|
Computational Audiology
Computational audiology is a branch of audiology that employs techniques from mathematics and computer science to improve clinical treatments and scientific understanding of the auditory system. Computational audiology is closely related to computational medicine, which uses quantitative models to develop improved methods for general disease diagnosis and treatment. Overview In contrast to traditional methods in audiology and hearing science research, computational audiology emphasizes predictive modeling and large-scale analytics (" big data") rather than inferential statistics and small-cohort hypothesis testing. The aim of computational audiology is to translate advances in hearing science, data science, information technology, and machine learning to clinical audiological care. Research to understand hearing function and auditory processing in humans as well as relevant animal species represents translatable work that supports this aim. Research and development to implement mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiology
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found ( outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referrals). In addition to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear). The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles, which transfer the vibrations of the eardrum into waves in the fluid and membranes of the inner ear. The hollow space of the middle ear is also known as the tympanic cavity and is surrounded by the tympanic part of the temporal bone. The auditory tube (also known as the Eustachian tube or the pharyngotympanic tube) joins the tympanic cavity with the nasal cavity (nasopharynx), allowing pressure to equalize between the middle ear and throat. The primary function of the middle ear is to efficiently transfer acoustic energy from compression waves in air to fluid–membrane waves within the cochlea. Structure Ossicles The middle ear contains three tiny bones known as the ossicles: '' malleus'', '' incus'', and ''stapes''. The ossicles were given their Latin names for their distinctive shapes; they ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular System
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. The brain uses information from the vestibular system in the head a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
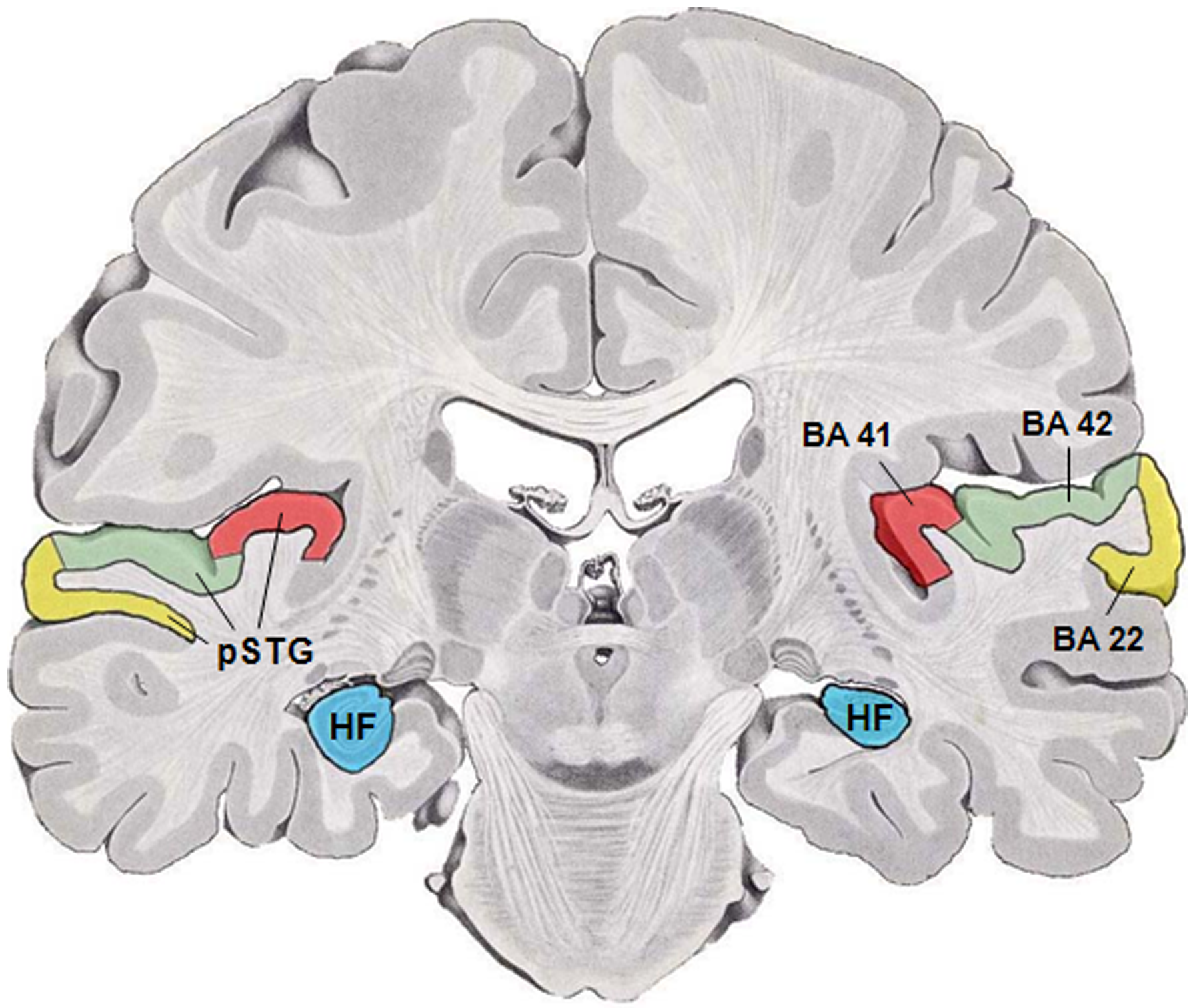
Auditory Cortex
The auditory cortex is the part of the temporal lobe that processes auditory information in humans and many other vertebrates. It is a part of the auditory system, performing basic and higher functions in hearing, such as possible relations to language switching.Cf. Pickles, James O. (2012). ''An Introduction to the Physiology of Hearing'' (4th ed.). Bingley, UK: Emerald Group Publishing Limited, p. 238. It is located bilaterally, roughly at the upper sides of the temporal lobes – in humans, curving down and onto the medial surface, on the superior temporal plane, within the lateral sulcus and comprising parts of the transverse temporal gyri, and the superior temporal gyrus, including the planum polare and planum temporale (roughly Brodmann areas 41 and 42, and partially 22). The auditory cortex takes part in the spectrotemporal, meaning involving time and frequency, analysis of the inputs passed on from the ear. The cortex then filters and passes on the information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory System
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system. System overview The outer ear funnels sound vibrations to the eardrum, increasing the sound pressure in the middle frequency range. The middle-ear ossicles further amplify the vibration pressure roughly 20 times. The base of the stapes couples vibrations into the cochlea via the oval window, which vibrates the perilymph liquid (present throughout the inner ear) and causes the round window to bulb out as the oval window bulges in. Vestibular and tympanic ducts are filled with perilymph, and the smaller cochlear duct between them is filled with endolymph, a fluid with a very different ion concentration and voltage. Vestibular duct perilymph vibrations bend organ of Corti outer cells (4 lines) causing prestin to be released in cell tips. This causes the cells to be chemically elongated and shrunk ( somatic motor), and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audiology
Audiology (from Latin , "to hear"; and from Greek , ''-logia'') is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies (e.g. behavioral hearing tests, otoacoustic emission measurements, and electrophysiologic tests), audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing (high, middle, or low frequencies) are affected, to what degree (severity of loss), and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found ( outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present, they will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation (e.g. hearing aids, cochlear implants, appropriate medical referrals). In addition to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Science
Information science (also known as information studies) is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of information. Practitioners within and outside the field study the application and the usage of knowledge in organizations in addition to the interaction between people, organizations, and any existing information systems with the aim of creating, replacing, improving, or understanding the information systems. Historically, information science (informatics) is associated with computer science, data science, psychology, technology, library science, healthcare, and intelligence agencies. However, information science also incorporates aspects of diverse fields such as archival science, cognitive science, commerce, law, linguistics, museology, management, mathematics, philosophy, public policy, and social sciences. Foundations Scope and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Pathology
Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as '' computers''. An especially well-known discipline of the study of computation is computer science. Physical process of Computation Computation can be seen as a purely physical process occurring inside a closed physical system called a computer. Examples of such physical systems are digital computers, mechanical computers, quantum computers, DNA computers, molecular computers, microfluidics-based computers, analog computers, and wetware computers. This point of view has been adopted by the physics of computation, a branch of theoretical physics, as well as the field of natural computing. An even more radical point of view, pancomputationalism (inaudible word), is the postulate of digital physics that argues that the evolution of the universe is its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Medicine
''In silico'' medicine (also known as "computational medicine") is the application of '' in silico'' research to problems involving health and medicine. It is the direct use of computer simulation in the diagnosis, treatment, or prevention of a disease. More specifically, ''in silico'' medicine is characterized by modeling, simulation, and visualization of biological and medical processes in computers with the goal of simulating real biological processes in a virtual environment. History The term ''in silico'' was first used in 1989 at a workshop "Cellular Automata: Theory and Applications" by a mathematician from National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM). The term ''in silico radiation oncology'', a precursor of generic ''in silico'' medicine was coined and first introduced by G. Stamatakos in Proceedings of the IEEE in 2002. The same researcher coined and introduced the more generic term ''in silico oncology''. ''In silico'' medicine is considered an extension of previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Biology
Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and Computer simulation, computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers. History Bioinformatics, the analysis of informatics processes in biological systems, began in the early 1970s. At this time, research in artificial intelligence was using network models of the human brain in order to generate new algorithms. This use of biological data pushed biological researchers to use computers to evaluate and compare large data sets in their own field. By 1982, researchers shared information via Punched card, punch cards. The amount of data grew exponentially by the end of the 1980s, requiring new computational method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms build a model based on sample data, known as training data, in order to make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed to do so. Machine learning algorithms are used in a wide variety of applications, such as in medicine, email filtering, speech recognition, agriculture, and computer vision, where it is difficult or unfeasible to develop conventional algorithms to perform the needed tasks.Hu, J.; Niu, H.; Carrasco, J.; Lennox, B.; Arvin, F.,Voronoi-Based Multi-Robot Autonomous Exploration in Unknown Environments via Deep Reinforcement Learning IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020. A subset of machine learning is closely related to computational statistics, which focuses on making predicti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)