killed, mostly on the island of Nias. It was among the top 10 most powerful recorded worldwide since 1900, with a magnitude of 8.6 that caused a relatively small tsunami. Damage ranged from hundreds of buildings destroyed in Nias to widespread power outages throughout the island of Sumatra. Following the mainshock, eight major aftershocks occurred ranging from 5.5 to 6.0 magnitudes. The earthquake occurred at 16:09:37 UTC (23:09:37 local time) on 28 March 2005. The hypocenter was located below the surface of the Indian Ocean, where subduction is forcing the Indo-Australian plate to the southwest under the Eurasian plate's Sunda edge. The area is west of Sibolga, Sumatra, or northwest of Jakarta, approximately halfway between the islands of Nias and Simeulue. Effects were felt as far away as Bangk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianshuihe Fault System
The Xianshuihe fault system or the Yushu-Ganzi-Xianshuihe fault system is a major active sinistral (left-lateral) Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, strike-slip fault zone in southwestern China, at the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. It has been responsible for many major earthquakes, and is one of the most seismically active fault zones in China. Tectonic setting The Xianshuihe fault system lies within the complex zone of continental collision between the Indian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It forms one of a set of sinistral fault zones that help accommodate the eastward spreading of the Tibetan Plateau. The fault zone defines the northern and eastern edges of the Qiangtang block (also known in part as the Sichuan-Yunnan block), and the southeastern boundary of the Bayan Har block. To the southeast it also forms the western margin of the South China Block. Geometry The Xianshuihe fault system comprises several distinct segments, with an overall length of 1,400 km. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Dawu Earthquake
The 1981 Dawu earthquake occurred on , in Sichuan, China. Registering a surface-wave magnitude of 6.8, the earthquake killed about 150 people and injured roughly 300 more. It caused comprehensive damage within close range of its epicenter. Background China has an extensive history of catastrophic earthquakes that ranges back to 1290. The first verified earthquake took place in Chih-li, killing roughly 100,000 people. The next great earthquake was probably the 1556 Shaanxi earthquake, the most devastating earthquake of all time. Roughly 830,000 were killed by the event. Other earthquakes in 1917, 1918, 1920, 1923, 1925, 1927, 1931, 1932, 1933, 1948, 1950, 1966, 1969, 1970, 1974, 1975, 1976 each killed at least one thousand people. Since 1981, earthquake fatalities have diminished greatly, though have not been stopped. As recently as 2008, an earthquake in Sichuan killed nearly 90,000 people. Characteristics The epicenter was pinpointed to Dawu County in Sichuan. Its official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
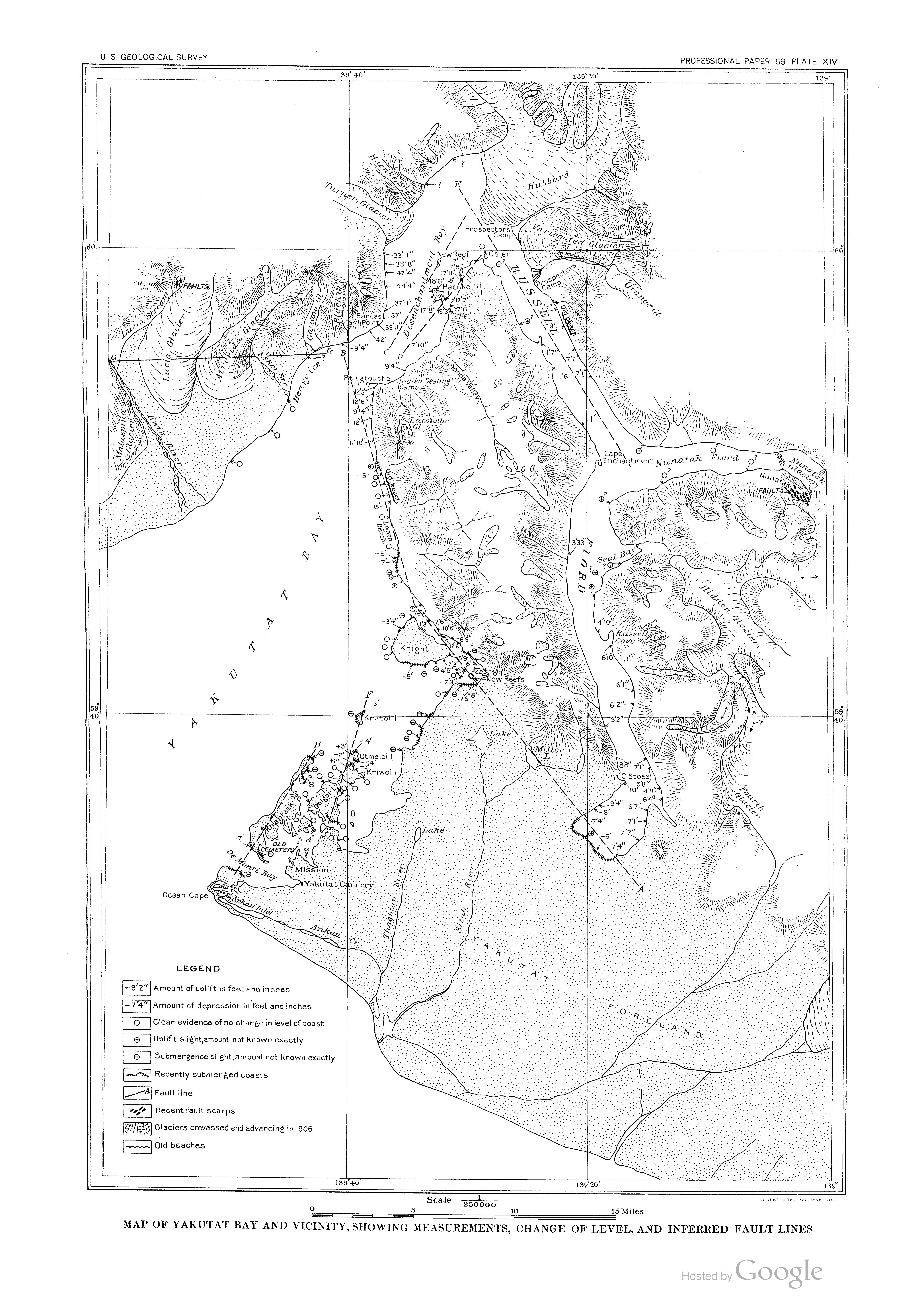
1899 Yakutat Bay Earthquakes
During September 1899 there was a series of severe earthquakes in the region around Yakutat Bay in Alaska. The most powerful of these occurred on September 3 and September 10 at about noon, local time. The area was sparsely populated and no fatalities were recorded, but the earthquakes were notable for the degree of elevation recorded, up to 47 feet, and for the effects on the glaciers in the region. Fieldwork on the effects of the earthquake was carried out between 1905 and 1910, and a summary report was published in 1912. The September 3rd large shock's magnitude is debated, but it ranges from 8.2–8.5. The second earthquake on September the 10th was also a comparably large shock, with magnitudes ranging from 8.2–8.6. Eyewitness accounts The most dramatic accounts came from a group of prospectors whose camp was close to a glacial stream about a mile SE of the ice cliff of Hubbard Glacier. After the initial shock on the morning of September 10, they rigged up a seismograph us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
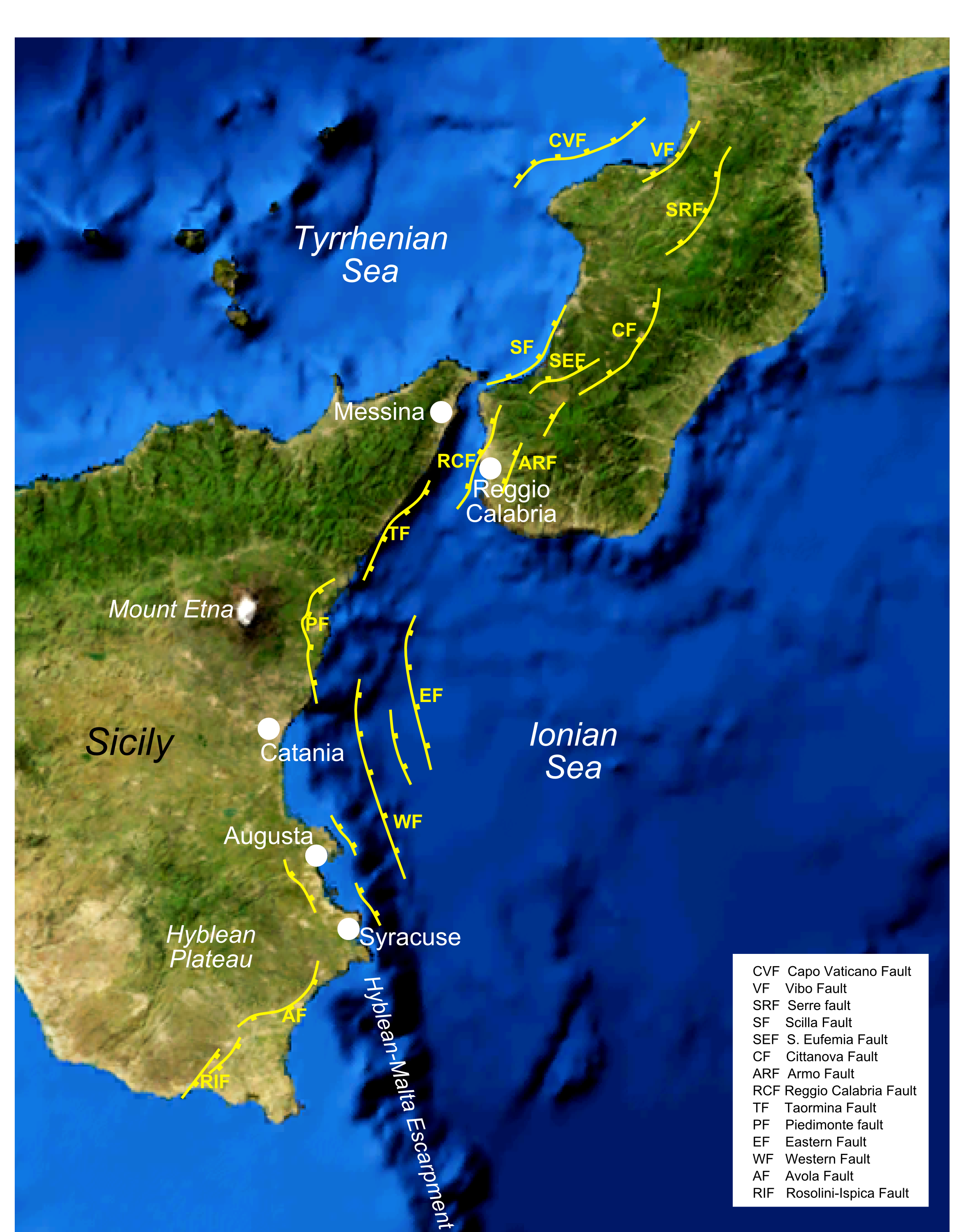
1783 Calabrian Earthquakes
The 1783 Calabrian earthquakes were a sequence of five strong earthquakes that hit the region of Calabria in southern Italy (then part of the Kingdom of Naples), the first two of which produced significant tsunamis. The epicenters form a clear alignment extending nearly 100 km from the Straits of Messina to about 18 km SSW of Catanzaro. The epicenter of the first earthquake occurred in the plain of Palmi. The earthquakes occurred over a period of nearly two months, all with estimated magnitudes of 5.9 or greater. Estimates of the total number of deaths lie in the range 32,000 to 50,000. Tectonic setting The southwestern part of Calabria and the eastern part of Sicily are areas of active crustal extension within the Siculo-Calabrian rift Zone. This 350 km long zone developed within the Apennine chain during the Pleistocene and takes up WNW–ESE directed extension. Events February 5 This earthquake, with an estimated magnitude of 7.0, affected a large ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
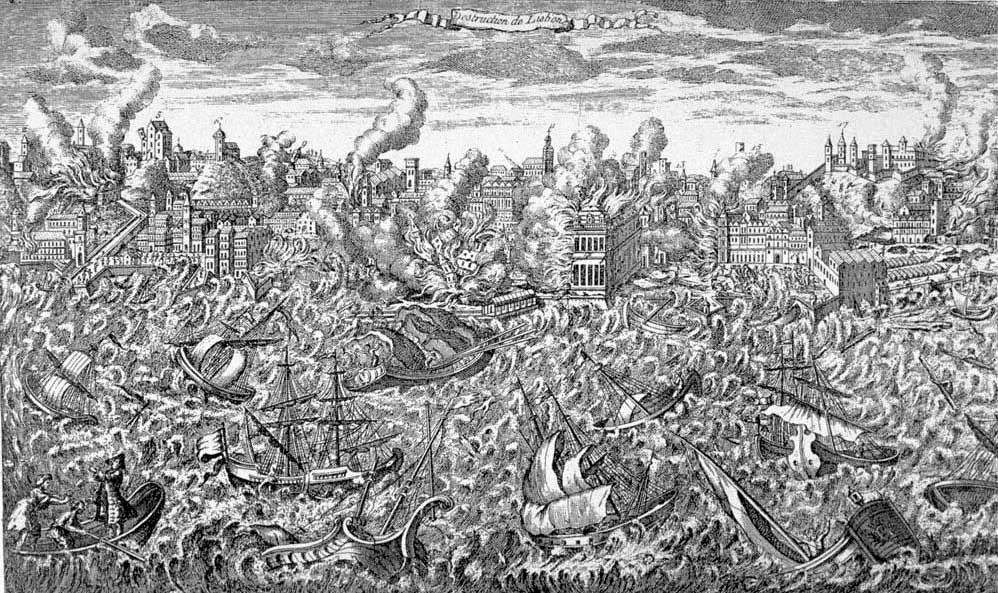
1755 Lisbon Earthquake
The 1755 Lisbon earthquake, also known as the Great Lisbon earthquake, impacted Portugal, the Iberian Peninsula, and Northwest Africa on the morning of Saturday, 1 November, All Saints' Day, Feast of All Saints, at around 09:40 local time. In combination with subsequent fires and a tsunami, the earthquake almost completely destroyed Lisbon and adjoining areas. Seismologists estimate the Lisbon earthquake had a magnitude of 7.7 or greater on the moment magnitude scale, with its epicenter in the Atlantic Ocean about west-southwest of Cape St. Vincent, a cape in Algarve region, and about southwest of Lisbon. Chronologically, it was the third known large-scale earthquake to hit the city (following those of 1332 and 1531 Lisbon earthquake, 1531). Estimates place the death toll in Lisbon around 30,000–40,000. A further 10,000 may have died in Morocco. The earthquake accentuated political tensions in Portugal and profoundly disrupted the Portuguese Empire. The event was widely di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral Patch Seamount
Coral Patch Seamount is a seamount (underwater mountain) between Madeira and mainland Portugal in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is an elongated long and wide mountain that rises to a depth of about , with nine volcanic cones on its summit. It has steeper southern slopes and a gentle northern slope. To its west lies Ampére Seamount, and together with several neighbouring seamounts it is one of the Horseshoe Seamounts. The seamount was probably formed by the Madeira hotspot in the Miocene, together with buckling processes in the oceanic crust. It was initially probably an island. There is evidence of submarine landslides and active faults which constitute a tsunami hazard; the 1755 Lisbon earthquake may have occurred north of the seamount. The name Coral Patch Seamount refers to the presence of cold water corals on the seamount. Their occurrence there was reported first in 1878, five years before the actual discovery of the seamount. They are only sparse on Coral Patch Seam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |