|
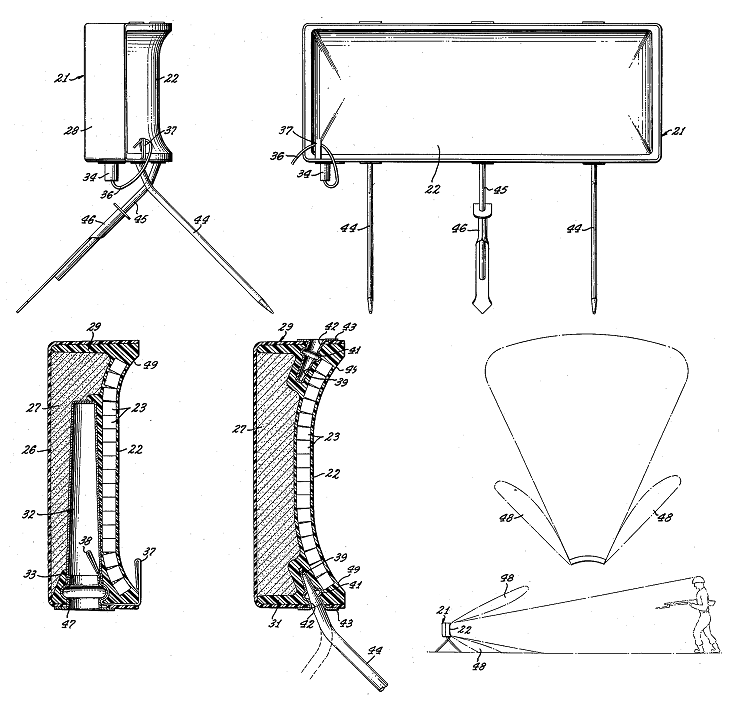
Claymore Mine
The Claymore mine is a directional anti-personnel mine developed for the United States Armed Forces. Its inventor, Norman MacLeod, named the mine after a claymore, large medieval Scottish sword. Unlike a conventional land mine, the Claymore may be command-detonated (fired by remote-control), and is directional, shooting a wide pattern of metal balls into a kill zone. The Claymore can also be activated by a booby-trap tripwire firing system for use in Area denial weapon, area denial operations. The Claymore fires steel balls out to about within a 60° arc in front of the device. It is used primarily in ambushes and as an anti-infiltration device against enemy infantry. It is also used against soft-skinned vehicle, unarmored vehicles. Many countries have developed and used mines like the Claymore. Examples include models MON-50, MON-90, MON-100, and MON-200 introduced by the Soviet Union and used by its successor Russia, as well as MRUD (Serbia), MAPED F1 (France), and Mini MS-80 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-personnel Mine
An anti-personnel mine or anti-personnel landmine (APL) is a form of land mine, mine designed for use against human, humans, as opposed to an anti-tank mine, which target vehicles. APLs are classified into: blast mines and fragmentation mines; the latter may or may not be a bounding mine. APLs are often designed to injure and mutilation, maim, not kill, their victims to overwhelm the logistical (mostly medical) support system of enemy forces that encounter them. Some types of APLs can also damage the tracks on armoured vehicles or the tires of wheeled vehicles. The International Campaign to Ban Landmines has sought to ban mines and destroy stockpile. For this purpose, it introduced in 1997 the Ottawa Treaty, which has not yet been accepted by over 30 states and has not guaranteed the protection of citizens against APLs planted by non-state armed groups. Use Anti-personnel mines are used in a similar manner to anti-tank mines, in static "mine fields" along national borders o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claymore
A claymore (; from , "great sword") is either the Scottish variant of the late medieval two-handed sword or the Scottish variant of the basket-hilted sword. The former is characterised as having a cross hilt of forward-sloping quillons with quatrefoil terminations and was in use from the 15th to 17th centuries. The word ''claymore'' was first used in reference to basket-hilted swords during the 18th century in Scotland and parts of England. This description was maybe not used during the 17th century, when basket-hilted swords were the primary military swords across Europe, but these basket-hilted, broad-bladed swords remained in service with officers of Scottish regiments into the 21st century. After the Acts of Union in 1707 (when Scottish and English regiments were integrated together), the swords were seen as a mark of distinction by Scottish officers over the more slender sabres used by their English contemporaries: a symbol of physical strength and prowess, and a link t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxy Resin
Epoxy is the family of basic components or cured end products of epoxy resins. Epoxy resins, also known as polyepoxides, are a class of reactive prepolymers and polymers which contain epoxide groups. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called ''epoxy''. The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane. Epoxy resins may be reacted ( cross-linked) either with themselves through catalytic homo polymerisation, or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines, acids (and acid anhydrides), phenols, alcohols and thiols (sometimes called mercaptans). These co-reactants are often referred to as hardeners or curatives, and the cross-linking reaction is commonly referred to as curing. Reaction of polyepoxides with themselves or with polyfunctional hardeners forms a thermosetting polymer, often with favorable mechanical properties and high thermal and chemical resistance. Epoxy has a wide range of applications, including metal coatings, composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mini MS-803 Mine
The Mini MS-803 is a small South African produced Claymore type landmine. The design is very simple, with a convex brown polystyrene case containing a PE9 plastic explosive charge with three hundred 6 x 8 millimeter cylindrical steel fragments embedded into it. The mine is supported by two pairs of wire legs, which can be used to stack the mines. On the top of the mine is a small hole for inserting a detonator, which is surrounded with a PETN booster charge. The mine is normally used with an S4 electrical detonator connected to an M57 electrical firing device which is also used with the similar but larger Shrapnel mine Mk 2. The mine could also be used with MUV type pull detonators and tripwires, but after the Ottawa mine ban treaty South Africa has said that it will not use this mine with victim activated fuses. When the mine is triggered, the fragments are launched in a 60 degree arc to a lethal range of between 15 and 30 meters. The fragment density is claimed to be two per mete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAPED F1
The MAPED F1 is a claymore-shaped plastic-bodied directional anti-personnel mine which is designed to wound or kill by fragmentation. It has been the standard directional anti-personnel mine of the French army since the late 1970s. The MAPED F1 body is flat on the back and convex on the front, it has a small aiming sight on the top left corner and plastic lugs in the bottom corners for attaching a pair of "A" frame support legs. The mine contains a plastic explosive charge to propel 500 steel ball fragments to a range of 50 meters in a 60° arc. The MAPED F1 is battery powered and is normally actuated by breakwire, but tripwire and command actuation are also possible. The MAPED F1 is surface mounted and it can be located visually or with metal detectors under most field conditions. The MAPED F1 can be defeated by blast overpressure from explosive breaching systems like the Giant Viper and MICLIC unless it is set up for command actuation. Mine operation The MAPED F1 uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MRUD
The MRUD (Mina usmerena rasprskavajućeg dejstva - Directed fragmentation mine) is a Yugoslav plastic bodied, convex rectangular directional type anti-personnel mine designed to wound or kill by fragmentation. It is broadly similar to the M18A1 Claymore mine. The casing is a light green color with two detonator wells and three crude sight lines on the top and an embossed grid pattern on the front of some early mines. Two detachable metal legs fit in slots on the bottom to secure the mine when it is ground mounted. The body of the MRUD is waterproof and the mine can be used in temperatures from −30˚ to +50˚ C. The mine body contains 900 grams of TNT-based explosive and 650 5.5-millimeter steel balls. When fired the fragmentation has a lethal arc of 60 degrees and a lethal range of 40–50 meters. The MRUD kit comes packed with a manual inductor, circuit test device and an EK-40-69 electric detonator. The mine can be command detonated from up to 30 meters away using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MON-200
The MON-200 is a directional type anti-personnel mine designed and manufactured in Soviet Union. It is an enlarged version of the MON-100 mine. Because of its large size, this directional fragmentation mine can also be used against light-skinned vehicles and helicopters. Number 200 in the code name means 200 meters of effective distance for seriously damaging people. Specifications * Mine type: Anti-personnel * Mine action: n/a * Material: Sheet metal * Shape: Circular * Colour: Green, olive * Total weight: 25 kgExplosive Ordnance Guide for Ukraine 2022 https://www.gichd.org/fileadmin/uploads/gichd/Publications/GICHD_Ukraine_Guide_2022_Second_Edition_web.pdf * Explosive content: 12 kg TNT * Operating pressure (kg): n/a * Length: n/a * Width: 130 mm * Height: n/a * Diameter: 434 mm See also *MON-50 *MON-90 *MON-100 The MON-100 is a circular, sheet metal bodied, directional type of anti-personnel mine designed and manufactured in the early 1960s by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MON-100
The MON-100 is a circular, sheet metal bodied, directional type of anti-personnel mine designed and manufactured in the early 1960s by the Soviet Union. It is designed to wound or kill by fragmentation and resembles a large bowl. The mine is reported to be deployed in Angola, Mozambique, South Africa and Zambia. Design The MON-100 mine body has a smooth, well finished appearance with a webbing handle mounted on the upper edge. It is usually attached to a mounting shackle by wing nuts on either side of the mine body (the shackle is connected to a spike for securing the mine to buildings, trees etc.). The concave face of the mine has a detonator cavity in its center (this is the side aimed at the target). The mine contains 2 kg of explosive to propel 450 steel rod fragments to a lethal range of 100 m (thus the "100" in the name), at maximum range the spread of the fragmentation is 9.5 m. The mine alone weighs 5 kg but with the shackle and mounting spike the weight is 7. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MON-90
MON-90 The MON-90 () is a Claymore-shaped, plastic bodied, directional type of anti-personnel mine designed in the Soviet Union. It is designed to wound or kill by fragmentation. The mine is similar in appearance to the MON-50, but is approximately twice the size with a much greater depth. Design The MON-90 has an attachment point on the bottom for connecting a special clamp which can be attached to wood, metal etc. but it has no scissor type legs. It has a sight centered on the top which is flanked by two detonator cavities. The mine contains 6.2 kg of RDX (PVV-5A) to propel approximately 2000 steel rod fragments to a lethal range of 90 meters in a 54° arc (60 m wide spread at 90 m range). The MON-90 is usually command actuated using a PN manual inductor and an EDP-R electric detonator (ZT non-electric detonator also available). It can also be actuated by a variety of booby trap (BT) switches including: *MUV series pull *MVE-72 electric breakwire *VP13 seism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MON-50
The MON-50 () is a Soviet rectangular, slightly convex, plastic bodied, directional type of anti-personnel mine designed to wound or kill by explosive fragmentation. It first entered service in 1965 and is a copy of the American M18 Claymore with a few differences.''Brassey's Essential Guide to Anti-personnel Landmines'', Eddie Banks, p.244 Its name is derived from Russian мина осколочная направленного (''mina oskolochnaya napravlennogo''), "directional fragmentation mine". Design Based on the American M18A1 Claymore, the MON-50 has folding scissor type legs for supporting and aiming, but it also has an attachment point on the bottom for connecting a special clamp/spike which can be attached to wood, metal etc. It has a peep sight centered on the top which is flanked by two detonator cavities. The mine contains 700 g of RDX (PVV-5A) to propel approximately 540 or 485 fragments to a lethal range of 50 meters in a 54° arc (spread of 45 meters at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft-skinned Vehicle
In military terminology, a soft-skinned vehicle, also known as a 'B' vehicle, is a vehicle that is not protected by vehicle armour. Lexicographer Eric Partridge believed the term soft-skinned vehicle first appeared in military parlance in the early 1940s. Soft-skinned or 'B' vehicles are often considered wheeled military vehicles such as light utility vehicles and trucks, but they can be any unarmoured wheeled or tracked vehicle that is not primarily designed to be employed for offensive purposes. They can be purpose-designed models specifically built for military service, militarised versions of commercial vehicle models or standard commercial civilian vehicles pressed into military service. In some cases this class of vehicles may be fitted with vehicle armour for crew defence. Historically in times of war, a number of military units have converted soft-skinned vehicles into armoured fighting vehicles. One of the first units to do so was the British Royal Naval Air Service. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |