|
Chain Rule
In calculus, the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the Function composition, composition of two differentiable functions and in terms of the derivatives of and . More precisely, if h=f\circ g is the function such that h(x)=f(g(x)) for every , then the chain rule is, in Lagrange's notation, h'(x) = f'(g(x)) g'(x). or, equivalently, h'=(f\circ g)'=(f'\circ g)\cdot g'. The chain rule may also be expressed in Leibniz's notation. If a variable depends on the variable , which itself depends on the variable (that is, and are dependent variables), then depends on as well, via the intermediate variable . In this case, the chain rule is expressed as \frac = \frac \cdot \frac, and \left.\frac\_ = \left.\frac\_ \cdot \left. \frac\_ , for indicating at which points the derivatives have to be evaluated. In integral, integration, the counterpart to the chain rule is the substitution rule. Intuitive explanation Intuitively, the chain rule states that knowing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations. Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", it has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus. The former concerns instantaneous Rate of change (mathematics), rates of change, and the slopes of curves, while the latter concerns accumulation of quantities, and areas under or between curves. These two branches are related to each other by the fundamental theorem of calculus. They make use of the fundamental notions of convergence (mathematics), convergence of infinite sequences and Series (mathematics), infinite series to a well-defined limit (mathematics), limit. It is the "mathematical backbone" for dealing with problems where variables change with time or another reference variable. Infinitesimal calculus was formulated separately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chain Rule En
A chain is a serial assembly of connected pieces, called links, typically made of metal, with an overall character similar to that of a rope in that it is flexible and curved in compression but linear, rigid, and load-bearing in tension. A chain may consist of two or more links. Chains can be classified by their design, which can be dictated by their use: * Those designed for lifting, such as when used with a hoist; for pulling; or for securing, such as with a bicycle lock, have links that are torus-shaped, which make the chain flexible in two dimensions (the fixed third dimension being a chain's length). Small chains serving as jewellery are a mostly decorative analogue of such types. * Those designed for transferring power in machines have links designed to mesh with the teeth of the sprockets of the machine, and are flexible in only one dimension. They are known as roller chains, though there are also non-roller chains such as block chains. Two distinct chains can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Constantin Carathéodory
Constantin Carathéodory (; 13 September 1873 – 2 February 1950) was a Greeks, Greek mathematician who spent most of his professional career in Germany. He made significant contributions to real and complex analysis, the calculus of variations, and measure theory. He also created an axiomatic formulation of thermodynamics. Carathéodory is considered one of the greatest mathematicians of his era and the most renowned Greek mathematics, Greek mathematician since Ancient history, antiquity. Origins Constantin Carathéodory was born in 1873 in Berlin to Greeks, Greek parents and grew up in Brussels. His father , a lawyer, served as the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman ambassador to Belgium, St. Petersburg and Berlin. His mother, Despina, née Petrokokkinos, was from the island of Chios. The Carathéodory family, originally from Bosna, Edirne, Bosna, was well established and respected in Istanbul, Constantinople, and its members held many important governmental positions. His grandfather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Division By Zero
In mathematics, division by zero, division (mathematics), division where the divisor (denominator) is 0, zero, is a unique and problematic special case. Using fraction notation, the general example can be written as \tfrac a0, where a is the dividend (numerator). The usual definition of the quotient in elementary arithmetic is the number which yields the dividend when multiplication, multiplied by the divisor. That is, c = \tfrac ab is equivalent to c \cdot b = a. By this definition, the quotient q = \tfrac is nonsensical, as the product q \cdot 0 is always 0 rather than some other number a. Following the ordinary rules of elementary algebra while allowing division by zero can create a mathematical fallacy, a subtle mistake leading to absurd results. To prevent this, the arithmetic of real numbers and more general numerical structures called field (mathematics), fields leaves division by zero undefined (mathematics), undefined, and situations where division by zero might occur m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continuous Function
In mathematics, a continuous function is a function such that a small variation of the argument induces a small variation of the value of the function. This implies there are no abrupt changes in value, known as '' discontinuities''. More precisely, a function is continuous if arbitrarily small changes in its value can be assured by restricting to sufficiently small changes of its argument. A discontinuous function is a function that is . Until the 19th century, mathematicians largely relied on intuitive notions of continuity and considered only continuous functions. The epsilon–delta definition of a limit was introduced to formalize the definition of continuity. Continuity is one of the core concepts of calculus and mathematical analysis, where arguments and values of functions are real and complex numbers. The concept has been generalized to functions between metric spaces and between topological spaces. The latter are the most general continuous functions, and their d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Difference Quotient
In single-variable calculus, the difference quotient is usually the name for the expression : \frac which when taken to the Limit of a function, limit as ''h'' approaches 0 gives the derivative of the Function (mathematics), function ''f''. The name of the expression stems from the fact that it is the quotient of the Difference (mathematics), difference of values of the function by the difference of the corresponding values of its argument (the latter is (''x'' + ''h'') - ''x'' = ''h'' in this case). The difference quotient is a measure of the average rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of the function over an Interval (mathematics), interval (in this case, an interval of length ''h''). The limit of the difference quotient (i.e., the derivative) is thus the instantaneous rate of change. By a slight change in notation (and viewpoint), for an interval [''a'', ''b''], the difference quotient : \frac is called the mean (or average) value of the derivative of ''f'' over th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limit Of A Function
Although the function is not defined at zero, as becomes closer and closer to zero, becomes arbitrarily close to 1. In other words, the limit of as approaches zero, equals 1. In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input which may or may not be in the domain of the function. Formal definitions, first devised in the early 19th century, are given below. Informally, a function assigns an output to every input . We say that the function has a limit at an input , if gets closer and closer to as moves closer and closer to . More specifically, the output value can be made ''arbitrarily'' close to if the input to is taken ''sufficiently'' close to . On the other hand, if some inputs very close to are taken to outputs that stay a fixed distance apart, then we say the limit ''does not exist''. The notion of a limit has many applications in modern calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Faà Di Bruno's Formula
Faà di Bruno's formula is an identity in mathematics generalizing the chain rule to higher derivatives. It is named after , although he was not the first to state or prove the formula. In 1800, more than 50 years before Faà di Bruno, the French mathematician Louis François Antoine Arbogast had stated the formula in a calculus textbook, which is considered to be the first published reference on the subject. Perhaps the most well-known form of Faà di Bruno's formula says that f(g(x))=\sum \frac\cdot f^(g(x))\cdot \prod_^n\left(g^(x)\right)^, where the sum is over all n-tuples of nonnegative integers (m_1,\ldots,m_n) satisfying the constraint 1\cdot m_1+2\cdot m_2+3\cdot m_3+\cdots+n\cdot m_n=n. Sometimes, to give it a memorable pattern, it is written in a way in which the coefficients that have the combinatorial interpretation discussed below are less explicit: : f(g(x)) =\sum \frac\cdot f^(g(x))\cdot \prod_^n\left(\frac\right)^. Combining the terms with the same value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of research in computer science that develops and studies methods and software that enable machines to machine perception, perceive their environment and use machine learning, learning and intelligence to take actions that maximize their chances of achieving defined goals. High-profile applications of AI include advanced web search engines (e.g., Google Search); recommendation systems (used by YouTube, Amazon (company), Amazon, and Netflix); virtual assistants (e.g., Google Assistant, Siri, and Amazon Alexa, Alexa); autonomous vehicles (e.g., Waymo); Generative artificial intelligence, generative and Computational creativity, creative tools (e.g., ChatGPT and AI art); and Superintelligence, superhuman play and analysis in strategy games (e.g., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
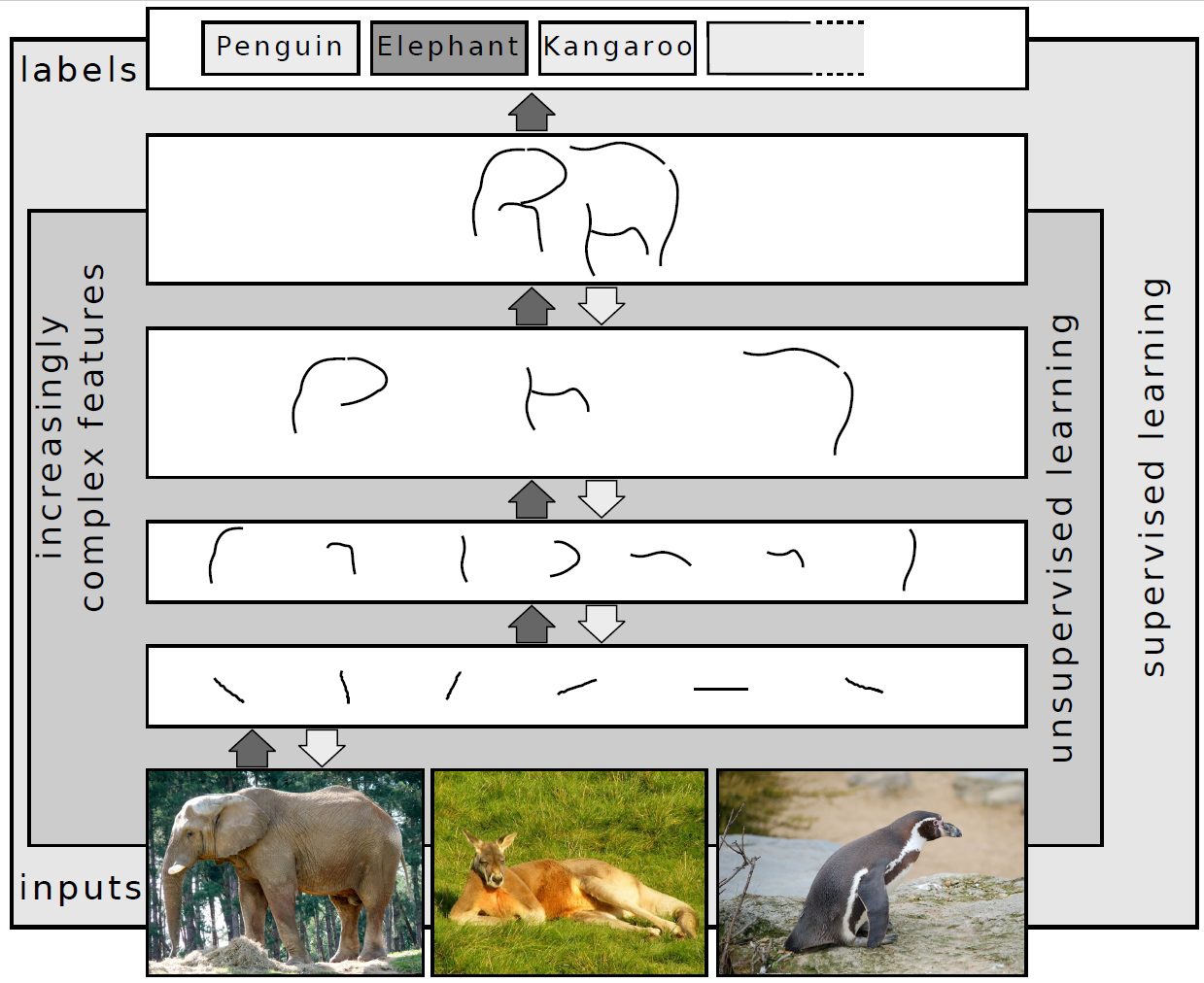
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neural Network (machine Learning)
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called ''artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the ''activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, neuron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gradient Descent
Gradient descent is a method for unconstrained mathematical optimization. It is a first-order iterative algorithm for minimizing a differentiable multivariate function. The idea is to take repeated steps in the opposite direction of the gradient (or approximate gradient) of the function at the current point, because this is the direction of steepest descent. Conversely, stepping in the direction of the gradient will lead to a trajectory that maximizes that function; the procedure is then known as ''gradient ascent''. It is particularly useful in machine learning for minimizing the cost or loss function. Gradient descent should not be confused with local search algorithms, although both are iterative methods for optimization. Gradient descent is generally attributed to Augustin-Louis Cauchy, who first suggested it in 1847. Jacques Hadamard independently proposed a similar method in 1907. Its convergence properties for non-linear optimization problems were first studied by Has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |