|
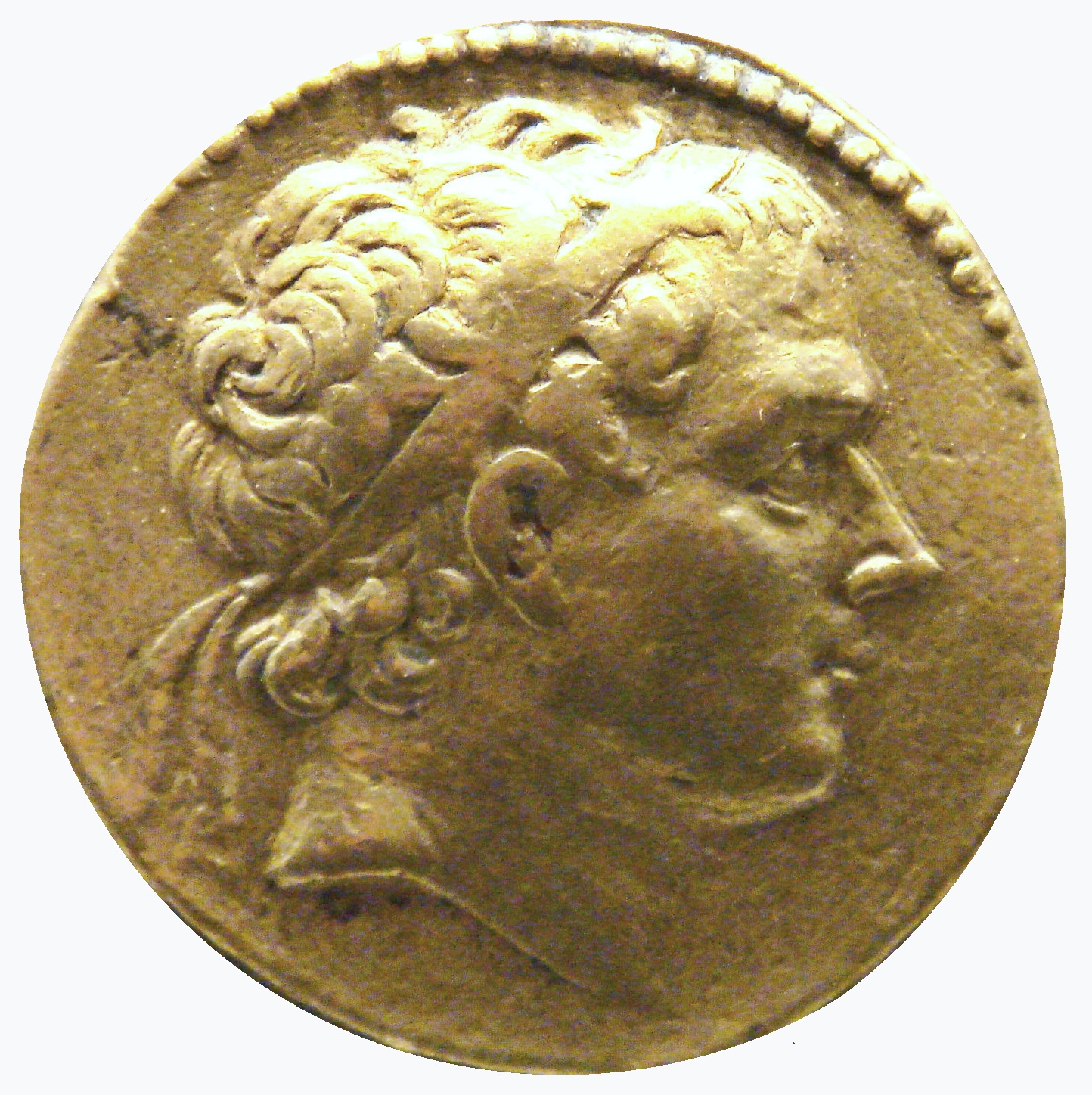
Cleopatra Thea
Cleopatra Thea ( el, Κλεοπάτρα Θεά, which means "Cleopatra the Goddess"; c. 164 – 121 BC) surnamed Eueteria (i.e., "good-harvest/fruitful season") was the ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire. She was queen consort of Syria from 150 to about 125 BC as the wife of three Syrian kings: Alexander Balas, Demetrius II Nicator, and Antiochus VII Sidetes. She ruled Syria from 125 BC after the death of Demetrius II Nicator, eventually in co-regency with her son Antiochus VIII Grypus until 121 or 120 BC.Aidan Dodson, Dyan Hilton, The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt, 2004Cleopatra Thea by Chris Bennett Biography Childhood and first marriage Cleopatra Thea grew up in Egypt as the daughter of |
Ptolemais In Phoenicia
Ptolemais was an ancient port city on the Canaanite coast in the region of Palestine (region), Palestine, in the location of the present-day city of Acre, Israel. It was also called Ptolemais in Canaan (or ''Akko'', ''Ake'', or ''Akre'' in Canaanite Language). It was an Ancient bishopric, which became a double Catholic titular see. In the Middle Ages, it was known as ''Acre, Palestine, Acre'' amongst some Western European crusaders, who started a new, militantly Latin chapter there. History Greek historians refer to the city as ''Ake'' ( grc, Ἄκη), meaning "cure." According to the Greek myth, Heracles found curative herbs here to heal his wounds. Josephus calls it ''Akre''. The name was changed to ''Antiochia Ptolemais'' ( grc, Ἀντιόχεια Πτολεμαΐς) shortly after Alexander the Great's conquest, and then to Ptolemais, probably by Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemy I Soter, after the Wars of the Diadochi lead to the partition of the kingdom of Alexander the Great and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
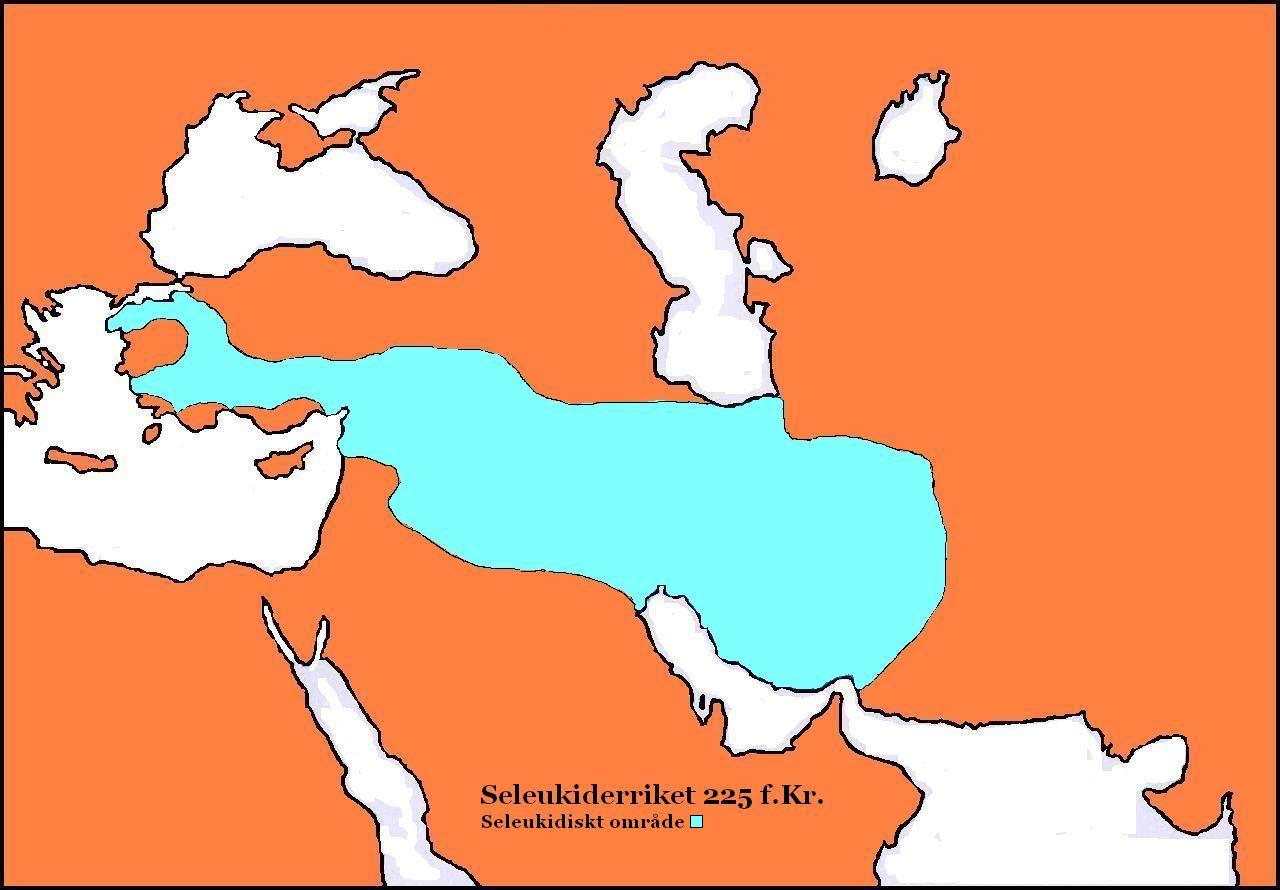
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BC, and formed part of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire following the 4th-century-BC conquests of Alexander the Great. The region later served as the political and cultural base of the Eastern Iranian Parni people and Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD). The Sasanian Empire, the last state of pre-Islamic Iran, also held the region and maintained the seven Parthian clans as part of their feudal aristocracy. Name The name "Parthia" is a continuation from Latin ', from Old Persian ', which was the Parthian language self-designator signifying "of the Parthians" who were an Iranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy V
egy, Iwaennetjerwymerwyitu Seteppah Userkare Sekhem-ankhamun Clayton (2006) p. 208. , predecessor = Ptolemy IV , successor = Ptolemy VI , horus = '' ḥwnw-ḫꜤj-m-nsw-ḥr-st-jt.f''''Khunukhaiemnisutkhersetitef'' The youth who has appeared as king on his father's throne , horus_hiero = H-wn:n-nw:W-A17-xa:a:W*Z4-Aa15:sw*A43-D2:Z1-Q1-t:O1-t:f:Z1:f , nebty = ''wr-pḥtj smn-tꜢwj snfr-tꜢmrj mnḥ-jb-ḫr-nṯrw''''Werpehty Sementawy Senefertameri Menekhibkhernetjeru''The one great of strength, who has established the Two Lands and made Ta-mery perfect (by) being efficacious before the gods , nebty_hiero = wr:r-F9*F9:Z9:D40-s-U32-wAD-M24-s-nfr-N16:N21\*N21:O5*t:O49-mnx-ib:Z1-x:r-nTr*Z1-nTr*Z1-nTr*Z1 , golden = '' wꜢḏ-Ꜥnḫ-n-ḥnmmt nb-ḥbw-sd-mj-ptḥ jty-mj-rꜤ''''Wadjankhenkhenmemet Nebkhebusedmiptah Itymire'' The one who has made the life of mankind flourish, a possessor of Sed festivals like Ptah and a sovereign like Ra , golden_h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III Megas
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman dominat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus VI Dionysus
Antiochus VI Dionysus (c. 148–142/1 BC), king of the Hellenistic Seleucid kingdom, was the son of Alexander Balas and Cleopatra Thea, daughter of Ptolemy VI of Egypt. Biography Antiochus VI did not actually rule. Either already in 145 or in early 144 BC he was nominated by the general Diodotus Tryphon as heir to the throne in opposition to Demetrius II, and remained the general's tool. In c. 142/141 BC, the young king died. While some ancient authors make Diodotus Tryphon responsible for the death of the king, others write that he died during a surgery.Ios. Ant. 13. 218; Liv. per. 55. See also * List of Syrian monarchs * Timeline of Syrian history __NOTOC__ This is a timeline of Syrian history, comprising important legal and territorial changes and political events in Syria and its predecessor states. To read about the background to these events, see History of Syria. Millennia: 1st ... References Footnotes External links Antiochus VIentry in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I Maccabees
The First Book of Maccabees, also known as First Maccabees (written in shorthand as 1 Maccabees or 1 Macc.), is a book written in Hebrew by an anonymousRappaport, U., ''47. 1 Maccabees'' in Barton, J. and Muddiman, J. (2001)The Oxford Bible Commentary, p. 711 Jewish author after the restoration of an independent Jewish kingdom by the Hasmonean dynasty, around the late 2nd century BC. The original Hebrew is lost and the most important surviving version is the Greek translation contained in the Septuagint. The book is held as canonical scripture by the Catholic, Orthodox, and Oriental Orthodox churches (except for the Orthodox Tewahedo), but not by Protestant denominations nor any major branches of Judaism; it is not part of the Hebrew Bible. Some Protestants consider it to be an apocryphal book (see also Deuterocanonical books). 1 Maccabees is best known for its account of an early victory in the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire: the recapture of Jerusalem in the year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemais Akko
Acre ( ), known locally as Akko ( he, עַכּוֹ, ''ʻAkō'') or Akka ( ar, عكّا, ''ʻAkkā''), is a city in the coastal plain region of the Northern District of Israel. The city occupies an important location, sitting in a natural harbour at the extremity of Haifa Bay on the coast of the Mediterranean's Levantine Sea."Old City of Acre." , World Heritage Center. World Heritage Convention. Web. 15 Apr 2013 Aside from coastal trading, it was also an important waypoint on the region's coastal road and the road cutting inland along the |
Balas
Balas ( fa, بالاس, also Romanized as Balās; also known as Balūs) is a village in Do Hezar Rural District, Khorramabad District, Tonekabon County, Mazandaran Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 108, in 36 families. References Populated places in Tonekabon County {{Tonekabon-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus IV
Antiochus IV Epiphanes (; grc, Ἀντίοχος ὁ Ἐπιφανής, ''Antíochos ho Epiphanḗs'', "God Manifest"; c. 215 BC – November/December 164 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king who ruled the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. He was a son of King Antiochus III the Great. Originally named Mithradates (alternative form '' Mithridates''), he assumed the name Antiochus after he ascended the throne. Notable events during Antiochus's reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of Judea and Samaria, and the rebellion of the Jewish Maccabees. Antiochus's accession to the throne was controversial, and he was seen as a usurper by some. After the death of his brother Seleucus IV Philopator in 175 BC, the "true" heir should have been Seleucus's son Demetrius I. However, Demetrius I was very young and a hostage in Rome at the time, and Antiochus seized the opportunity to declare himself king instead, successfully rall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrius I Soter
Demetrius I (Greek: ''Δημήτριος Α`'', 185 – June 150 BC), surnamed Soter (Greek: ''Σωτήρ'' - "Savior"), reigned as king (basileus) of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire from November 162 – June 150 BC. Demetrius grew up in Rome as a hostage, but returned to Greek Syria and overthrew his young cousin Antiochus V Eupator and regent Lysias. Demetrius took control during a turbulent time of the Empire, and spent much of his time fighting off revolts and challenges to his power from threats such as Timarchus and Alexander Balas. Biography Early confinement and escape Demetrius was born around 185 BC. He was sent to Rome as a hostage at a young age during the reign of his father Seleucus IV Philopator and his mother Laodice IV.Appian, ''Roman History: Syrian Wars'' 8.46 Rome taking prominent Seleucid family members hostage was one of the terms of the Treaty of Apamea that had ended the Roman-Seleucid War. His father was likely murdered by his finance minister Heliod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus VIII Grypus
Antiochus VIII Epiphanes/Callinicus/Philometor, nicknamed Grypus ( gr, Γρυπός, "hook-nose"), was the ruler of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire from 125 to 96 BC. He was the younger son of Demetrius II and Cleopatra Thea. He may have spent his early life in Athens and returned to Syria after the deaths of his father and brother Seleucus V. At first he was joint ruler with his mother. Fearing her influence, Antiochus VIII had Cleopatra Thea poisoned in 121 BC. Political instability affected most of Antiochus VIII's reign. From 116 BC he fought a civil war against his half-brother Antiochus IX. Antiochus VIII's wife, the Ptolemaic Egyptian princess Tryphaena, had her sister and the wife of Antiochus IX, the former Cleopatra IV of Egypt, murdered in 112 BC; Antiochus IX killed Tryphaena in revenge. In 102 BC, Antiochus VIII's aunt Cleopatra III of Egypt, the mother of the two rival queens, gave him the hand of her daughter Cleopatra Selene in marriage. Antiochus VIII was ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |