|
Cost–volume–profit Analysis
Cost–volume–profit (CVP), in managerial economics, is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions. Overview A critical part of CVP analysis is the point where total revenues equal total costs (both fixed and variable costs). At this break-even point, a company will experience no income or loss. This break-even point can be an initial examination that precedes a more detailed CVP analysis. CVP analysis employs the same basic assumptions as in breakeven analysis. The assumptions underlying CVP analysis are: * The behavior of both costs and revenues is linear throughout the relevant range of activity. (This assumption precludes the concept of volume discounts on either purchased materials or sales.) * Costs can be classified accurately as either fixed or variable. * Changes in activity are the only factors that affect costs. * All units produced are sold (there is no ending finished goods inventory). * When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Managerial Economics
Managerial economics is a branch of economics involving the application of economic methods in the managerial decision-making process.• Trefor Jones (2004). ''Business Economics and Managerial Decision Making'', WileyDescriptionand chapter-previewlinks • Nick Wilkinson (2005). ''Managerial Economics: A Problem-Solving Approach'', Cambridge University PressDescriptionanpreview. • Maria Moschandreas (2000). ''Business Economics'', 2nd Edition, Thompson Learning.Descriptionand chapter-previelinks Economics is the study of the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services. Managerial economics involves the use of economic theories and principles to make decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources. Managers use economic frameworks in order to optimise profits, resource allocation and the overall output of the firm, whilst improving efficiency and minimising unproductive activities. These frameworks assist organisations to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contribution Margin
Contribution margin (CM), or dollar contribution per unit, is the selling price per unit minus the variable cost per unit. "Contribution" represents the portion of sales revenue that is not consumed by variable costs and so contributes to the coverage of fixed costs. This concept is one of the key building blocks of break-even analysis.Farris, Paul W.; Neil T. Bendle; Phillip E. Pfeifer; David J. Reibstein (2010). ''Marketing Metrics: The Definitive Guide to Measuring Marketing Performance.'' Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education, Inc. . The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses the definitions, purposes, and constructs of classes of measures that appear in ''Marketing Metrics'' as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Project In cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin—the marginal profit per unit sale—is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throughput Accounting
Throughput accounting (TA) is a principle-based and simplified management accounting approach that provides managers with decision support information for enterprise profitability improvement. TA is relatively new in management accounting. It is an approach that identifies factors that limit an organization from reaching its goal, and then focuses on simple measures that drive behavior in key areas towards reaching organizational goals. TA was proposed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt as an alternative to traditional cost accounting. As such, Throughput Accounting is neither cost accounting nor costing because it is cash focused and does not allocate all costs (variable and fixed expenses, including overheads) to products and services sold or provided by an enterprise. Considering the laws of variation, only costs that vary totally with units of output (see definition of T below for TVC) e.g. raw materials, are allocated to products and services which are deducted from sales to determine Thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activity-based Costing
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each. Therefore, this model assigns more indirect costs ( overhead) into direct costs compared to conventional costing. CIMA, the Chartered Institute of Management Accountants, defines ABC as an approach to the costing and monitoring of activities which involves tracing resource consumption and costing final outputs. Resources are assigned to activities, and activities to cost objects based on consumption estimates. The latter utilize cost drivers to attach activity costs to outputs. The Institute of Cost & Management Accountants of Bangladesh (ICMAB) defines activity-based costing as an accounting method which identifies the activities which a firm performs and then assigns indirect costs to cost objects. Objectives With ABC, a company can soundly estimate the cost elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Target Income Sales
In cost accounting, target income sales are the sales necessary to achieve a given target income (or targeted income). It can be measured either in units or in currency (sales proceeds), and can be computed using contribution margin similarly to break-even point: :\begin &\text & &= \frac\\ &\text & &= \frac \end See also * Break-even * Cost–volume–profit analysis Cost–volume–profit (CVP), in managerial economics, is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions. Overview A critical part of CVP analysis is the point where total revenu ... Management accounting {{econ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Break-even Analysis
The break-even point (BEP) in economics, business—and specifically cost accounting—is the point at which total cost and total revenue are equal, i.e. "even". There is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even", though opportunity costs have been paid and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In short, all costs that must be paid are paid, and there is neither profit nor loss. Overview The break-even point (BEP) or break-even level represents the sales amount—in either unit (quantity) or revenue (sales) terms—that is required to cover total costs, consisting of both fixed and variable costs to the company. Total profit at the break-even point is zero. It is only possible for a firm to pass the break-even point if the dollar value of sales is higher than the variable cost per unit. This means that the selling price of the goods must be higher than what the company paid for the good or its components for them to cover the initial price they paid (v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breakeven
Break-even (or break even), often abbreviated as B/E in finance, (sometimes called point of equilibrium) is the point of balance making neither a profit nor a loss. Any number below the break-even point constitutes a loss while any number above it shows a profit. The term originates in finance but the concept has been applied in other fields. In economics In economics and business, specifically cost accounting, the break-even point (BEP) is the point at which cost or expenses and revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even". A profit or loss has not been made, although opportunity costs have been "paid" and capital has received the risk-adjusted, expected return. In other words, it is the point at which the total revenue of a business exceeds its total costs, and the business begins to create wealth instead of consuming it. It is shown graphically as the point where the total revenue and total cost curves meet. In the linear case the break-even p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Mapping
In plane geometry, a shear mapping is a linear map that displaces each point in a fixed direction, by an amount proportional to its signed distance from the line that is parallel to that direction and goes through the origin. This type of mapping is also called shear transformation, transvection, or just shearing. An example is the mapping that takes any point with coordinates (x,y) to the point (x + 2y,y). In this case, the displacement is horizontal by a factor of 2 where the fixed line is the x-axis, and the signed distance is the y coordinate. Note that points on opposite sides of the reference line are displaced in opposite directions. Shear mappings must not be confused with rotations. Applying a shear map to a set of points of the plane will change all angles between them (except straight angles), and the length of any line segment that is not parallel to the direction of displacement. Therefore, it will usually distort the shape of a geometric figure, for example tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matching Principle
In accrual accounting, the matching principle instructs that an expense should be reported in the same period in which the corresponding revenue is earned, and is associated with accrual accounting and the revenue recognition principle states that revenues should be recorded during the period in which they are earned, regardless of when the transfer of cash occurs. By recognizing costs in the period they are incurred, a business can see how much money was spent to generate revenue, reducing "noise" from timing mismatch between when costs are incurred and when revenue is realized. Conversely, cash basis accounting calls for the recognition of an expense when the cash is paid, regardless of when the expense was actually incurred.Accounting Principles by Wild, Shaw, Chiappetta If no cause-and-effect relationship exists (''e.g.,'' a sale is impossible), costs are recognized as expenses in the accounting period they expired: ''i.e.,'' when have been used up or consumed (''e.g.,'' of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost Accounting
Cost accounting is defined as "a systematic set of procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services in the aggregate and in detail. It includes methods for recognizing, classifying, allocating, aggregating and reporting such costs and comparing them with standard costs." (IMA) Often considered a subset of managerial accounting, its end goal is to advise the management on how to optimize business practices and processes based on cost efficiency and capability. Cost accounting provides the detailed cost information that management needs to control current operations and plan for the future. Cost accounting information is also commonly used in financial accounting, but its primary function is for use by managers to facilitate their decision-making. Origins of Cost Accounting All types of businesses, whether manufacturing, trading or producing services, require cost accounting to track their activities. Cost accounting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
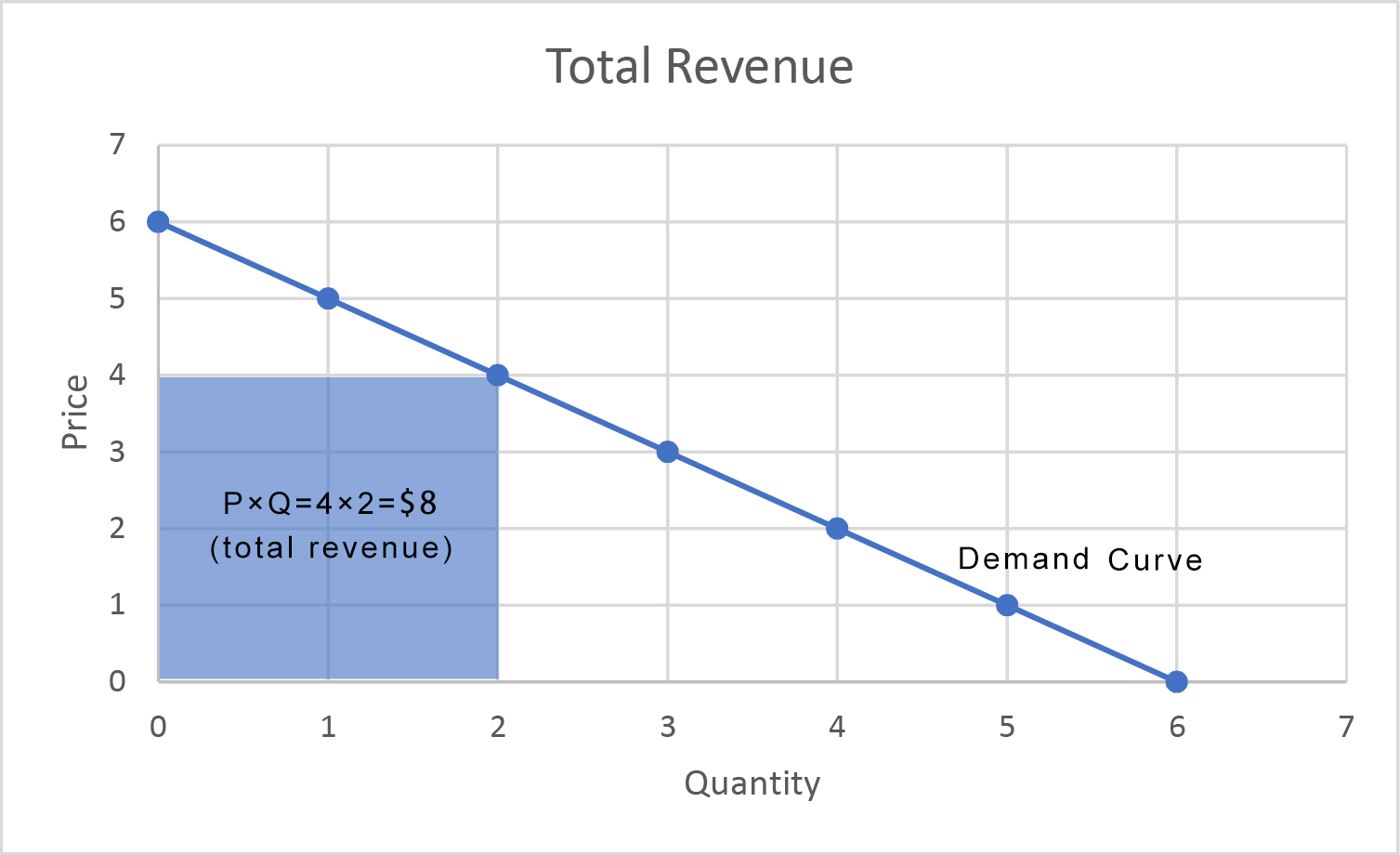
Total Revenue
Total revenue is the total receipts a seller can obtain from selling goods or services to buyers. It can be written as ''P × Q'', which is the price of the goods multiplied by the quantity of the sold goods. Perfect competitor A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve that is infinitely elastic. That is, there is exactly one price that it can sell at – the market price. At any lower price it could get more revenue by selling the same amount at the market price, while at any higher price no one would buy any quantity. Total revenue equals the market price times the quantity the firm chooses to produce and sell. Monopoly As with a perfect competitor, a monopolist’s total revenue is the total receipts it can obtain from selling goods or services to buyers. It can be written as P\times Q, which is the price of the goods multiplied by the quantity of the sold goods. A monopolist's total revenue can be graphed as in Figure 1, in which Price (P) is the height of the box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |