|
Coping Planning
Coping planning is an approach to Social support, supporting people who are Distress (medicine), distressed.Stallman, H. M. & Wilson, C. J. (2018). Can the mental health of Australians be improved by dual strategy for promotion and prevention? ''Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry'', 52(6), 602. It is part of a Biopsychosocial model, biopsychosocial approach to mental health and well-being that comprises healthy environments, Triple P (parenting program), responsive parenting, Belongingness, belonging, healthy activities, Coping (psychology), coping, psychological resilience and treatment of illness.Stallman, H. M. (2018). Coping planning: a patient-centred and strengths-focused approach to suicide prevention training. ''Australasian Psychiatry'', 26(2), 141–144. Coping planning normalises distress as a universal human experience. It draws on a health-focused approach to coping, to improve emotion regulation and decrease the memory of unpleasant emotions. Coping plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Social Support
Social support is the perception and actuality that one is cared for, has assistance available from other people, and, most popularly, that one is part of a supportive social network. These supportive resources can be emotional (e.g., nurturance), informational (e.g., advice), or companionship (e.g., sense of belonging); tangible (e.g., financial assistance) or intangible (e.g., personal advice). Social support can be measured as the perception that one has assistance available, the actual received assistance, or the degree to which a person is integrated in a social network. Support can come from many sources, such as family, friends, pets, neighbors, coworkers, organizations, etc. Social support is studied across a wide range of disciplines including psychology, communications, medicine, sociology, nursing, public health, education, rehabilitation, and social work. Social support has been linked to many benefits for both physical and mental health, but "social support" (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Emotional Regulation
The self-regulation of emotion or emotion regulation is the ability to respond to the ongoing demands of experience with the range of emotions in a manner that is socially tolerable and sufficiently flexible to permit spontaneous reactions as well as the ability to delay spontaneous reactions as needed. It can also be defined as extrinsic and intrinsic processes responsible for monitoring, evaluating, and modifying emotional reactions. The self-regulation of emotion belongs to the broader set of emotion regulation processes, which includes both the regulation of one's own feelings and the regulation of other people's feelings. Emotion regulation is a complex process that involves initiating, inhibiting, or modulating one's state or behavior in a given situation — for example, the subjective experience (feelings), cognitive responses (thoughts), emotion-related physiological responses (for example heart rate or hormonal activity), and emotion-related behavior (bodily actions or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Psychological Stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the environment. Excessive amounts of stress, however, can increase the risk of strokes, heart attacks, ulcers, and mental illnesses such as depression and also aggravate pre-existing conditions. Psychological stress can be external and related to the environment, but may also be caused by internal perceptions that cause an individual to experience anxiety or other negative emotions surrounding a situation, such as pressure, discomfort, etc., which they then deem stressful. Hans Selye (1974) proposed four variations of stress. On one axis he locates good stress ( eustress) and bad stress (distress). On the other is over-stress (hyperstress) and understress (hypostress). Selye advocates balancing these: the ultimate goal would be to balance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Human Behavior
Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity (Energy (psychological), mentally, Physical activity, physically, and Social action, socially) of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external Stimulation, stimuli throughout their life. Behavior is driven by genetic and environmental factors that affect an individual. Behavior is also driven, in part, by thoughts and feelings, which provide insight into individual Psyche (psychology), psyche, revealing such things as attitude (psychology), attitudes and value (personal and cultural), values. Human behavior is shaped by Trait theory, psychological traits, as personality types vary from person to person, producing different actions and behavior. Social behavior accounts for actions directed at others. It is concerned with the considerable influence of Social relation, social interaction and culture, as well as ethics, interpersonal relationships, politics, and Conflict (process), conflict. Some behaviors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Counseling Psychology
Counseling or Counselling psychology is an international discipline. It is practiced in the United States and Canada, the United Kingdom and Ireland, Australia and New Zealand, Hong Kong and Korea, and South Africa. Counseling psychology in the United States initially focused on vocational counseling but later focused upon adjustment counseling. It currently includes many sub-disciplines, for example marriage and family counseling, rehabilitation counseling, clinical mental health counseling, educational counseling, etc. In each setting, they are all required to follow the same guidelines. The Society for Counseling Psychology in the United States states:Counseling Psychology is a generalist health service (HSP) specialty in professional psychology that uses a broad range of culturally informed and culturally sensitive practices to help people improve their well-being, prevent and alleviate distress and maladjustment, resolve crises, and increase their ability to function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inpatient Care
Inpatient care is the care of patients whose condition requires admission to a hospital. Progress in modern medicine and the advent of comprehensive out-patient clinics ensure that patients are only admitted to a hospital when they are extremely ill or have severe physical trauma. Progress Patients enter inpatient care mainly from previous ambulatory care such as referral from a family doctor, or through emergency medicine departments. The patient formally becomes an " inpatient" at the writing of an admission note. Likewise, it is formally ended by writing a discharge note. Planning for patient discharge Health care professionals involved in rehabilitation are often involved in discharge planning for patients. When considering patient discharge, there are a number of factors to take into consideration: the patient's current state, their place of residence and the type of support available. When considering the patient's current state, although the patient may be eligible f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
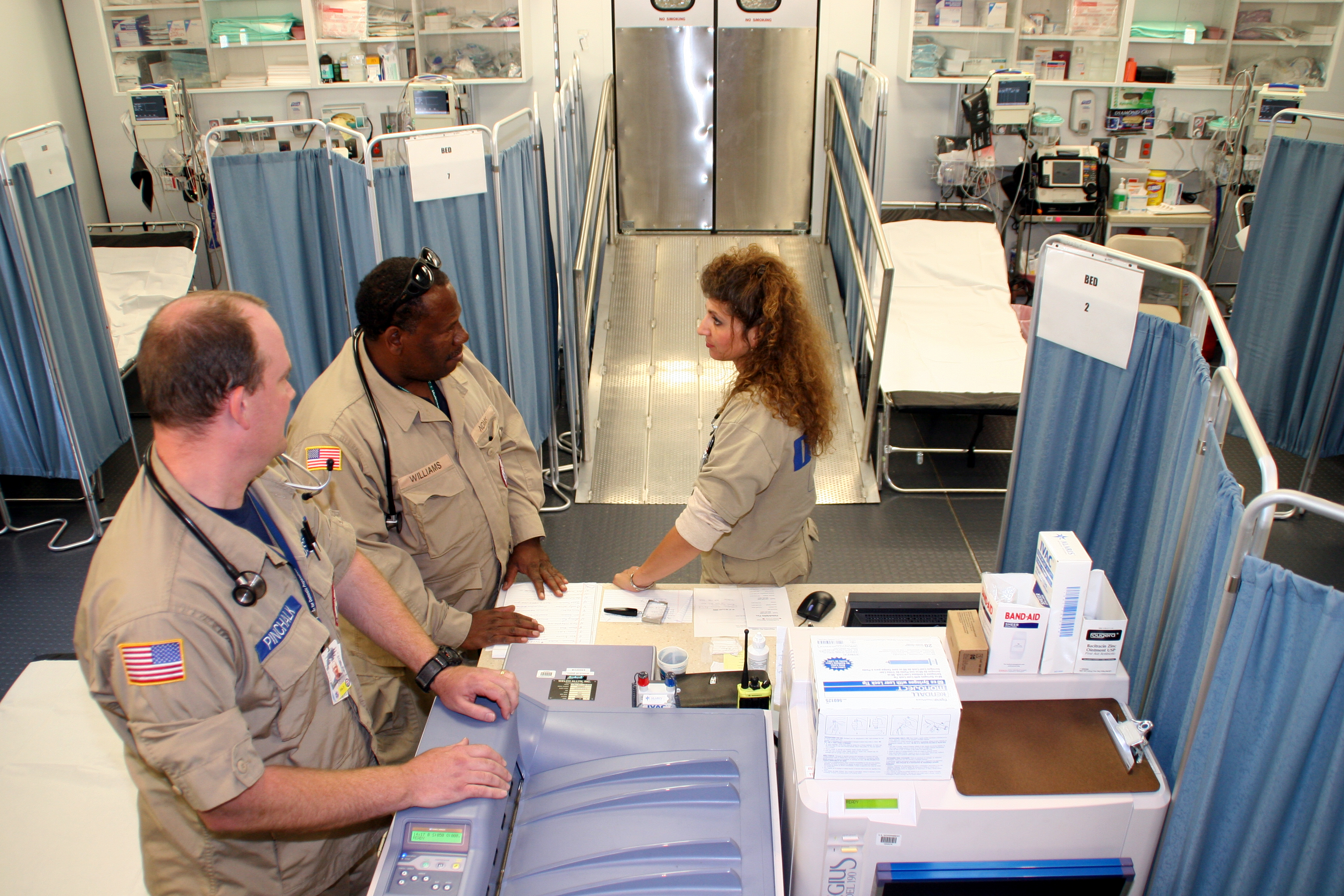
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the Acute (medicine), acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be Medical emergency, life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Telephone Counseling
Telephone counseling (also known as telephone therapy, telephone-based or telephone-delivered psychological treatment) refers to the use of the telephone to deliver any type of psychological treatment or therapy (such as cognitive behavioral therapy) for mental health difficulties (like depression, anxiety). Telephone therapy can be as effective as traditional, face-to-face therapy. Along with online therapy, it is a type of telepsychology service. In telephone-based therapy, there is verbal communication, but no non-verbal communication which is present in video calls, for example. Effectiveness Psychological treatment delivered through the telephone can be as effective for adults with depression or anxiety as face-to-face therapy. For adults with depression, telephone therapy can even be more effective than traditional therapy. For adults with anxiety, telephone-based treatment can be more effective than having to be on a waitlist before receiving treatment. For telephone ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ironic Process Theory
Ironic process theory (IPT), also known as the Pink elephant paradox or White bear phenomenon, suggests that when an individual intentionally tries to avoid thinking a certain thought or feeling a certain emotion, a paradoxical effect is produced: the attempted avoidance not only fails in its object but in fact causes the thought or emotion to occur more frequently and more intensely. IPT is also known as "ironic rebound," or "the white bear problem." The phenomenon was identified through thought suppression studies in experimental psychology. Social psychologist Daniel Wegner first studied ironic process theory in a laboratory setting in 1987. Ironic mental processes have been shown in a variety of situations, where they are usually created by or worsened by stress. In extreme cases, ironic mental processes result in intrusive thoughts about doing something immoral or out of character, which can be troubling to the individual. These findings have since guided clinical practice. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Help-seeking
Help-seeking theory postulates that people follow a series of predictable steps to seek help for their inadequacies, it is a series of well-ordered and purposeful cognitive and behavioral steps, each leading to specific types of solutions. Help-seeking theory falls into two categories where some consider similarity in the process' (e.g. Cepeda-Benito & Short, 1998) while others consider it as dependent upon the problem (e.g. Di Fabio & Bernaud, 2008). In general help-seeking behaviors are dependent upon three categories, attitudes (beliefs and willingness) towards help-seeking, intention to seek help, and actual help-seeking behavior. Help-seeking was, «in the early studies of socialization and personality development», often viewed as an indicator of dependency and therefore took «on connotations of immaturity, passivity, and even incompetence». Now, there is general agreement that ''adaptive'' help-seeking is an important and effective self-regulated learning strategy. Def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Needs Assessment
A needs assessment is a systematic process for determining and addressing needs, or "gaps", between current conditions, and desired conditions, or "wants". Needs assessments can help improve policy or program decisions, individuals, education, training, organizations, communities, or products. There are three types of need in a needs assessment: perceived need, expressed need and relative need. # Perceived needs are defined by what people think about their needs; each standard changes with each respondent. # Expressed needs are defined by the number of people who have sought help and focuses on circumstances where feelings are translated into action. A major weakness of expressed needs assumes that all people with needs seek help. # Relative needs are concerned with equity and must consider differences in population and social pathology. History Considered the "father of needs assessment", Roger Kaufman developed a model for determining needs defined as a gap in results. Kau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |