|
Color (Hungarian Band)
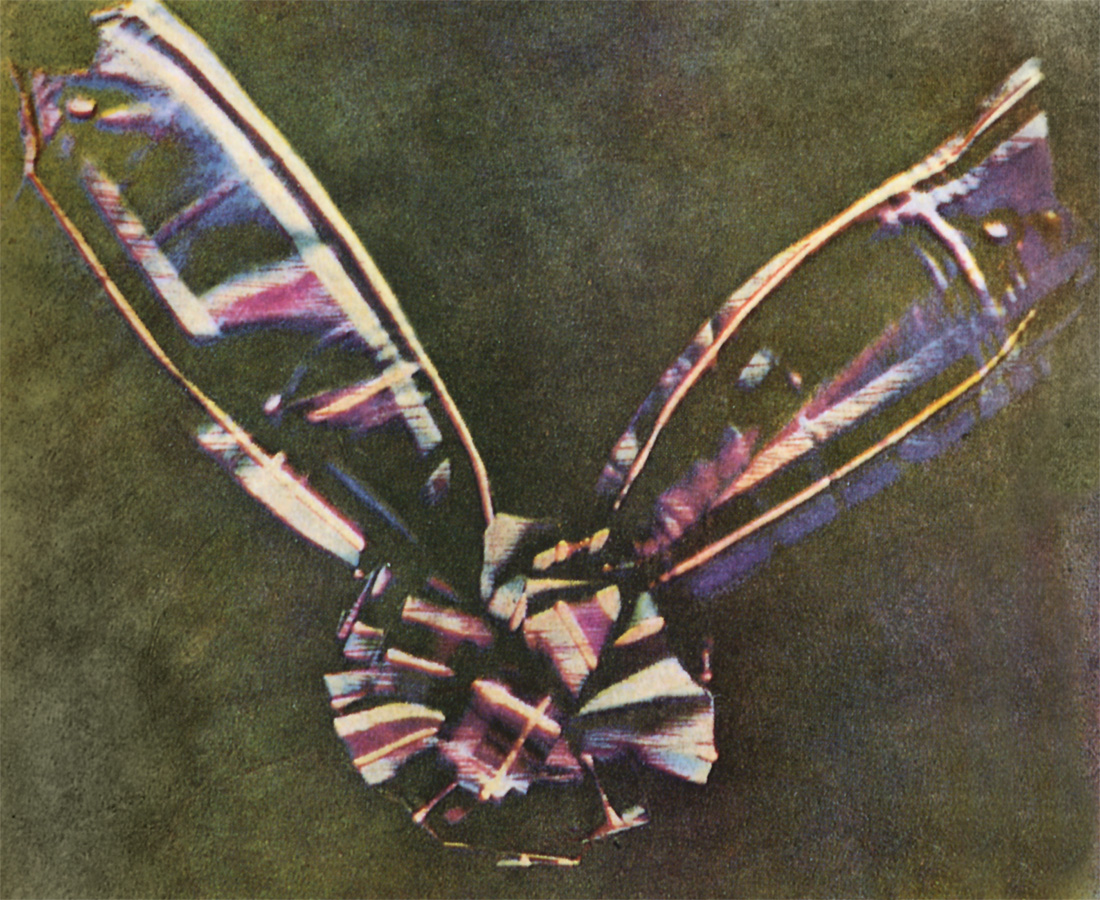
Color (American English) or colour (Commonwealth English) is the visual perception based on the electromagnetic spectrum. Though color is not an inherent property of matter, color perception is related to an object's light absorption, reflection, emission spectra and interference. For most humans, color are perceived in the visible light spectrum with three types of cone cells (trichromacy). Other animals may have a different number of cone cell types or have eyes sensitive to different wavelength, such as bees that can distinguish ultraviolet, and thus has a different color sensitivity range. Animal perception of color originates from different light wavelength or spectral sensitivity in cone cell types, which is then processed by the brain. Colors have perceived properties such as hue, colorfulness (saturation) and luminance. Colors can also be additively mixed (commonly used for actual light) or subtractively mixed (commonly used for materials). If the colors are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Of Style
A style guide or manual of style is a set of standards for the writing, Typesetting, formatting, and design of documents. It is often called a style sheet, although that term also has Style sheet (other), multiple other meanings. The standards can be applied either for general use, or be required usage for an individual publication, a particular organization, or a specific field. A style guide establishes standard wikt:style#Noun, style requirements to improve communication by ensuring wikt:consistency#Noun, consistency both within a document, and across multiple documents. Because practices vary, a style guide may set out standards to be used in areas such as punctuation, capitalization, citing sources, formatting of numbers and dates, Table (information), table appearance and other areas. The style guide may require certain best practices in writing style, usage, Composition (language), language composition, Composition (visual arts), visual composition, orthography, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Sensitivity
Spectral sensitivity is the relative efficiency of detection, of light or other signal, as a function of the frequency or wavelength of the signal. In visual neuroscience, spectral sensitivity is used to describe the different characteristics of the photopigments in the rod cells and cone cells in the retina of the eye. It is known that the rod cells are more suited to scotopic vision and cone cells to photopic vision, and that they differ in their sensitivity to different wavelengths of light. It has been established that the maximum spectral sensitivity of the human eye under daylight conditions is at a wavelength of 555 nm, while at night the peak shifts to 507 nm. In photography, film and sensors are often described in terms of their spectral sensitivity, to supplement their characteristic curves that describe their responsivity. A database of camera spectral sensitivity is created and its space analyzed. For X-ray films, the spectral sensitivity is chosen to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
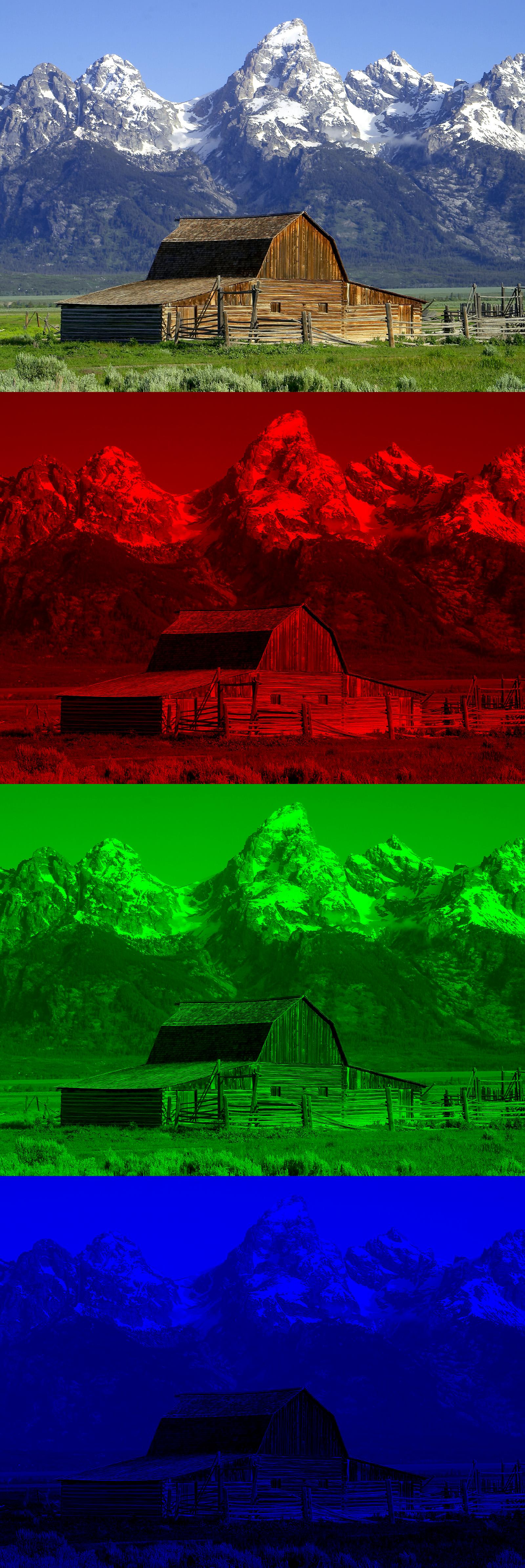
RGB Color Model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which the red, green and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials of the three additive primary colors, red, green, and blue. The main purpose of the RGB color model is for the sensing, representation, and display of images in electronic systems, such as televisions and computers, though it has also been used in conventional photography. Before the electronic age, the RGB color model already had a solid theory behind it, based in human perception of colors. RGB is a ''device-dependent'' color model: different devices detect or reproduce a given RGB value differently, since the color elements (such as phosphors or dyes) and their response to the individual red, green, and blue levels vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, or even in the same device over time. Thus an RGB value does not define the same ''color'' acro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Television
Color television or Colour television is a television transmission technology that includes color information for the picture, so the video image can be displayed in color on the television set. It improves on the monochrome or black-and-white television technology, which displays the image in shades of gray ( grayscale). Television broadcasting stations and networks in most parts of the world upgraded from black-and-white to color transmission between the 1960s and the 1980s. The invention of color television standards was an important part of the history and technology of television. Transmission of color images using mechanical scanners had been conceived as early as the 1880s. A demonstration of mechanically scanned color television was given by John Logie Baird in 1928, but its limitations were apparent even then. Development of electronic scanning and display made a practical system possible. Monochrome transmission standards were developed prior to World War II, but civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Photography
Color photography is photography that uses media capable of capturing and reproducing colors. By contrast, black-and-white or gray- monochrome photography records only a single channel of luminance (brightness) and uses media capable only of showing shades of gray. In color photography, electronic sensors or light-sensitive chemicals record color information at the time of exposure. This is usually done by analyzing the spectrum of colors into three channels of information, one dominated by red, another by green and the third by blue, in imitation of the way the normal human eye senses color. The recorded information is then used to reproduce the original colors by mixing various proportions of red, green and blue light ( RGB color, used by video displays, digital projectors and some historical photographic processes), or by using dyes or pigments to remove various proportions of the red, green and blue which are present in white light ( CMY color, used for prints on paper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Printing
Color printing or colour printing is the reproduction of an image or text in color (as opposed to simpler black and white or monochrome printing). Any natural scene or color photograph can be optically and physiologically dissected into three primary colors, red, green and blue, roughly equal amounts of which give rise to the perception of white, and different proportions of which give rise to the visual sensations of all other colors. The additive combination of any two primary colors in roughly equal proportion gives rise to the perception of a secondary color. For example, red and green yields yellow, red and blue yields magenta (a purple hue), and green and blue yield cyan (a turquoise hue). Only yellow is counter-intuitive. Yellow, cyan and magenta are merely the "basic" secondary colors: unequal mixtures of the primaries give rise to perception of many other colors all of which may be co Modern techniques While there are many techniques for reproducing images in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Reproduction
Color reproduction is an aspect of color science concerned with producing light spectra that evoke a desired color, either through additive (light emitting) or subtractive (surface color) models. It converts physical correlates of color perception ( CIE 1931 XYZ color space tristimulus values and related quantities) into light spectra that can be experienced by observers. In this way, it is the opposite of colorimetry. It is concerned with the faithful reproduction of a color in one medium, with a color in another, so it is a central concept in color management and relies heavily on color calibration. For example, food packaging must be able to faithfully reproduce the colors of the foods therein in order to appeal to a customer. This involves proper color calibration of at least four devices: * Lighting, which must have a high color rendering index and not give a color cast A colour cast is a tint of a particular colour, usually unwanted, that evenly affects a photographic i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Model
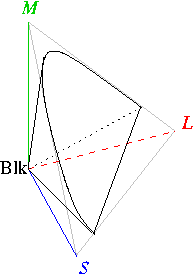
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description of how the components are to be interpreted (viewing conditions, etc.), taking account of visual perception, the resulting set of colors is called "color space." This article describes ways in which human color vision can be modeled, and discusses some of the models in common use. Tristimulus color space One can picture this space as a region in three-dimensional Euclidean space if one identifies the ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' axes with the stimuli for the long-wavelength (''L''), medium-wavelength (''M''), and short-wavelength (''S'') light receptors. The origin, (''S'',''M'',''L'') = (0,0,0), corresponds to black. White has no definite position in this diagram; rather it is defined according to the color temperature or white balance as desired or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital representation. A color space may be arbitrary, i.e. with physically realized colors assigned to a set of physical color swatches with corresponding assigned color names (including discrete numbers infor examplethe Pantone collection), or structured with mathematical rigor (as with the NCS System, Adobe RGB and sRGB). A "color space" is a useful conceptual tool for understanding the color capabilities of a particular device or digital file. When trying to reproduce color on another device, color spaces can show whether shadow/highlight detail and color saturation can be retained, and by how much either will be compromised. A " color model" is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamerism (color)
In colorimetry, metamerism is a perceived matching of colors with different (nonmatching) spectral power distributions. Colors that match this way are called metamers. A spectral power distribution describes the proportion of total light given off (emitted, transmitted, or reflected) by a color sample at each visible wavelength; it defines the complete information about the light coming from the sample. However, the human eye contains only three color receptors (three types of cone cells), which means that all colors are reduced to three sensory quantities, called the tristimulus values. Metamerism occurs because each type of cone responds to the cumulative energy from a broad range of wavelengths, so that different combinations of light across all wavelengths can produce an equivalent receptor response and the same tristimulus values or color sensation. In color science, the set of sensory spectral sensitivity curves is numerically represented by color matching functions. Sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtractive Color
Subtractive color or subtractive color mixing predicts the spectral power distribution of light after it passes through successive layers of partially absorbing media. This idealized model is the essential principle of how dyes and inks are used in color printing and photography where the perception of color is elicited after white light passes through microscopic "stacks" of partially absorbing media allowing some wavelengths of light to reach the eye and not others. Process The subtractive color mixing model predicts the resultant spectral power distribution of light filtered through overlaid partially absorbing materials on a reflecting or transparent surface. Each layer partially absorbs some wavelengths of light from the illumination spectrum while letting others pass through, resulting in a colored appearance. The resultant spectral power distribution is predicted by sequentially taking the product of the spectral power distributions of the incoming light and transmissiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Color
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model that predicts the appearance of colors made by coincident component lights, i.e. the perceived color can be predicted by summing the numeric representations of the component colors. Modern formulations of Grassmann's laws describe the additivity in the color perception of light mixtures in terms of algebraic equations. Additive color predicts perception and not any sort of change in the photons of light themselves. These predictions are only applicable in the limited scope of color matching experiments where viewers match small patches of uniform color isolated against a grey or black background. Additive color models are applied in the design and testing of electronic displays that are used to render realistic images containing diverse sets of color using phosphors that emit light of a limited set of primary colors. Examination with a sufficiently powerful magnifying lens will reveal that each pixel in CRT, L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |