|
Color–flavor Locking
Color–flavor locking (CFL) is a phenomenon that is expected to occur in ultra-high-density strange matter, a form of quark matter. The quarks form Cooper pairs, whose color properties are correlated with their flavor properties in a one-to-one correspondence between three color pairs and three flavor pairs. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, the color-flavor-locked phase is the highest-density phase of three-flavor colored matter. Color-flavor-locked Cooper pairing If each quark is represented as \psi^\alpha_i, with color index \alpha taking values 1, 2, 3 corresponding to red, green, and blue, and flavor index i taking values 1, 2, 3 corresponding to up, down, and strange, then the color-flavor-locked pattern of Cooper pairing is :\langle \psi^\alpha_i C \gamma_5 \psi^\beta_j \rangle \propto \delta^\alpha_i\delta^\beta_j - \delta^\alpha_j\delta^\beta_i = \epsilon^\epsilon_ This means that a Cooper pair of an up quark and a down quark must ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strange Matter
Strange matter (or strange quark matter) is quark matter containing strange quarks. In nature, strange matter is hypothesized to occur in the core of neutron stars, or, more speculatively, as isolated droplets that may vary in size from femtometers (strangelets) to kilometers, as in the hypothetical strange stars. At high enough density, strange matter is expected to be color superconducting. Ordinary matter, also referred to as atomic matter, is composed of atoms, with nearly all matter concentrated in the atomic nuclei. Nuclear matter is a liquid composed of neutrons and protons, and they are themselves composed of up and down quarks. Quark matter is a condensed form of matter composed entirely of quarks. When quark matter does not contain strange quarks, it is sometimes referred to as non-strange quark matter. Context In particle physics and astrophysics, the term 'strange matter' is used in two different contexts, one broader and the other more specific and hypothetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiral Symmetry
A chiral phenomenon is one that is not identical to its mirror image (see the article on mathematical chirality). The spin of a particle may be used to define a handedness, or helicity, for that particle, which, in the case of a massless particle, is the same as chirality. A symmetry transformation between the two is called parity transformation. Invariance under parity transformation by a Dirac fermion is called chiral symmetry. Chirality and helicity The helicity of a particle is positive (“right-handed”) if the direction of its spin is the same as the direction of its motion. It is negative (“left-handed”) if the directions of spin and motion are opposite. So a standard clock, with its spin vector defined by the rotation of its hands, has left-handed helicity if tossed with its face directed forwards. Mathematically, ''helicity'' is the sign of the projection of the spin vector onto the momentum vector: “left” is negative, “right” is positive. The chiralit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
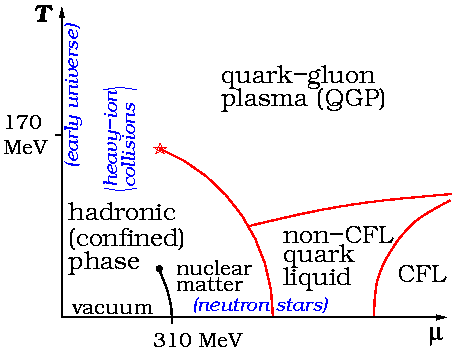
Quark Matter
Quark matter or QCD matter (quantum chromodynamic) refers to any of a number of hypothetical phases of matter whose degrees of freedom include quarks and gluons, of which the prominent example is quark-gluon plasma. Several series of conferences in 2019, 2020, and 2021 were devoted to this topic. Quarks are liberated into quark matter at extremely high temperatures and/or densities, and some of them are still only theoretical as they require conditions so extreme that they cannot be produced in any laboratory, especially not at equilibrium conditions. Under these extreme conditions, the familiar structure of matter, where the basic constituents are nuclei (consisting of nucleons which are bound states of quarks) and electrons, is disrupted. In quark matter it is more appropriate to treat the quarks themselves as the basic degrees of freedom. In the standard model of particle physics, the strong force is described by the theory of QCD. At ordinary temperatures or densities this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Superconductivity
Color superconductivity is a phenomenon where matter carries color charge without loss, similar to how conventional superconductors carry electric charge without loss. It is predicted to occur in quark matter if the baryon density is sufficiently high (well above nuclear density) and the temperature is not too high (well below 1012 kelvins). Color superconducting phases are to be contrasted with the normal phase of quark matter, which is just a weakly interacting Fermi liquid of quarks. In theoretical terms, a color superconducting phase is a state in which the quarks near the Fermi surface become correlated in Cooper pairs, which condense. In phenomenological terms, a color superconducting phase breaks some of the symmetries of the underlying theory, and has a very different spectrum of excitations and very different transport properties from the normal phase. Description Analogy with superconducting metals It is well known that at low temperature many metals become sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperon
In particle physics, a hyperon is any baryon containing one or more strange quarks, but no charm, bottom, or top quark. This form of matter may exist in a stable form within the core of some neutron stars. Hyperons are sometimes generically represented by the symbol Y. History and research The first research into hyperons happened in the 1950s and spurred physicists on to the creation of an organized classification of particles. The term was coined by French physicist Louis Leprince-Ringuet in 1953, and announced for the first time at the cosmic ray conference at Bagnères de Bigorre in July of that year, agreed upon by Leprince-Ringuet, Bruno Rossi, C.F. Powell, William B. Fretter and Bernard Peters. Today, research in this area is carried out on data taken at many facilities around the world, including CERN, Fermilab, SLAC, JLAB, Brookhaven National Laboratory, KEK, GSI and others. Physics topics include searches for CP violation, measurements of spin, studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluon
A gluon ( ) is an elementary particle that acts as the exchange particle (or gauge boson) for the strong force between quarks. It is analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles. Gluons bind quarks together, forming hadrons such as protons and neutrons. Gluons are vector gauge bosons that mediate strong interactions of quarks in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). Gluons themselves carry the color charge of the strong interaction. This is unlike the photon, which mediates the electromagnetic interaction but lacks an electric charge. Gluons therefore participate in the strong interaction in addition to mediating it, making QCD significantly harder to analyze than quantum electrodynamics (QED). Properties The gluon is a vector boson, which means, like the photon, it has a spin of 1. While massive spin-1 particles have three polarization states, massless gauge bosons like the gluon have only two polarization states because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Superposition
Quantum superposition is a fundamental principle of quantum mechanics. It states that, much like waves in classical physics, any two (or more) quantum states can be added together ("superposed") and the result will be another valid quantum state; and conversely, that every quantum state can be represented as a sum of two or more other distinct states. Mathematically, it refers to a property of solutions to the Schrödinger equation; since the Schrödinger equation is linear, any linear combination of solutions will also be a solution(s) . An example of a physically observable manifestation of the wave nature of quantum systems is the interference peaks from an electron beam in a double-slit experiment. The pattern is very similar to the one obtained by diffraction of classical waves. Another example is a quantum logical qubit state, as used in quantum information processing, which is a quantum superposition of the "basis states" , 0 \rangle and , 1 \rangle . Here ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulator (electrical)
An electrical insulator is a material in which electric current does not flow freely. The atoms of the insulator have tightly bound electrons which cannot readily move. Other materials—semiconductors and conductors—conduct electric current more easily. The property that distinguishes an insulator is its resistivity; insulators have higher resistivity than semiconductors or conductors. The most common examples are non-metals. A perfect insulator does not exist because even insulators contain small numbers of mobile charges (charge carriers) which can carry current. In addition, all insulators become electrically conductive when a sufficiently large voltage is applied that the electric field tears electrons away from the atoms. This is known as the breakdown voltage of an insulator. Some materials such as glass, paper and PTFE, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superfluid
Superfluidity is the characteristic property of a fluid with zero viscosity which therefore flows without any loss of kinetic energy. When stirred, a superfluid forms vortices that continue to rotate indefinitely. Superfluidity occurs in two isotopes of helium (helium-3 and helium-4) when they are liquefied by cooling to cryogenic temperatures. It is also a property of various other exotic states of matter theorized to exist in astrophysics, high-energy physics, and theories of quantum gravity. The theory of superfluidity was developed by Soviet theoretical physicists Lev Landau and Isaak Khalatnikov. Superfluidity is often coincidental with Bose–Einstein condensation, but neither phenomenon is directly related to the other; not all Bose–Einstein condensates can be regarded as superfluids, and not all superfluids are Bose–Einstein condensates. Superfluidity of liquid helium Superfluidity was discovered in helium-4 by Pyotr Kapitsa and independently by John F. Alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics Letters B
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physics. ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark Matter
Quark matter or QCD matter (quantum chromodynamic) refers to any of a number of hypothetical phases of matter whose degrees of freedom include quarks and gluons, of which the prominent example is quark-gluon plasma. Several series of conferences in 2019, 2020, and 2021 were devoted to this topic. Quarks are liberated into quark matter at extremely high temperatures and/or densities, and some of them are still only theoretical as they require conditions so extreme that they cannot be produced in any laboratory, especially not at equilibrium conditions. Under these extreme conditions, the familiar structure of matter, where the basic constituents are nuclei (consisting of nucleons which are bound states of quarks) and electrons, is disrupted. In quark matter it is more appropriate to treat the quarks themselves as the basic degrees of freedom. In the standard model of particle physics, the strong force is described by the theory of QCD. At ordinary temperatures or densities this f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |