|
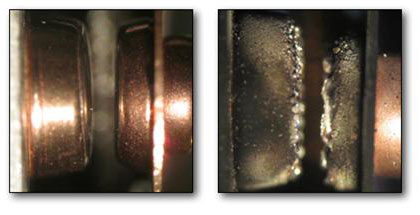
Contact Protection
Contact protection methods are designed to mitigate the wear and degradation occurring during the normal use of contacts within an electromechanical switch, relay or contactor and thus avoid an excessive increase in contact resistance or switch failure. Contact wear Every time the contacts of an electromechanical switch, relay or contactor are opened or closed, there is a certain amount of contact wear. The sources of the wear are high current densities in microscopic areas, and the electric arc. Contact wear includes material transfer between contacts, loss of contact material due to splattering and evaporation, and oxidation or corrosion of the contacts due to high temperatures and atmospheric influences. While a pair of contacts is closed, only a small part of the contacts are in intimate contact due to asperities and low-conductivity films. Because of the constriction of the current to a very small area, the current density frequently becomes so high that it melts a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switch
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle swi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snubber
A snubber is a device used to suppress ("snub") a phenomenon such as voltage transients in electrical systems, pressure transients in fluid systems (caused by for example water hammer) or excess force or rapid movement in mechanical systems. Electrical systems Snubbers are frequently used in electrical systems with an inductive load where the sudden interruption of current flow leads to a large counter-electromotive force: a rise in voltage across the current switching device that opposes the change in current, in accordance with Faraday's law. This transient can be a source of electromagnetic interference (EMI) in other circuits. Additionally, if the voltage generated across the device is beyond what the device is intended to tolerate, it may damage or destroy it. The snubber provides a short-term alternative current path around the current switching device so that the inductive element may be safely discharged. Inductive elements are often unintentional, arising from the cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switches
In electrical engineering, a switch is an electrical component that can disconnect or connect the conducting path in an electrical circuit, interrupting the electric current or diverting it from one conductor to another. The most common type of switch is an electromechanical device consisting of one or more sets of movable electrical contacts connected to external circuits. When a pair of contacts is touching current can pass between them, while when the contacts are separated no current can flow. Switches are made in many different configurations; they may have multiple sets of contacts controlled by the same knob or actuator, and the contacts may operate simultaneously, sequentially, or alternately. A switch may be operated manually, for example, a light switch or a keyboard button, or may function as a sensing element to sense the position of a machine part, liquid level, pressure, or temperature, such as a thermostat. Many specialized forms exist, such as the toggle switc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting Voltage
In electrical and electronics engineering, wetting current is the minimum electric current needing to flow through a contact to break through the surface film resistance at a contact. It is typically far below the contact's nominal maximum current rating. A thin film of oxidation, or an otherwise passivated layer, tends to form in most environments, particularly those with high humidity, and, along with surface roughness, contributes to the contact resistance at an interface. Providing a sufficient amount of wetting current is a crucial step in designing Control engineering, systems that use delicate switches with small contact pressure as sensor inputs. Failing to do this might result in switches remaining electrically "open" when pressed, due to contact oxidation. Capacitor discharge solution In some low voltage applications, where switching current is below the manufacturer's wetting current specification, a capacitor discharge method may be employed by placing a small capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wetting Current
In electrical and electronics engineering, wetting current is the minimum electric current needing to flow through a contact to break through the surface film resistance at a contact. It is typically far below the contact's nominal maximum current rating. A thin film of oxidation, or an otherwise passivated layer, tends to form in most environments, particularly those with high humidity, and, along with surface roughness, contributes to the contact resistance at an interface. Providing a sufficient amount of wetting current is a crucial step in designing systems that use delicate switches with small contact pressure as sensor inputs. Failing to do this might result in switches remaining electrically "open" when pressed, due to contact oxidation. Capacitor discharge solution In some low voltage applications, where switching current is below the manufacturer's wetting current specification, a capacitor discharge method may be employed by placing a small capacitor across the swit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Resistance
The term contact resistance refers to the contribution to the total resistance of a system which can be attributed to the contacting interfaces of electrical leads and connections as opposed to the intrinsic resistance. This effect is described by the term electrical contact resistance (ECR) and arises as the result of the limited areas of true contact at an interface and the presence of resistive surface films or oxide layers. ECR may vary with time, most often decreasing, in a process known as resistance creep. The idea of potential drop on the injection electrode was introduced by William Shockley to explain the difference between the experimental results and the model of gradual channel approximation. In addition to the term ECR, ''interface resistance'', ''transitional resistance'', or just simply ''correction term'' are also used. The term ''parasitic resistance'' is used as a more general term, of which it is usually assumed that contact resistance is a major component. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Suppression
Arc suppression is the reduction of sparks formed when current-carrying contacts are separated. The spark is a luminous discharge of highly energized electrons and ions, and is an electric arc. Uses There are several possible areas of use of arc suppression methods, among them metal film deposition and sputtering, arc flash protection, electrostatic processes where electrical arcs are not desired (such as powder painting, air purification, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film poling) and contact current arc suppression. In industrial, military and consumer electronic design, the latter method generally applies to devices such as electromechanical power switches, relays and contactors. In this context, arc suppression is contact protection. Contact protection Every time an electrical power device (for example: heaters, lamps, motors, transformers or similar power loads) turns on or off, its switch, relay or contactor transitions either from a closed to an open state (break arc) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Suppression
Arc suppression is the reduction of sparks formed when current-carrying contacts are separated. The spark is a luminous discharge of highly energized electrons and ions, and is an electric arc. Uses There are several possible areas of use of arc suppression methods, among them metal film deposition and sputtering, arc flash protection, electrostatic processes where electrical arcs are not desired (such as powder painting, air purification, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film poling) and contact current arc suppression. In industrial, military and consumer electronic design, the latter method generally applies to devices such as electromechanical power switches, relays and contactors. In this context, arc suppression is contact protection. Contact protection Every time an electrical power device (for example: heaters, lamps, motors, transformers or similar power loads) turns on or off, its switch, relay or contactor transitions either from a closed to an open state (break arc) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Coefficient
A temperature coefficient describes the relative change of a physical property that is associated with a given change in temperature. For a property ''R'' that changes when the temperature changes by ''dT'', the temperature coefficient α is defined by the following equation: :\frac = \alpha\,dT Here α has the dimension of an inverse temperature and can be expressed e.g. in 1/K or K−1. If the temperature coefficient itself does not vary too much with temperature and \alpha\Delta T \ll 1, a linear approximation will be useful in estimating the value ''R'' of a property at a temperature ''T'', given its value ''R''0 at a reference temperature ''T''0: :R(T) = R(T_0)(1 + \alpha\Delta T), where Δ''T'' is the difference between ''T'' and ''T''0. For strongly temperature-dependent α, this approximation is only useful for small temperature differences Δ''T''. Temperature coefficients are specified for various applications, including electric and magnetic properties of materials a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varistor
A varistor is an electronic component with an electrical resistance that varies with the applied voltage. Also known as a voltage-dependent resistor (VDR), it has a nonlinear, non- ohmic current–voltage characteristic that is similar to that of a diode. Unlike a diode however, it has the same characteristic for both directions of traversing current. Traditionally, varistors were indeed constructed by connecting two rectifiers, such as the copper-oxide or germanium-oxide rectifier in antiparallel configuration. At low voltage the varistor has a high electrical resistance which decreases as the voltage is raised. Modern varistors are primarily based on sintered ceramic metal-oxide materials which exhibit directional behavior only on a microscopic scale. This type is commonly known as the metal-oxide varistor (MOV). Varistors are used as control or compensation elements in circuits either to provide optimal operating conditions or to protect against excessive transient voltages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
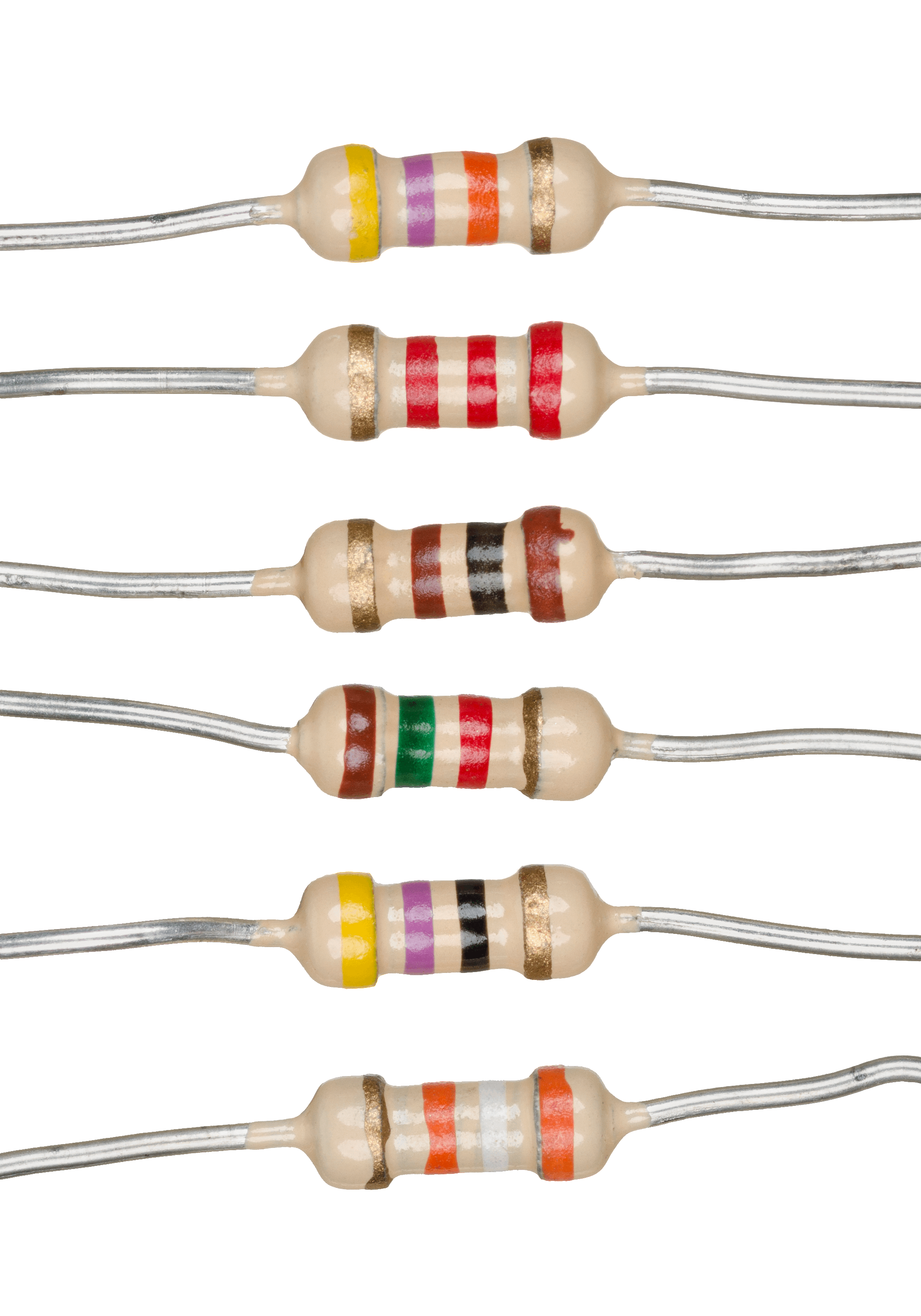
Resistor
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in electronic equipment. Practical resistors as discrete components can be composed of various compounds and forms. Resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transient Voltage Suppressor
A 'surge protector'' (or spike suppressor, surge suppressor, surge diverter, surge protection device (SPD) or transient voltage surge suppressor (TVSS) is an appliance or device intended to protect electrical devices from voltage spikes in alternating current (AC) circuits. A voltage spike is a transient event, typically lasting 1 to 30 microseconds, that may reach over 1,000 volts. Lightning that hits a power line can give a spike of over 100,000 volts and can burn through wiring insulation and cause fires, but even modest spikes can destroy a wide variety of electronic devices, computers, battery chargers, modems and TVs etc, that happen to be plugged in at the time. Typically the surge device will trigger at a set voltage, around 3 to 4 times the mains voltage, and divert the current to earth. Some devices may absorb the spike and release it as heat. They are generally rated according to the amount of energy in joules they can absorb. some company have surge protection devic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |