|
Character Sum
In mathematics, a character sum is a sum \sum \chi(n) of values of a Dirichlet character χ '' modulo'' ''N'', taken over a given range of values of ''n''. Such sums are basic in a number of questions, for example in the distribution of quadratic residues, and in particular in the classical question of finding an upper bound for the least quadratic non-residue ''modulo'' ''N''. Character sums are often closely linked to exponential sums by the Gauss sums (this is like a finite Mellin transform). Assume χ is a nonprincipal Dirichlet character to the modulus ''N''. Sums over ranges The sum taken over all residue classes mod ''N'' is then zero. This means that the cases of interest will be sums \Sigma over relatively short ranges, of length ''R'' < ''N'' say, : A fundamental improvement on the trivial estimate is the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legendre Symbol
In number theory, the Legendre symbol is a multiplicative function with values 1, −1, 0 that is a quadratic character modulo an odd prime number ''p'': its value at a (nonzero) quadratic residue mod ''p'' is 1 and at a non-quadratic residue (''non-residue'') is −1. Its value at zero is 0. The Legendre symbol was introduced by Adrien-Marie Legendre in 1798 in the course of his attempts at proving the law of quadratic reciprocity. Generalizations of the symbol include the Jacobi symbol and Dirichlet characters of higher order. The notational convenience of the Legendre symbol inspired introduction of several other "symbols" used in algebraic number theory, such as the Hilbert symbol and the Artin symbol. Definition Let p be an odd prime number. An integer a is a quadratic residue modulo p if it is congruent to a perfect square modulo p and is a quadratic nonresidue modulo p otherwise. The Legendre symbol is a function of a and p defined as :\left(\frac\right) = \ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematika
''Mathematika'' is a peer-reviewed mathematics journal that publishes both pure and applied mathematical articles. The journal was founded by Harold Davenport in the 1950s. The journal is published by the London Mathematical Society, on behalf of the journal's owner University College London. Indexing and abstracting According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 0.844. The journal in indexing in the following bibliographic databases: * MathSciNet * Science Citation Index Expanded * Web of Science * Zentralblatt MATH zbMATH Open, formerly Zentralblatt MATH, is a major reviewing service providing reviews and abstracts for articles in pure and applied mathematics, produced by the Berlin office of FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastruct ... References {{reflist London Mathematical Society Mathematics education in the United Kingdom Mathematics journals Publications established in 1954 Quarterly journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus (mathematics)
In mathematics, genus (plural genera) has a few different, but closely related, meanings. Intuitively, the genus is the number of "holes" of a surface. A sphere has genus 0, while a torus has genus 1. Topology Orientable surfaces The genus of a connected, orientable surface is an integer representing the maximum number of cuttings along non-intersecting closed simple curves without rendering the resultant manifold disconnected. It is equal to the number of handles on it. Alternatively, it can be defined in terms of the Euler characteristic ''χ'', via the relationship ''χ'' = 2 − 2''g'' for closed surfaces, where ''g'' is the genus. For surfaces with ''b'' boundary components, the equation reads ''χ'' = 2 − 2''g'' − ''b''. In layman's terms, it's the number of "holes" an object has ("holes" interpreted in the sense of doughnut holes; a hollow sphere would be considered as having zero holes in this sense). A torus has 1 su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Function
In mathematics, the term linear function refers to two distinct but related notions: * In calculus and related areas, a linear function is a function whose graph is a straight line, that is, a polynomial function of degree zero or one. For distinguishing such a linear function from the other concept, the term affine function is often used. * In linear algebra, mathematical analysis, and functional analysis, a linear function is a linear map. As a polynomial function In calculus, analytic geometry and related areas, a linear function is a polynomial of degree one or less, including the zero polynomial (the latter not being considered to have degree zero). When the function is of only one variable, it is of the form :f(x)=ax+b, where and are constants, often real numbers. The graph of such a function of one variable is a nonvertical line. is frequently referred to as the slope of the line, and as the intercept. If ''a > 0'' then the gradient is positive and the graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow method of checking the primality of a given number n, called trial division, tests whether n is a multiple of any integer between 2 and \sqrt. Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error, and the AKS primality test, which alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Weil
André Weil (; ; 6 May 1906 – 6 August 1998) was a French mathematician, known for his foundational work in number theory and algebraic geometry. He was a founding member and the ''de facto'' early leader of the mathematical Bourbaki group. The philosopher Simone Weil was his sister. The writer Sylvie Weil is his daughter. Life André Weil was born in Paris to agnostic Alsatian Jewish parents who fled the annexation of Alsace-Lorraine by the German Empire after the Franco-Prussian War in 1870–71. Simone Weil, who would later become a famous philosopher, was Weil's younger sister and only sibling. He studied in Paris, Rome and Göttingen and received his doctorate in 1928. While in Germany, Weil befriended Carl Ludwig Siegel. Starting in 1930, he spent two academic years at Aligarh Muslim University in India. Aside from mathematics, Weil held lifelong interests in classical Greek and Latin literature, in Hinduism and Sanskrit literature: he had taught himself Sanskrit in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperelliptic Curve
In algebraic geometry, a hyperelliptic curve is an algebraic curve of genus ''g'' > 1, given by an equation of the form y^2 + h(x)y = f(x) where ''f''(''x'') is a polynomial of degree ''n'' = 2''g'' + 1 > 4 or ''n'' = 2''g'' + 2 > 4 with ''n'' distinct roots, and ''h''(''x'') is a polynomial of degree 3. Therefore, in giving such an equation to specify a non-singular curve, it is almost always assumed that a non-singular model (also called a smooth completion), equivalent in the sense of birational geometry, is meant. To be more precise, the equation defines a quadratic extension of C(''x''), and it is that function field that is meant. The singular point at infinity can be removed (since this is a curve) by the normalization (integral closure) process. It turns out that after doing this, there is an open cover of the curve by two affine charts: the one already given by y^2 = f(x) and another one given by w^2 = v^f(1/v) . The glueing maps between the two charts are given by (x ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elliptic Curve
In mathematics, an elliptic curve is a smooth, projective, algebraic curve of genus one, on which there is a specified point . An elliptic curve is defined over a field and describes points in , the Cartesian product of with itself. If the field's characteristic is different from 2 and 3, then the curve can be described as a plane algebraic curve which consists of solutions for: :y^2 = x^3 + ax + b for some coefficients and in . The curve is required to be non-singular, which means that the curve has no cusps or self-intersections. (This is equivalent to the condition , that is, being square-free {{no footnotes, date=December 2015 In mathematics, a square-free element is an element ''r'' of a unique factorization domain ''R'' that is not divisible by a non-trivial square. This means that every ''s'' such that s^2\mid r is a unit of ''R''. A ... in .) It is always understood that the curve is really sitting in the projective plane, with the point being the uniqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobi Symbol
Jacobi symbol for various ''k'' (along top) and ''n'' (along left side). Only are shown, since due to rule (2) below any other ''k'' can be reduced modulo ''n''. Quadratic residues are highlighted in yellow — note that no entry with a Jacobi symbol of −1 is a quadratic residue, and if ''k'' is a quadratic residue modulo a coprime ''n'', then , but not all entries with a Jacobi symbol of 1 (see the and rows) are quadratic residues. Notice also that when either ''n'' or ''k'' is a square, all values are nonnegative. The Jacobi symbol is a generalization of the Legendre symbol. Introduced by Jacobi in 1837, it is of theoretical interest in modular arithmetic and other branches of number theory, but its main use is in computational number theory, especially primality testing and integer factorization; these in turn are important in cryptography. Definition For any integer ''a'' and any positive odd integer ''n'', the Jacobi symbol is defined as the product of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
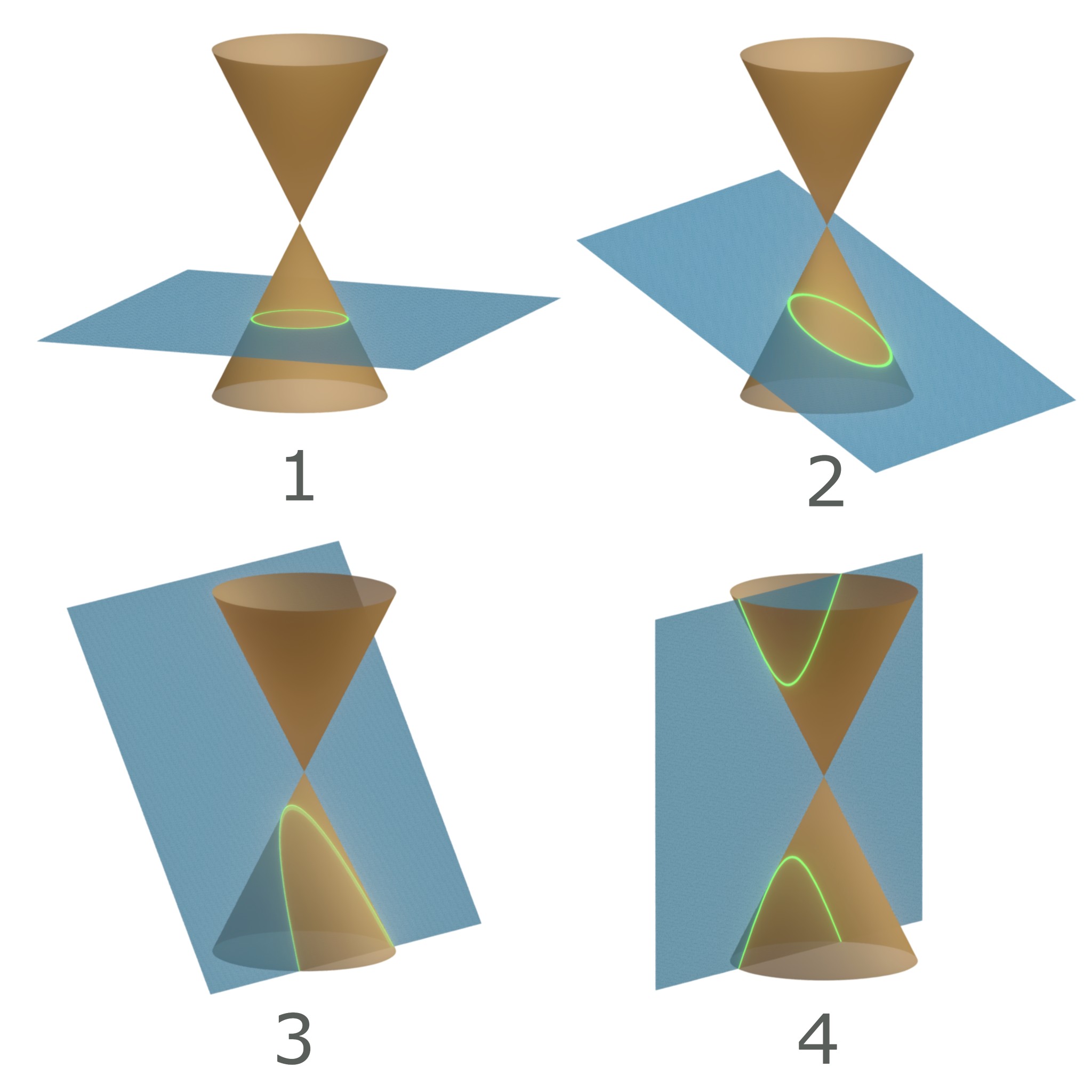
Conic Section
In mathematics, a conic section, quadratic curve or conic is a curve obtained as the intersection of the surface of a cone with a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though historically it was sometimes called a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties. The conic sections in the Euclidean plane have various distinguishing properties, many of which can be used as alternative definitions. One such property defines a non-circular conic to be the set of those points whose distances to some particular point, called a ''focus'', and some particular line, called a ''directrix'', are in a fixed ratio, called the ''eccentricity''. The type of conic is determined by the value of the eccentricity. In analytic geometry, a conic may be defined as a plane algebraic curv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Zeta-function
In number theory, the local zeta function (sometimes called the congruent zeta function or the Hasse–Weil zeta function) is defined as :Z(V, s) = \exp\left(\sum_^\infty \frac (q^)^m\right) where is a non-singular -dimensional projective algebraic variety over the field with elements and is the number of points of defined over the finite field extension of . Making the variable transformation gives : \mathit (V,u) = \exp \left( \sum_^ N_m \frac \right) as the formal power series in the variable u. Equivalently, the local zeta function is sometimes defined as follows: : (1)\ \ \mathit (V,0) = 1 \, : (2)\ \ \frac \log \mathit (V,u) = \sum_^ N_m u^\ . In other words, the local zeta function with coefficients in the finite field is defined as a function whose logarithmic derivative generates the number of solutions of the equation defining in the degree extension Formulation Given a finite field ''F'', there is, up to isomorphism, only one field ''Fk'' wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |