|
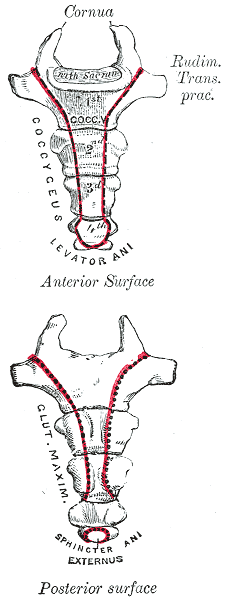
Coccygeus Muscle
The coccygeus muscle or ischiococcygeus is a muscle of the pelvic floor, located posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament. Structure The coccygeus muscle is posterior to levator ani and anterior to the sacrospinous ligament in the pelvic floor. It is a triangular plane of muscular and tendinous fibers. It arises by its apex from the spine of the ischium and sacrospinous ligament. It is inserted by its base into the margin of the coccyx and into the side of the lowest piece of the sacrum. In combination with the levator ani, it forms the pelvic diaphragm. The pudendal nerve runs between the coccygeus muscle and the piriformis muscle, superficial to the coccygeus muscle. Nerve supply The coccygeus muscle is innervated by the pudendal nerve, which runs between it and the piriformis muscle. Function The coccygeus muscle assists the levator ani and piriformis muscle in closing in the back part of the outlet of the pelvis. This helps to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrospinous Ligament
The sacrospinous ligament (small or anterior sacrosciatic ligament) is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the spine of the ischium, a bony protuberance on the human pelvis. Its fibres are intermingled with the sacrotuberous ligament. Structure The sacrotuberous ligament passes behind the sacrospinous ligament. In its entire length, the sacrospinous ligament covers the equally triangular coccygeus muscle, to which its closely connected.Gray's Anatomy 1918 Function The presence of the ligament in the greater sciatic notch creates an opening (foramen), the greater sciatic foramen, and also converts the lesser sciatic notch into the lesser sciatic foramen.Platzer (2004), p 188 The greater sciatic foramen lies above the ligament, and the lesser sciatic foramen lies below it. The pudendal vessels and nerve pass behind the sacrospinous ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrospinous Ligament
The sacrospinous ligament (small or anterior sacrosciatic ligament) is a thin, triangular ligament in the human pelvis. The base of the ligament is attached to the outer edge of the sacrum and coccyx, and the tip of the ligament attaches to the spine of the ischium, a bony protuberance on the human pelvis. Its fibres are intermingled with the sacrotuberous ligament. Structure The sacrotuberous ligament passes behind the sacrospinous ligament. In its entire length, the sacrospinous ligament covers the equally triangular coccygeus muscle, to which its closely connected.Gray's Anatomy 1918 Function The presence of the ligament in the greater sciatic notch creates an opening (foramen), the greater sciatic foramen, and also converts the lesser sciatic notch into the lesser sciatic foramen.Platzer (2004), p 188 The greater sciatic foramen lies above the ligament, and the lesser sciatic foramen lies below it. The pudendal vessels and nerve pass behind the sacrospinous ligament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccydynia
Coccydynia is a medical term meaning pain in the coccyx or tailbone area, often brought on by a fall onto the coccyx or by persistent irritation usually from sitting. Synonyms Coccydynia is also known as coccygodynia, coccygeal pain, coccyx pain, or coccalgia. Anatomy Structure Coccydynia occurs in the lowest part of the spine, the coccyx, which is believed to be a vestigial tail, or in other words the “tail bone”. The name coccyx is derived from the Greek word for cuckoo due to its beak like appearance. The coccyx itself is made up of 3 to 5 vertebrae, some of which may be fused together. The ventral side of the coccyx is slightly concave whereas the dorsal aspect is slightly convex. Both of these sides have transverse grooves that show where the vestigial coccygeal units had previously fused. The coccyx attaches to the sacrum from the dorsal grooves, with the attachment being either a symphysis or as a true synovial joint, and also to the gluteus maximus muscle, the coccy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccyx
The coccyx ( : coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since '' Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensor Coccygis
The coccyx ( : coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horses. In tailless primates (e.g. humans and other great apes) since '' Nacholapithecus'' (a Miocene hominoid),Nakatsukasa 2004, ''Acquisition of bipedalism'' (SeFig. 5entitled ''First coccygeal/caudal vertebra in short-tailed or tailless primates.''.) the coccyx is the remnant of a vestigial tail. In animals with bony tails, it is known as ''tailhead'' or ''dock'', in bird anatomy as ''tailfan''. It comprises three to five separate or fused coccygeal vertebrae below the sacrum, attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between the sacrum and the coccyx. Structure The coccyx is formed of three, four or five rudimentary vertebrae. It articulates superiorly with the sacrum. In each of the first three segments m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woman
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female humans regardless of age. Typically, women inherit a pair of X chromosomes, one from each parent, and are capable of pregnancy and giving birth from puberty until menopause. More generally, sex differentiation of the female fetus is governed by the lack of a present, or functioning, SRY-gene on either one of the respective sex chromosomes. Female anatomy is distinguished from male anatomy by the female reproductive system, which includes the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina, and vulva. A fully developed woman generally has a wider pelvis, broader hips, and larger breasts than an adult man. Women have significantly less facial and other body hair, have a higher body fat composition, and are on average shorter and less muscular than men. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piriformis Muscle
The piriformis muscle () is a flat, pyramidally-shaped muscle in the gluteal region of the lower limbs. It is one of the six muscles in the lateral rotator group. The piriformis muscle has its origin upon the front surface of the sacrum, and inserts onto the greater trochanter of the femur. Depending upon the given position of the leg, it acts either as external (lateral) rotator of the thigh or as abductor of the thigh. It is innervated by the piriformis nerve. Structure The piriformis is a flat muscle, and is pyramidal in shape. Origin The piriformis muscle originates from the anterior (front) surface of the sacrum by three fleshy digitations attached to the second, third, and fourth sacral vertebra. It also arises from the superior margin of the greater sciatic notch, the gluteal surface of the ilium (near the posterior inferior iliac spine), the sacroiliac joint capsule, and (sometimes) the sacrotuberous ligament (more specifically, the superior part of the pelvic s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Nerve
The pudendal nerve is the main nerve of the perineum. It carries sensation from the external genitalia of both sexes and the skin around the anus and perineum, as well as the motor supply to various pelvic muscles, including the male or female external urethral sphincter and the external anal sphincter. If damaged, most commonly by childbirth, lesions may cause sensory loss or fecal incontinence. The nerve may be temporarily blocked as part of an anaesthetic procedure. The pudendal canal that carries the pudendal nerve is also known by the eponymous term "Alcock's canal", after Benjamin Alcock, an Irish anatomist who documented the canal in 1836. Structure The pudendal nerve is paired, meaning there are two nerves, one on the left and one on the right side of the body. Each is formed as three roots immediately converge above the upper border of the sacrotuberous ligament and the coccygeus muscle. The three roots become two cords when the middle and lower root join to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Diaphragm
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is composed of muscle fibers of the levator ani, the coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue which span the area underneath the pelvis. The pelvic diaphragm is a muscular partition formed by the levatores ani and coccygei, with which may be included the parietal pelvic fascia on their upper and lower aspects. The pelvic floor separates the pelvic cavity above from the perineal region (including perineum) below. Both males and females have a pelvic floor. To accommodate the birth canal, a female's pelvic cavity is larger than a male's. Structure The right and left levator ani lie almost horizontally in the floor of the pelvis, separated by a narrow gap that transmits the urethra, vagina, and anal canal. The levator ani is usually considered in three parts: pubococcygeus, puborectalis, and iliococcygeus. The pubococcygeus, the main part of the levator, runs backward from the body of the pubis toward the coccyx and may be damaged dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischium
The ischium () forms the lower and back region of the hip bone (''os coxae''). Situated below the ilium and behind the pubis, it is one of three regions whose fusion creates the coxal bone. The superior portion of this region forms approximately one-third of the . Structure The i ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levator Ani
The levator ani is a broad, thin muscle group, situated on either side of the pelvis. It is formed from three muscle components: the pubococcygeus, the iliococcygeus, and the puborectalis. It is attached to the inner surface of each side of the lesser pelvis, and these unite to form the greater part of the pelvic floor. The coccygeus muscle completes the pelvic floor, which is also called the ''pelvic diaphragm''. It supports the viscera in the pelvic cavity, and surrounds the various structures that pass through it. The levator ani is the main pelvic floor muscle and painfully contracts during vaginismus. It also contracts rhythmically during orgasm. Structure The levator ani is made up of 3 parts: * Iliococcygeus muscle * Pubococcygeus muscle * Puborectalis muscle The iliococcygeus arises from the inner side of the ischium (the lower and back part of the hip bone) and from the posterior part of the tendinous arch of the obturator fascia, and is attached to the coccyx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.png)
