|
Child Psychopathology
Child psychopathology refers to the scientific study of mental disorders in children and adolescents. Oppositional defiant disorder, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, and autism spectrum disorder are examples of psychopathology that are typically first diagnosed during childhood. Mental health providers who work with children and adolescents are informed by research in developmental psychology, clinical child psychology, and family systems. Lists of child and adult mental disorders can be found in the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Edition (ICD-10), published by the World Health Organization (WHO) and in the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', Fifth Edition (DSM-5), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). In addition, the '' Diagnostic Classification of Mental Health and Developmental Disorders of Infancy and Early Childhood'' (DC: 0-3R) is used in assessing mental health and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitting, or occur as single episodes. Many disorders have been described, with signs and symptoms that vary widely between specific disorders. Such disorders may be diagnosed by a mental health professional, usually a clinical psychologist or psychiatrist. The causes of mental disorders are often unclear. Theories may incorporate findings from a range of fields. Mental disorders are usually defined by a combination of how a person behaves, feels, perceives, or thinks. This may be associated with particular regions or functions of the brain, often in a social context. A mental disorder is one aspect of mental health. Cultural and religious beliefs, as well as social norms, should be taken into account when making a diagnosis. Service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperament
In psychology, temperament broadly refers to consistent individual differences in behavior that are biologically based and are relatively independent of learning, system of values and attitudes. Some researchers point to association of temperament with formal dynamical features of behavior, such as energetic aspects, plasticity, sensitivity to specific reinforcers and emotionality. Temperament traits (such as Neuroticism, Sociability, Impulsivity, etc.) are distinct patterns in behavior throughout a lifetime, but they are most noticeable and most studied in children. Babies are typically described by temperament, but longitudinal research in the 1920s began to establish temperament as something which is stable across the lifespan. Definition Temperament has been defined as "the constellation of inborn traits that determine a child's unique behavioral style and the way he or she experiences and reacts to the world." Classification schemes Many classification schemes for tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
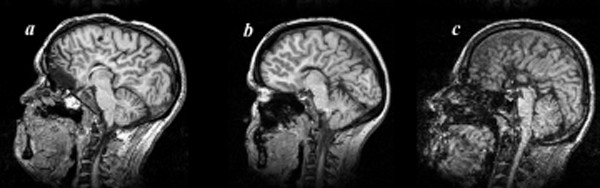
Agenesis Of The Corpus Callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum (ACC) is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum. It occurs when the development of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain, in the embryo is disrupted. The result of this is that the fibers that would otherwise form the corpus callosum are instead longitudinally oriented along the ipsilateral ventricular wall and form structures called Probst bundles. In addition to agenesis, other degrees of callosal defects exist, including hypoplasia (underdevelopment or thinness), hypogenesis (partial agenesis) or dysgenesis (malformation). ACC is found in many syndromes and can often present alongside hypoplasia of the cerebellar vermis. When this is the case, there can also be an enlarged fourth ventricle or hydrocephalus; this is called Dandy–Walker malformation. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of ACC and other callosal disorders vary greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental And Clinical Psychopharmacology
''Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Psychological Association. It was established in 1993 and covers research in clinical psychology. The current editor-in-chief is William W. Stoops (University of Kentucky Department of Behavioral Science). The journal has implemented the Transparency and Openness Promotion (TOP) Guidelines. The TOP Guidelines provide structure to research planning and reporting and aim to make research more transparent, accessible, and reproducible. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed by MEDLINE/PubMed and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Obsession may refer to: Psychology * Celebrity worship syndrome, obsessive addictive disorder to a celebrity's personal and professional life * Fixation (psychology), a persistent attachment to an object or idea * Idée fixe (psychology), a preoccupation of mind believed to be firmly resistant to any attempt to modify it * Obsessive love, an overwhelming, obsessive desire to possess another person * Obsessive–compulsive disorder, an anxiety disorder characterized by obsessive thoughts Arts, entertainment, and media Films * '' Ossessione'' (1943), an Italian crime drama * ''Obsession'' (1949 film), a British thriller also released as ''The Hidden Room'' * ''Obsession'' (1954 film), a French-language crime drama * ''Obsession'' (1976 film), a psychological thriller/mystery directed by Brian De Palma * ''Obsession'' (1997 film), a Franco-German drama starring Daniel Craig * ''Obsession'' (2022 film), a Nigerian drama * ''Circle of Two'', 1981 Canadian drama also distribute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by excessive amounts of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that are pervasive, impairing in multiple contexts, and otherwise age-inappropriate. ADHD symptoms arise from executive dysfunction, and emotional dysregulation is often considered a core symptom. In children, problems paying attention may result in poor school performance. ADHD is associated with other neurodevelopmental and mental disorders as well as some non-psychiatric disorders, which can cause additional impairment, especially in modern society. Although people with ADHD struggle to focus on tasks they are not particularly interested in completing, they are often able to maintain an unusually prolonged and intense level of attention for tasks they do find interesting or rewarding; this is known as hyperfocus. The precise causes of ADHD are unknown in the majority of cases. Genetic factors play an impor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunedin Longitudinal Study
The Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study (also known as the Dunedin Study) is a detailed study of human health, development and behaviour. Based at the University of Otago in New Zealand, the Dunedin Study has followed the lives of 1037 babies born between 1 April 1972 and 31 March 1973 at Dunedin's Queen Mary Maternity Hospital since their birth. Teams of national and international collaborators work on the Dunedin Study, including a team at Duke University in the United States. The research is constantly evolving to encompass research made possible by new technology and seeks to answer questions about how people's early years impact mental and physical health as they age. The study is now in its fifth decade and has produced over 1300 publications and reports, many of which have influenced or helped inform policy makers in New Zealand and overseas; many of these can be found on the publications section of their website. History The Dunedin Study was the ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Transporter
The serotonin transporter (SERT or 5-HTT) also known as the sodium-dependent serotonin transporter and solute carrier family 6 member 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC6A4 gene. SERT is a type of monoamine transporter protein that transports the neurotransmitter serotonin from the synaptic cleft back to the presynaptic neuron, in a process known as serotonin reuptake. This transport of serotonin by the SERT protein terminates the action of serotonin and recycles it in a sodium-dependent manner. Many antidepressant medications of the SSRI and tricyclic antidepressant classes work by binding to SERT and thus reducing serotonin reuptake. It is a member of the sodium:neurotransmitter symporter family. A repeat length polymorphism in the promoter of this gene has been shown to affect the rate of serotonin uptake and may play a role in sudden infant death syndrome, aggressive behavior in Alzheimer disease patients, post-traumatic stress disorder and depression-susce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amygdala
The amygdala (; plural: amygdalae or amygdalas; also '; Latin from Greek, , ', 'almond', 'tonsil') is one of two almond-shaped clusters of nuclei located deep and medially within the temporal lobes of the brain's cerebrum in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown to perform a primary role in the processing of memory, decision making, and emotional responses (including fear, anxiety, and aggression), the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system. The term "amygdala" was first introduced by Karl Friedrich Burdach in 1822. Structure The regions described as amygdala nuclei encompass several structures of the cerebrum with distinct connectional and functional characteristics in humans and other animals. Among these nuclei are the basolateral complex, the cortical nucleus, the medial nucleus, the central nucleus, and the intercalated cell clusters. The basolateral complex can be further subdivided into the lateral, the basal, and the accessory basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borderline Personality Disorder
Borderline personality disorder (BPD), also known as emotionally unstable personality disorder (EUPD), is a personality disorder characterized by a long-term pattern of unstable interpersonal relationships, distorted sense of self, and strong emotional reactions. Those affected often engage in self-harm and other dangerous behaviors, often due to their difficulty with returning their emotional level to a healthy or normal baseline. They may also struggle with a feeling of emptiness, fear of abandonment, and detachment from reality. Symptoms of BPD may be triggered by events considered normal to others. BPD typically begins by early adulthood and occurs across a variety of situations. Substance use disorders, depression, and eating disorders are commonly associated with BPD. Some 8 to 10% of people affected by the disorder may die by suicide. The disorder is often stigmatized in both the media and the psychiatric field and as a result is often underdiagnosed. The causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substance Abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behaviour occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.. Drugs most often associated with this term include: alcohol, amphetamines, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, cannabis, cocaine, hallucinogens (although there is no known ''psychedelic'', one of the three categories of hallucinogens, that has been found to have any addictive potential), methaqualone, and opioids. The exact cause of substance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychological Evaluation
Psychological evaluation is a method to assess an individual's behavior, personality, cognitive abilities, and several other domains. A common reason for a psychological evaluation is to identify psychological factors that may be inhibiting a person's ability to think, behave, or regulate emotion functionally or constructively. It is the mental equivalent of physical examination. Other psychological evaluations seek to better understand the individual's unique characteristics or personality to predict things like workplace performance or customer relationship management. History Modern ''Psychological evaluation'' has been around for roughly 200 years, with roots that stem as far back as 2200 B.C.Gregory, R. J. (2010). Psychological testing: history, principles, and applications. (7th ed., pp. 1-29 inclusive). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon. It started in China, and many psychologists throughout Europe worked to develop methods of testing into the 1900s. The first tests focused on apt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |