|
Ching Shih
Zheng Yi Sao (1775–1844; born Shi Yang, a.k.a. Shi Xianggu), also known as Ching Shih, was a Chinese pirate leader who was active in the South China Sea from 1801 to 1810. Born as Shi Yang in 1775 to humble origins, she married a pirate named Zheng Yi at age 26 in 1801. She was named Zheng Yi Sao ("wife of Zheng Yi") by the people of Guangdong. After the death of her husband in 1807, she took control of his pirate confederation with the support of his adopted son Zhang Bao, with whom she entered into a relationship and later married. As the unofficial commander of the Guangdong Pirate Confederation, her fleet was composed of 400 junks and between 40,000 to 60,000 pirates in 1805. Her ships entered into conflict with several major powers, such as the East India Company, the Portuguese Empire, and Qing China. In 1810, Zheng Yi Sao negotiated a surrender to the Qing authorities which allowed her and Zhang Bao to retain a substantial fleet and avoid prosecution. At the time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinhui District
Xinhui, alternately romanized as Sunwui and also known as Kuixiang, is an urban district of Jiangmen in Guangdong, China. It grew from a separate city founded at the confluence of the Tan and West Rivers. It has a population of about 735,500, 98% of whom are Han Chinese but many of whom speak a dialect of Cantonese as their first language. Xinhui is best known in China for its ''chenpi'', a kind of dried Mandarin orange peel. Geography Xinhui is situated at the confluence of the Tan and West Rivers in the southwestern area of the Pearl River Delta. It borders the South China Sea and adjoins Macao and Hong Kong. It comprises a total area of . Geologists have shown that Xinhui originated as a shallow bay at the mouth of the Pearl River about 5000 years ago, with its southeastern portion consisting of a chain of islands. The movement of the Tan and West Rivers eventually formed a delta that became the present alluvial plain over the course of the last nine hundred years. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procuring (prostitution)
Procuring or pandering is the facilitation or provision of a prostitute or other sex worker in the arrangement of a sex act with a customer. A procurer, colloquially called a pimp (if male) or a madam (if female, though the term pimp has still extensively been used for female procurers as well) or a brothel keeper, is an agent for prostitutes who collects part of their earnings. The procurer may receive this money in return for advertising services, physical protection, or for providing and possibly monopolizing a location where the prostitute may solicit clients. Like prostitution, the legality of certain actions of a madam or a pimp vary from one region to the next. Examples of procuring include: * Trafficking a person into a country for the purpose of soliciting sex * Operating a business where prostitution occurs * Transporting a prostitute to the location of their arrangement * Deriving financial gain from the prostitution of another Etymology ''Procurer'' The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongxing, Guangxi
Dongxing (: ) is a county-level city within Fangchenggang, Guangxi, People's Republic of China, on the border with Móng Cái, in Vietnam. The city spans an area of 549 square kilometers, and has a population of approximately 130,000 as of 2011. History During the Mạc dynasty (1533-1592), the land south of the Shiwandashan Mountains was ceded to the Ming dynasty. Jiangping was a melting pot of Vietnamese and Chinese, however, the region was neglected by the Vietnamese government. During the 18th and 19th, the area became a hotbed of piracy (see: Pirates of the South China Coast). After the end of the Sino-French War in 1885, Jiangping, Bailong Peninsula, and the Jing Islands were ceded by the French to Qing China. The Jing Islands are home to the Gin people, a group of ethnic Vietnamese in China. During the Qing Dynasty, the area was administered as Fangcheng County (). Dongxing was briefly established as a city in 1950 but was merged back into Fangcheng County by 1952. On D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nguyễn Dynasty
The Nguyễn dynasty (chữ Nôm: 茹阮, vi, Nhà Nguyễn; chữ Hán: 阮朝, vi, Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1883. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the August Revolution. The Nguyễn Phúc family established feudal rule over large amounts of territory as the Nguyễn lords by the 16th century before defeating the Tây Sơn dynasty and establishing their own imperial rule in the 19th century. The dynastic rule began with Gia Long ascending the throne in 1802, after ending the previous Tây Sơn dynasty. The Nguy� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Junk 1804
Chinese can refer to: * Something related to China * Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity **''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation ** List of ethnic groups in China, people of various ethnicities in contemporary China ** Han Chinese, the largest ethnic group in the world and the majority ethnic group in Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, Taiwan, and Singapore ** Ethnic minorities in China, people of non-Han Chinese ethnicities in modern China ** Ethnic groups in Chinese history, people of various ethnicities in historical China ** Nationals of the People's Republic of China ** Nationals of the Republic of China ** Overseas Chinese, Chinese people residing outside the territories of Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan * Sinitic languages, the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family ** Chinese language, a group of related languages spoken predominantly in China, sharing a written script (Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adoption
Adoption is a process whereby a person assumes the parenting of another, usually a child, from that person's biological or legal parent or parents. Legal adoptions permanently transfer all rights and responsibilities, along with filiation, from the biological parents to the adoptive parents. Unlike guardianship or other systems designed for the care of the young, adoption is intended to effect a permanent change in status and as such requires societal recognition, either through legal or religious sanction. Historically, some societies have enacted specific laws governing adoption, while others used less formal means (notably contracts that specified inheritance rights and parental responsibilities without an accompanying transfer of filiation). Modern systems of adoption, arising in the 20th century, tend to be governed by comprehensive statutes and regulations. History Antiquity ;Adoption for the well-born While the modern form of adoption emerged in the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han Chinese, Han people, the majority ethnic group in China. Although the primary capital of Beijing fell in 1644 to a rebellion led by Li Zicheng (who established the short-lived Shun dynasty), numerous rump state, rump regimes ruled by remnants of the House of Zhu, Ming imperial family—collectively called the Southern Ming—survived until 1662. The Ming dynasty's founder, the Hongwu Emperor (r. 1368–1398), attempted to create a society of self-sufficient rural communities ordered in a rigid, immobile system that would guarantee and support a permanent class of soldiers for his dynasty: the empire's standing army exceeded one million troops and the naval history of China, navy's dockyards in Nanjin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zheng Qi (pirate)
Zheng Qi (also spelled Ching Tsih or Cheng Chi; born Zheng Yaohuang; 1760 – September 1802) was a powerful Chinese pirate operating from Canton (Guangdong) and throughout the South China Sea in the late 1700s. History He was born Zheng Yaohuang in Xin'an County, Guangdong, Qing China (modern Shenzhen and Hong Kong) in 1760. He was the seventh son of his pirate father Zheng Lianfu (鄭連福) and his wife Lin Xiu (林秀), hence the nickname Zheng Qi. Zheng Qi was recruited by Tay Son dynasty in 1788, and later became one of the most important subordinates under Chen Tianbao. From 1788 to 1799, Zheng frequently attacked southern coast of Qing China together with Mo Guanfu, Liang Wengeng (梁文庚) and Fan Wencai (樊文才). The Qing navy feared them. In 1795, Zheng Qi abducted a 12-year-old boy named He Song (何送) and raised him as his adopted son. Few years later, Zheng Qi gave him a captive female as his bride and seven hundred of silver (''liang'') to set up store ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
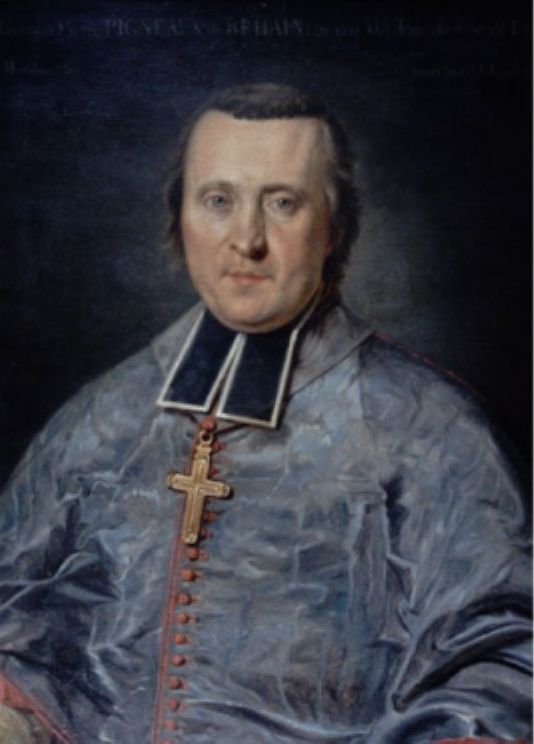
Gia Long
Gia Long ( (''North''), ('' South''); 8 February 1762 – 3 February 1820), born Nguyễn Phúc Ánh (阮福暎) or Nguyễn Ánh, was the founding emperor of the Nguyễn dynasty, the last dynasty of Vietnam. His dynasty would rule the unified territories that constitute modern-day Vietnam until 1945. A nephew of the last Nguyễn lord who ruled over south Vietnam, Nguyễn Ánh was forced into hiding in 1777 as a fifteen-year-old when his family was slain in the Tây Sơn revolt. After several changes of fortune in which his loyalists regained and again lost Saigon, he befriended the French Catholic Bishop Pierre Pigneau de Behaine. Pigneau championed his cause to the French government and managed to recruit volunteers when that fell through to help Nguyễn Ánh regain the throne. From 1789, Nguyễn Ánh was once again in the ascendancy and began his northward march to defeat the Tây Sơn, reaching the border with China by 1802, which had previously been under the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tây Sơn Wars
The Tây Sơn Rebellion was a massive peasant rebellion and an interregnum in the late eighteenth century Dai Viet (present-day Vietnam) against the ruling Vietnamese elites and monarchs, during the context of a 250-year-long disintegration period. The rebellion was led by three Tayson brothers, Nguyễn Nhạc, Nguyễn Huệ, and Nguyễn Lữ, who eventually overthrew all ruling clans and the reigning Lê dynasty in southern and northern Dai Viet. Background By the mid-18th century, the Dai Viet kingdom had been fragmented for 200 years. The ruling Lê dynasty monarchs stood as the figurehead of the nation, while Trinh lords in Tonkin and Nguyen lords in Cochinchina were the actual rulers on their own domains. The population expanded to over 7.2 million by the 1740s. European trade to Tonkin was suspended in 1700 while trade in Cochinchina also declined, causing major decreases in revenues for both the lords and their domains. Drought, famines, diseases (smallpox) were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tây Sơn Dynasty
The Tây Sơn dynasty (, vi, Nhà Tây Sơn (Chữ Nôm: 茹西山); vi, Tây Sơn triều ( Hán tự: 西山朝) was a ruling dynasty of Vietnam, founded in the wake of a rebellion against both the Nguyễn lords and the Trịnh lords before subsequently establishing themselves as a new dynasty. The Tây Sơn were led by three brothers, referred to by modern Vietnamese historians as the Tây Sơn brothers because of their origin in the district of Tây Sơn.Kim, p. 359. The Tây Sơn dynasty ended the century-long war between the Trịnh and Nguyễn families, fought off an attack by Qing China, and united the country for the first time in 200 years. Under the most prominent of the Tây Sơn brothers, Nguyễn Huệ—later the emperor Quang Trung—Vietnam experienced an age of relative peace and prosperity. His heir, however, was not capable of properly ruling the country, allowing the exiled Nguyễn lord Nguyễn Ánh to retake the south of Vietnam and eventually p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
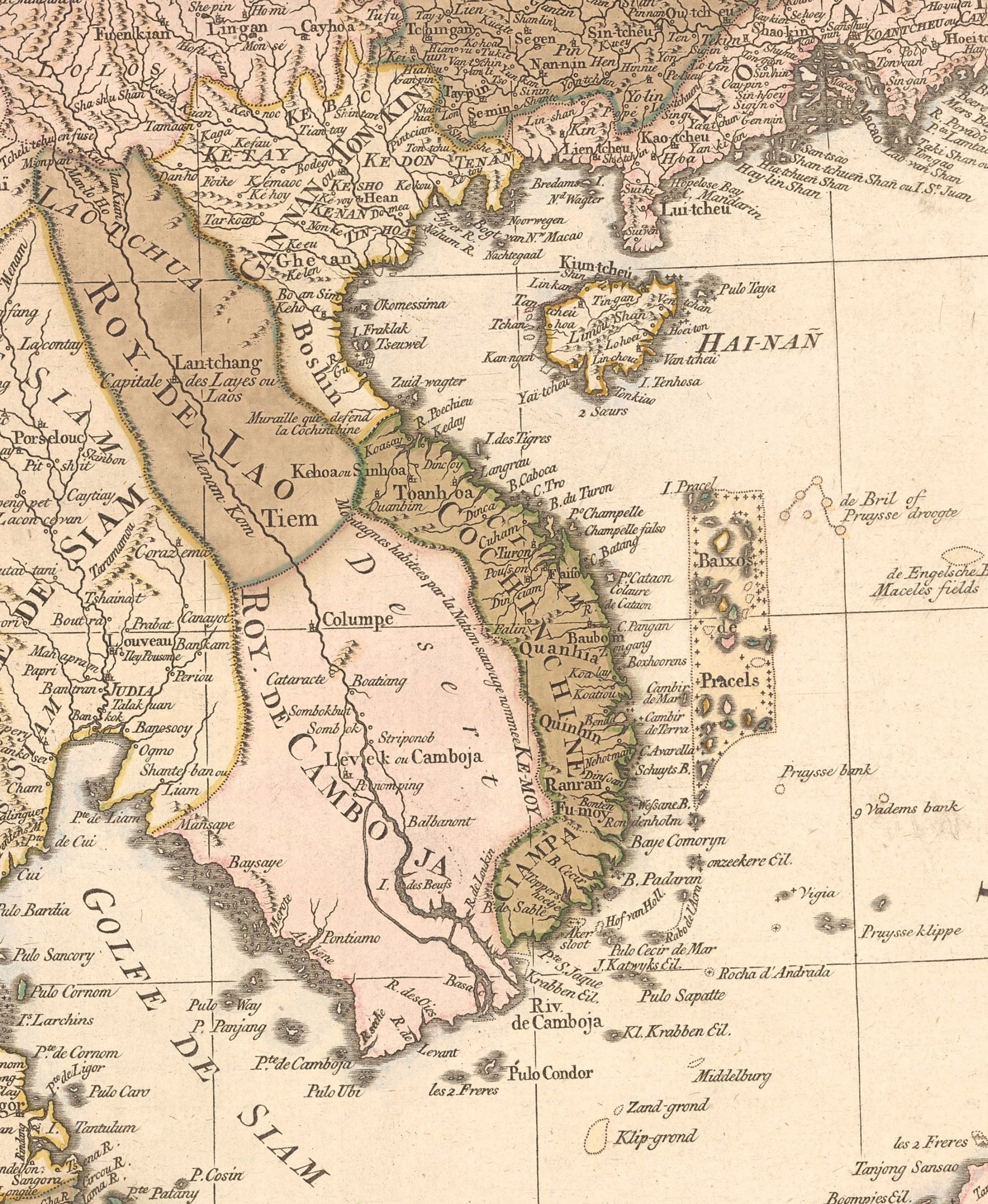
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam borders China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (commonly known as Saigon). Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam under Chinese rule from 111 BC, until the first dynasty emerged in 939. Successive monarchical dynasties absorbed Chinese influences through Confucianism and Buddhism, and expan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |