|
Western Digital
Western Digital Corporation is an American data storage company headquartered in San Jose, California. Established in 1970, the company is one of the world's largest manufacturers of hard disk drives (HDDs). History 1970s Western Digital was founded on April 23, 1970, by Alvin B. Phillips, a Motorola employee, as General Digital Corporation, initially a manufacturer of MOS test equipment. It was originally based in Newport Beach, California, shortly thereafter moving to Santa Ana, California, and would go on to become one of the largest technology firms headquartered in Orange County. It rapidly became a specialty semiconductor maker, with start-up capital provided by several individual investors and industrial giant Emerson Electric. Around July 1971, it adopted its current name and soon introduced its first product, the ''WD1402A'' UART. During the early 1970s, the company focused on making and selling calculator chips, and by 1975, Western Digital was the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MCP-1600
The MCP-1600 is a multi-chip 16-bit microprocessor introduced by Western Digital in 1975 and produced through the early 1980s. Used in the Pascal MicroEngine, the WD16 processor in the Alpha Microsystems AM-100, and the DEC LSI-11 microcomputer, a cost-reduced and compact implementation of the DEC PDP-11. Description There are three types of chips in the chip-set: * CP1611 RALU - Register ALU chip * CP1621 CON - Control chip * CP1631 MICROM - Mask-programmed microcode ROM chip (512 – 22 bit words) The chips use a 3.3MHz four phase clock and three power supply voltages (+5V, +12V, and -5V), as required by the N-channel silicon gate process then available at Western Digital. Internally the MCP-1600 is a (relatively fast) 8-bit processor that can be micro-programmed to emulate a 16-bit CPU. All byte operations execute in one clock period; word operations and branches take two clocks. Up to four MICROMs are supported, but usually two or three could hold the neede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Teresa, San Jose
Santa Teresa is a :Neighborhoods in San Jose, California, neighborhood of San Jose, California, United States, located in South San Jose. Founded in 1834, Santa Teresa was originally established as Rancho Santa Teresa by the Bernal family, a prominent Californio clan. Today, Santa Teresa is largely a residential area, but also home to numerous Silicon Valley tech campuses. Santa Teresa is the southernmost urban district of San Jose, bordering the largely protected Coyote Valley, California, Coyote Valley to its south. It is bound by the Santa Teresa Hills to its south and the Bayshore Freeway (101) to its east. History Santa Teresa was founded in 1834 as Rancho Santa Teresa, a ranchos of California, rancho grant given by Governor José Figueroa to Don José Joaquín Bernal, a retired soldier who came to Alta California as part of the De Anza Expedition in 1776. Prior to receiving the rancho grant, José Joaquín Bernal had already settled in the area since 1826. Bernal named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
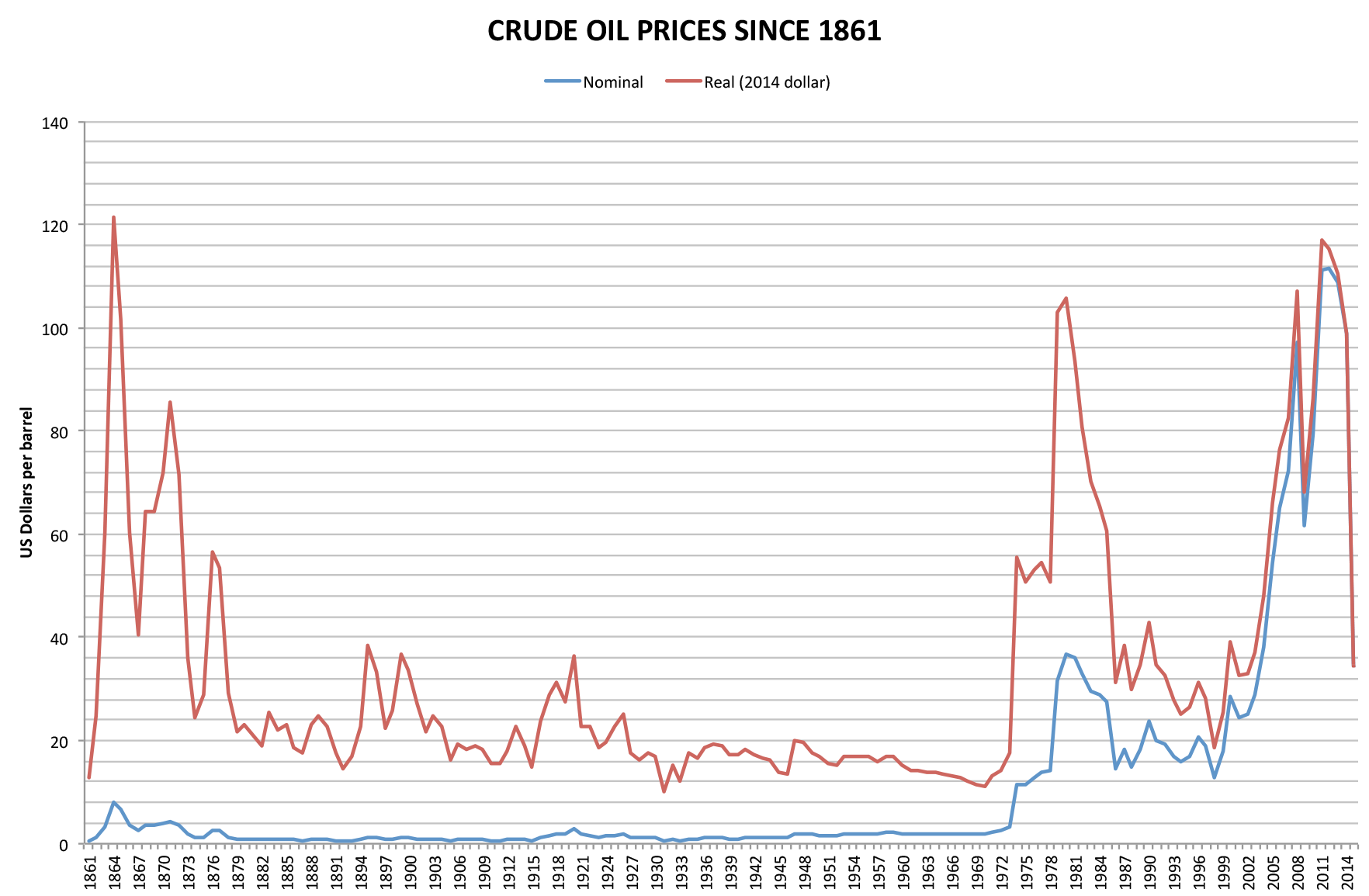
1973 Oil Crisis
In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against countries that had supported Israel at any point during the 1973 Yom Kippur War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the 1967 Six-Day War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Estado Novo (Portugal), Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US to nearly US globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE), is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, optical disc drives, and tape drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface ( ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended ID ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
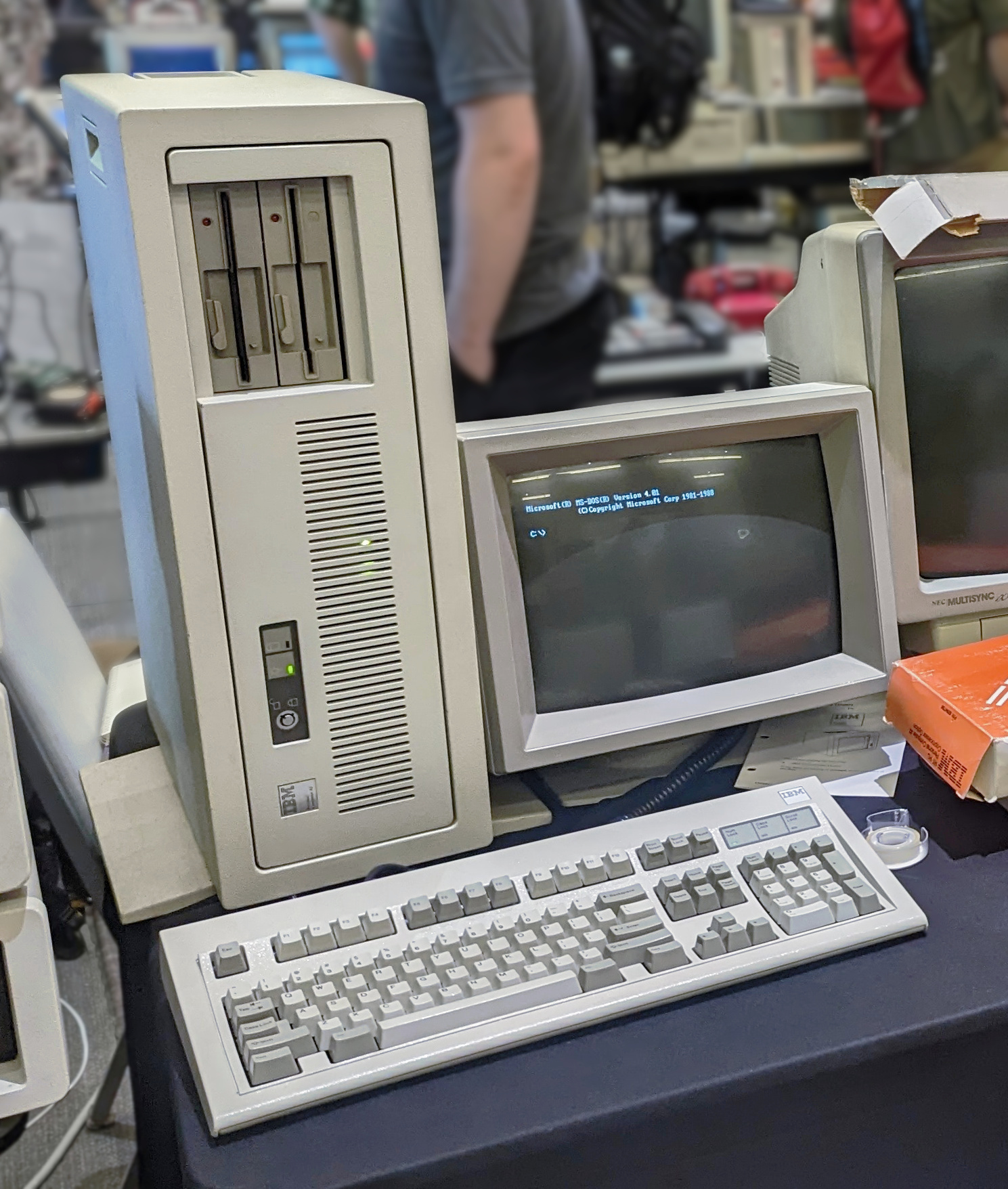
IBM Personal Computer/AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 80286 microprocessor. Name IBM did not specify an expanded form of ''AT'' on the machine, press releases, brochures or documentation, but some sources expand the term as ''Advanced Technology'', including at least one internal IBM document. History IBM's 1984 introduction of the AT was seen as an unusual move for the company, which typically waited for competitors to release new products before producing its own models. At $4,000–6,000, it was only slightly more expensive than considerably slower IBM models. The announcement surprised rival executives, who admitted that matching IBM's prices would be difficult. No major competitor showed a comparable computer at COMDEX Las Vegas that year. Features The AT is IBM PC compatible, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with disk read-and-write head, magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual Block (data storage), blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small disk enclosure, rectangular box. Hard disk drives were introduced by IBM in 1956, and were the dominant secondary storage device for History of general-purpose CPUs, general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Digital FD1771
The FD1771, sometimes WD1771, is a floppy disk controller chip, the first in a line of floppy disk controllers produced by Western Digital. It uses single density FM encoding introduced in the IBM 3740. Later models in the series added support for MFM encoding and increasingly added onboard circuitry that formerly had to be implemented in external components. Originally packaged as 40-pin dual in-line package (DIP) format,"The FD1771 is a single-chip floppy disk formatter/controller that interfaces with most available disk drives and virtually all types of computers." The FD1771 was announced on July 19, 1976, and sold for $60 each in lots of 100. later models moved to a 28-pin format that further lowered implementation costs. Derivatives The FD1771 was succeeded by many derivatives that were mostly software-compatible: *The FD1781 was designed for double density, but required external modulation and demodulation circuitry, so it could support MFM, M2FM, GCR or other doubl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UCSD Pascal
UCSD Pascal is a Pascal programming language system that runs on the UCSD p-System, a portable, highly machine-independent operating system. UCSD Pascal was first released in 1977. It was developed at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD). The p-System In 1977, the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) Institute for Information Systems developed UCSD Pascal to provide students with a common environment that could run on any of the then available microcomputers as well as campus DEC PDP-11 minicomputers. The operating system became known as UCSD p-System. There were three operating systems that IBM offered for its original IBM PC. The first was UCSD p-System, with IBM PC DOS and CP/M-86 as the other two. Vendor SofTech Microsystems emphasized p-System's application portability, with virtual machines for 20 CPUs as of the IBM PC's release. It predicted that users would be able to use applications they purchased on future computers running p-System; advertisem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal MicroEngine
Pascal MicroEngine is a series of microcomputer products manufactured by Western Digital from 1979 through the mid-1980s, designed specifically to run the UCSD p-System efficiently. Compared to other microcomputers, which use a machine language p-code interpreter, the Pascal MicroEngine has its interpreter implemented in microcode; p-code is its machine language. The most common programming language used on the p-System is Pascal. The MicroEngine runs a special release III p-System. The enhancements of release III were incorporated into release IV which was made publicly available for other platforms but not for the MicroEngine. Products The MicroEngine series of products was offered at various levels of integration: * WD-9000 five chip microprocessor chip set * WD-900 single board computer * WD-90 packaged system * SB-1600 MicroEngine single board computer * ME-1600 Modular MicroEngine packaged system The MicroEngine chipset was based on the MCP-1600 chipset, which formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Digital WD16
The WD16 is a 16-bit microprocessor introduced by Western Digital in October 1976. It is based on the MCP-1600 chipset, a general-purpose design that was also used to implement the DEC LSI-11 low-end minicomputer and the Pascal MicroEngine processor. The three systems differed primarily in their microcode, giving each system a unique instruction set architecture (ISA). The WD16 implements an extension of the PDP-11 instruction set architecture but is not machine code compatible with the PDP-11. The instruction set and microcoding were created by Dick Wilcox and Rich Notari. The WD16 is an example of orthogonal CISC architecture. Most two-operand instructions can operate memory-to-memory with any addressing mode and some instructions can result in up to ten memory accesses. The WD16 is implemented in five 40-pin DIP packages. Maximum clock speed is 3.3 MHz. Its interface to memory is via a 16-bit multiplexed data/address bus. The WD16 is best known for its use in Alph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDP-11
The PDP–11 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers originally sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) from 1970 into the late 1990s, one of a set of products in the Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series. In total, around 600,000 PDP-11s of all models were sold, making it one of DEC's most successful product lines. The PDP-11 is considered by some experts to be the most popular minicomputer. The PDP–11 included a number of innovative features in its instruction set and additional general-purpose registers that made it easier to program than earlier models in the PDP series. Further, the innovative Unibus system allowed external devices to be more easily interfaced to the system using direct memory access, opening the system to a wide variety of peripherals. The PDP–11 replaced the PDP–8 in many real-time computing applications, although both product lines lived in parallel for more than 10 years. The ease of programming of the PDP–11 made it popular for general-pur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until he was forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the early 1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the Programmed Data Processor, PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |