|
Consensus Clustering
Consensus clustering is a method of aggregating (potentially conflicting) results from multiple clustering algorithms. Also called cluster ensembles or aggregation of clustering (or partitions), it refers to the situation in which a number of different (input) clusterings have been obtained for a particular dataset and it is desired to find a single (consensus) clustering which is a better fit in some sense than the existing clusterings. Consensus clustering is thus the problem of reconciling clustering information about the same data set coming from different sources or from different runs of the same algorithm. When cast as an optimization problem, consensus clustering is known as median partition, and has been shown to be NP-complete, even when the number of input clusterings is three. Consensus clustering for unsupervised learning is analogous to ensemble learning in supervised learning. Issues with existing clustering techniques * Current clustering techniques do not address a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Clustering Algorithm
Cluster analysis or clustering is the data analyzing technique in which task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some specific sense defined by the analyst) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis refers to a family of algorithms and tasks rather than one specific algorithm. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genetic Algorithm
In computer science and operations research, a genetic algorithm (GA) is a metaheuristic inspired by the process of natural selection that belongs to the larger class of evolutionary algorithms (EA). Genetic algorithms are commonly used to generate high-quality solutions to optimization and search problems via biologically inspired operators such as selection, crossover, and mutation. Some examples of GA applications include optimizing decision trees for better performance, solving sudoku puzzles, hyperparameter optimization, and causal inference. Methodology Optimization problems In a genetic algorithm, a population of candidate solutions (called individuals, creatures, organisms, or phenotypes) to an optimization problem is evolved toward better solutions. Each candidate solution has a set of properties (its chromosomes or genotype) which can be mutated and altered; traditionally, solutions are represented in binary as strings of 0s and 1s, but other encod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Heikki Mannila
Heikki Olavi Mannila (born 4 January 1960 in Espoo) is a Finnish computer scientist, the president of the Academy of Finland.''Kuka kukin on 2007'', p. 585. Helsinki 2006. Mannila earned his Ph.D. in 1985 from the University of Helsinki under the supervision of Esko Ukkonen and for many years he was a professor at the University of Helsinki himself. From 2004 to 2008 he was Academy Professor at the Academy of Finland. He became Vice President for Academic Affairs at Aalto University in 2009, and was appointed by the Finnish government as president of the Academy of Finland for a term lasting from 2012 to 2017.Heikki Mannila appointed as President of the Academy of Finland , Finnish Ministry of Education and Culture, December 19, 2011, retrieved 2012-02-25. The a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
K-means
''k''-means clustering is a method of vector quantization, originally from signal processing, that aims to partition of a set, partition ''n'' observations into ''k'' clusters in which each observation belongs to the cluster (statistics), cluster with the nearest mean (cluster centers or cluster centroid), serving as a prototype of the cluster. This results in a partitioning of the data space into Voronoi cells. ''k''-means clustering minimizes within-cluster variances (squared Euclidean distances), but not regular Euclidean distances, which would be the more difficult Weber problem: the mean optimizes squared errors, whereas only the geometric median minimizes Euclidean distances. For instance, better Euclidean solutions can be found using k-medians clustering, ''k''-medians and k-medoids, ''k''-medoids. The problem is computationally difficult (NP-hardness, NP-hard); however, efficient heuristic algorithms converge quickly to a local optimum. These are usually similar to the ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
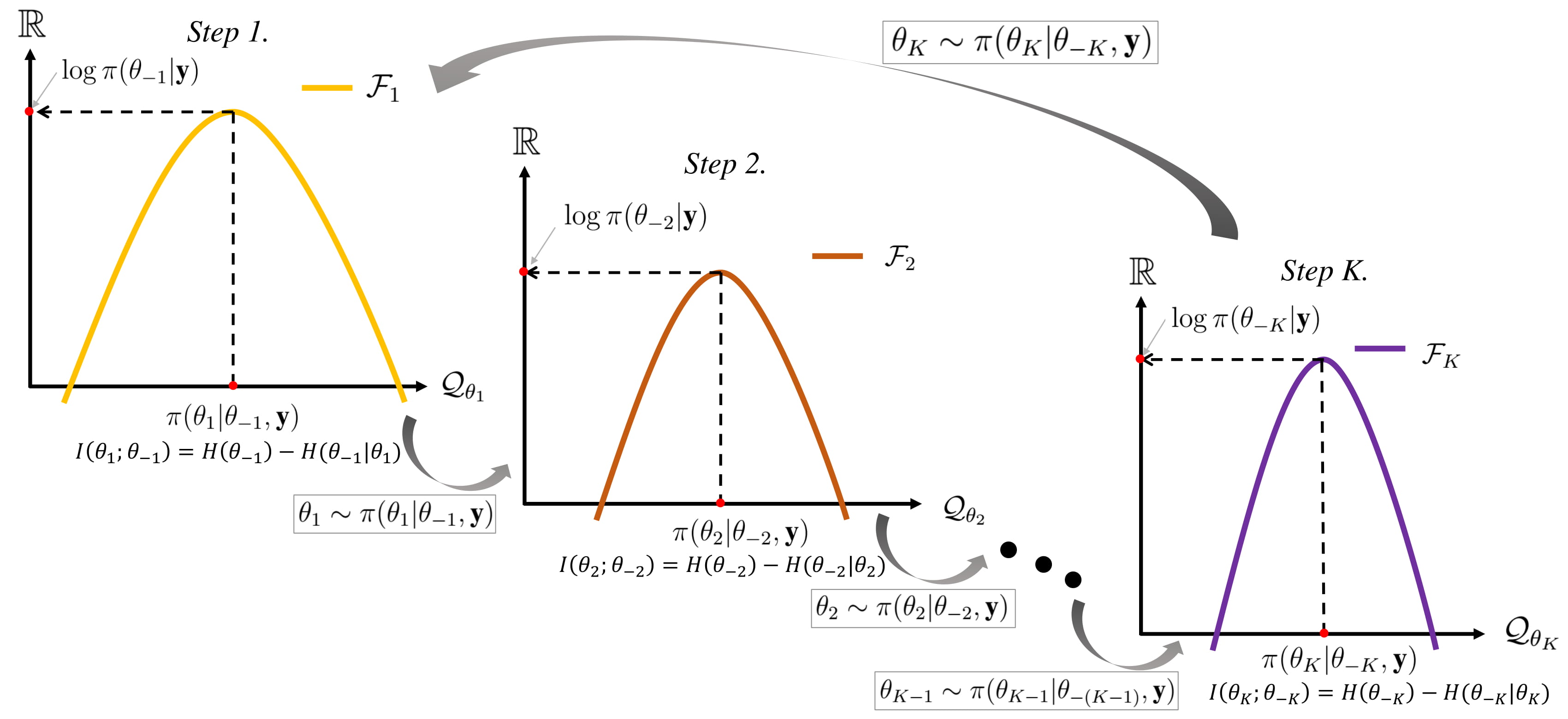
Gibbs Sampling
In statistics, Gibbs sampling or a Gibbs sampler is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) algorithm for sampling from a specified multivariate distribution, multivariate probability distribution when direct sampling from the joint distribution is difficult, but sampling from the Conditional probability distribution, conditional distribution is more practical. This sequence can be used to approximate the joint distribution (e.g., to generate a histogram of the distribution); to approximate the marginal distribution of one of the variables, or some subset of the variables (for example, the unknown parameters or latent variables); or to compute an integral (such as the expected value of one of the variables). Typically, some of the variables correspond to observations whose values are known, and hence do not need to be sampled. Gibbs sampling is commonly used as a means of statistical inference, especially Bayesian inference. It is a randomized algorithm (i.e. an algorithm that makes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bayesian Probability
Bayesian probability ( or ) is an interpretation of the concept of probability, in which, instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon, probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of propositional logic that enables reasoning with hypotheses; that is, with propositions whose truth or falsity is unknown. In the Bayesian view, a probability is assigned to a hypothesis, whereas under frequentist inference, a hypothesis is typically tested without being assigned a probability. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the Bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability. This, in turn, is then updated to a posterior probability in the light of new, relevant data (evidence). The Bayesian interpretation provides a standard set of procedur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carla Brodley
Carla E. Brodley is a computer scientist specializing in machine learning. Brodley is a Fellow of the ACM, the Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), and the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS). She is the Dean of Inclusive Computing at Northeastern University, where she serves as the Executive Director for the Center for Inclusive Computing and holds a tenured appointment in Khoury College of Computer Sciences. Brodley served as dean of Khoury College from 2014-2021. She is a proponent for greater enrollment of women and under-represented minorities in computer science. Education and career Brodley is a 1985 graduate of McGill University. At McGill, she initially chose to major in English, quickly switching to economics, but switched again to a double major in mathematics and computer science after taking and enjoying a computer programming course as a sophomore. After working as a consultant and computer programmer in Boston, sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bipartite Graph
In the mathematics, mathematical field of graph theory, a bipartite graph (or bigraph) is a Graph (discrete mathematics), graph whose vertex (graph theory), vertices can be divided into two disjoint sets, disjoint and Independent set (graph theory), independent sets U and V, that is, every edge (graph theory), edge connects a Vertex (graph theory), vertex in U to one in V. Vertex sets U and V are usually called the ''parts'' of the graph. Equivalently, a bipartite graph is a graph that does not contain any odd-length cycle (graph theory), cycles. The two sets U and V may be thought of as a graph coloring, coloring of the graph with two colors: if one colors all nodes in U blue, and all nodes in V red, each edge has endpoints of differing colors, as is required in the graph coloring problem.. In contrast, such a coloring is impossible in the case of a non-bipartite graph, such as a Gallery of named graphs, triangle: after one node is colored blue and another red, the third vertex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dot Product
In mathematics, the dot product or scalar productThe term ''scalar product'' means literally "product with a Scalar (mathematics), scalar as a result". It is also used for other symmetric bilinear forms, for example in a pseudo-Euclidean space. Not to be confused with scalar multiplication. is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers (usually coordinate vectors), and returns a single number. In Euclidean geometry, the dot product of the Cartesian coordinates of two Euclidean vector, vectors is widely used. It is often called the inner product (or rarely the projection product) of Euclidean space, even though it is not the only inner product that can be defined on Euclidean space (see ''Inner product space'' for more). It should not be confused with the cross product. Algebraically, the dot product is the sum of the Product (mathematics), products of the corresponding entries of the two sequences of numbers. Geometrically, it is the product of the Euc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
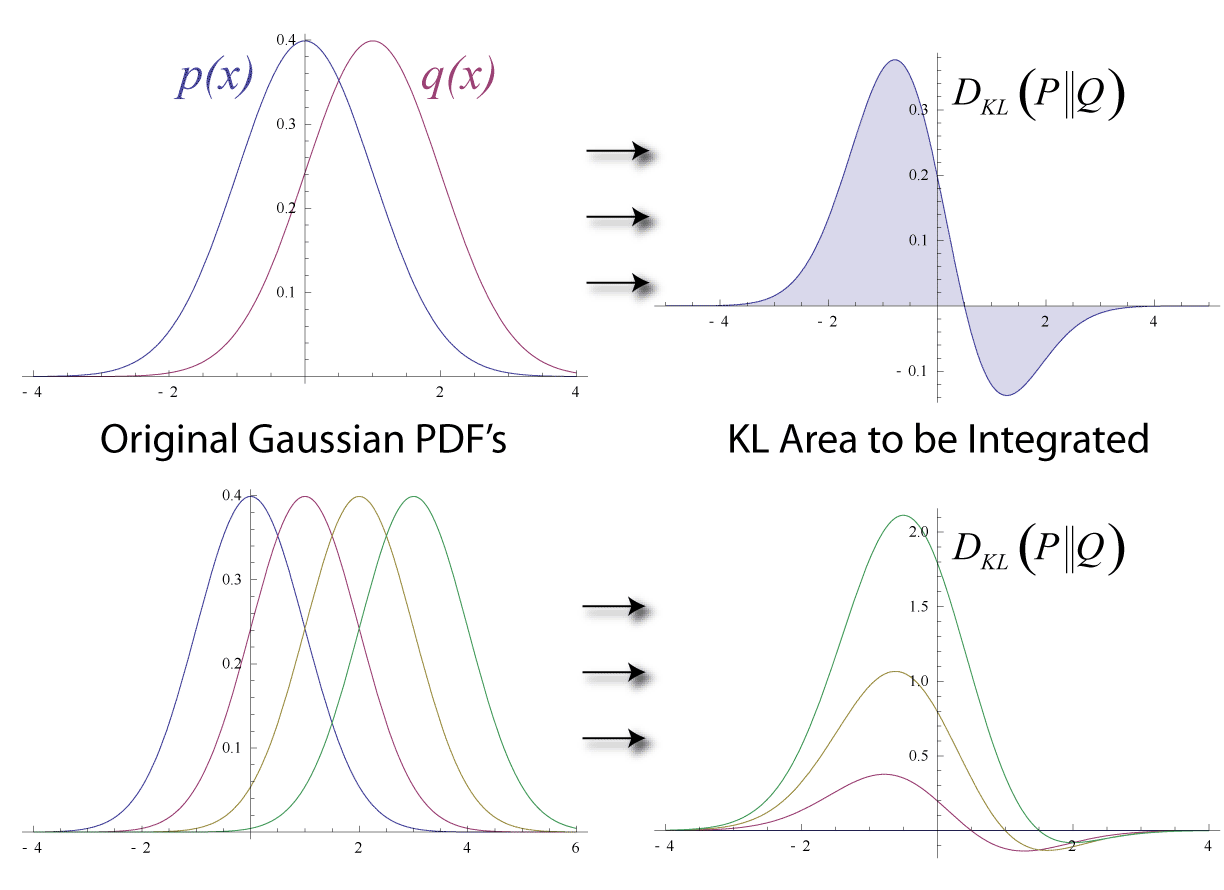
Kullback–Leibler Divergence
In mathematical statistics, the Kullback–Leibler (KL) divergence (also called relative entropy and I-divergence), denoted D_\text(P \parallel Q), is a type of statistical distance: a measure of how much a model probability distribution is different from a true probability distribution . Mathematically, it is defined as D_\text(P \parallel Q) = \sum_ P(x) \, \log \frac\text A simple interpretation of the KL divergence of from is the expected excess surprise from using as a model instead of when the actual distribution is . While it is a measure of how different two distributions are and is thus a distance in some sense, it is not actually a metric, which is the most familiar and formal type of distance. In particular, it is not symmetric in the two distributions (in contrast to variation of information), and does not satisfy the triangle inequality. Instead, in terms of information geometry, it is a type of divergence, a generalization of squared distance, and for cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
EM Algorithm
EM, Em or em may refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Em, the E minor musical scale * Em, the E minor chord * Electronic music, music that employs electronic musical instruments and electronic music technology in its production * Encyclopedia Metallum, an online metal music database * Eminem, American rapper Other uses in arts and entertainment * ''Em'' (comic strip), a comic strip by Maria Smedstad Companies and organizations * Em (restaurant), a restaurant in Mexico City * Aero Benin (IATA code), a defunct airline * Empire Airlines (IATA code), a charter and cargo airline based in Idaho, US * Erasmus Mundus, an international student-exchange program * '' Estado de Minas'', a Brazilian newspaper * European Movement, an international lobbying association * ExxonMobil, a large oil company formed from the merger of Exxon and Mobil in 1999 * La République En Marche! (sometimes shortened to "En Marche!"), a major French political party Economics * Emerging markets, nations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Categorical Variable
In statistics, a categorical variable (also called qualitative variable) is a variable that can take on one of a limited, and usually fixed, number of possible values, assigning each individual or other unit of observation to a particular group or nominal category on the basis of some qualitative property. In computer science and some branches of mathematics, categorical variables are referred to as enumerations or enumerated types. Commonly (though not in this article), each of the possible values of a categorical variable is referred to as a level. The probability distribution associated with a random categorical variable is called a categorical distribution. Categorical data is the statistical data type consisting of categorical variables or of data that has been converted into that form, for example as grouped data. More specifically, categorical data may derive from observations made of qualitative data that are summarised as counts or cross tabulations, or from observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |