|
Tokat
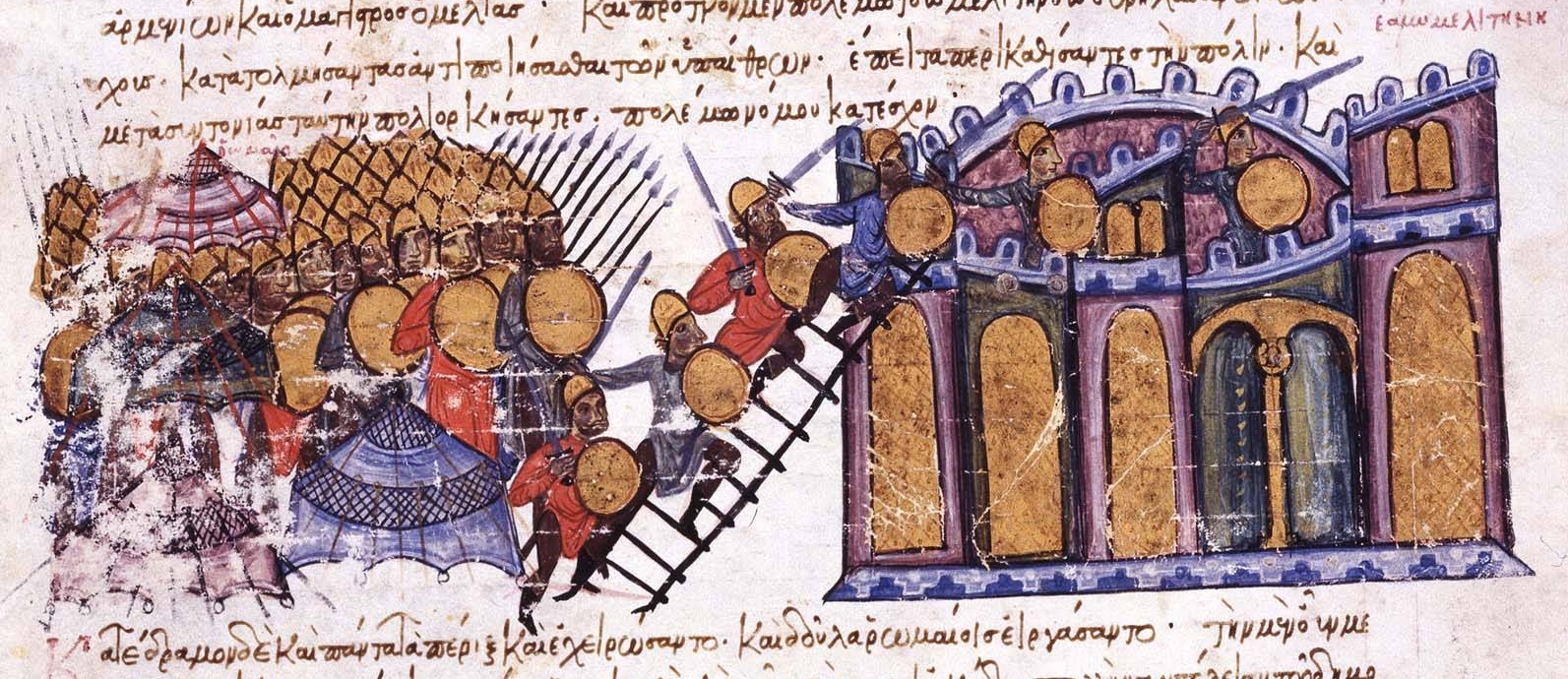
Tokat is a city of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is the seat of Tokat Province and Tokat District.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 22 May 2023. Its population is 163,405 (2022). It is located at the confluence of the Tokat River (Tokat Suyu) with the Yeşilırmak. History  The city was established in the Hittite era. During the time of King
The city was established in the Hittite era. During the time of King [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokat Müzesi Binasının Dış Görünümü
Tokat is a city of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is the seat of Tokat Province and Tokat District.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 22 May 2023. Its population is 163,405 (2022). It is located at the confluence of the Tokat River (Tokat Suyu) with the Yeşilırmak (river), Yeşilırmak. History  The city was established in the Hittites, Hittite era. During the time of King Mithradates VI of Pontus, it was one of his many strongholds in Asia Minor.
Known as Evdokia or Eudoxia, ecclesiastically it was later incorporated into the western part ...
The city was established in the Hittites, Hittite era. During the time of King Mithradates VI of Pontus, it was one of his many strongholds in Asia Minor.
Known as Evdokia or Eudoxia, ecclesiastically it was later incorporated into the western part ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokat Kale
Tokat is a city of Turkey in the mid-Black Sea region of Anatolia. It is the seat of Tokat Province and Tokat District.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 22 May 2023. Its population is 163,405 (2022). It is located at the confluence of the Tokat River (Tokat Suyu) with the Yeşilırmak. History  The city was established in the Hittite era. During the time of King
The city was established in the Hittite era. During the time of King [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokat Province
Tokat Province () is a province in northern Turkey. Its area is 10,042 km2, and its population is 596,454 (2022). Its adjacent provinces are Amasya to the northwest, Yozgat to the southwest, Sivas to the southeast, and Ordu to the northeast. Its capital is Tokat, which lies inland of the middle Black Sea region, 422 kilometers from Ankara. The governor is Numan Hatipoğlu, appointed in 2022. Tokat Valiliği. Retrieved 24 June 2024. Etymology Evliya Çelebi explained the name of the city as Tok-at in return for the satiety of horses because of its rich barley in Turkish etymology. The Ottoman historian İsmail Hakkı explained Uzunçarşılı as Toh-kat, which means "walled city", and Özhan Öztürk, in his work called Pontus, used the word "Dahyu", which means "country, chastity" in Avesta and wa ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokat District
Tokat District (also: ''Merkez'', meaning "central" in Turkish) is a district of the Tokat Province of Turkey. Its seat is the city of Tokat.İl Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 22 May 2023. Its area is 2,003 km2, and its population is 206,621 (2022). Composition There are five in Tokat District: * Çamlıbel * *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume De Jerphanion
Guillaume de Jerphanion, born at Pontevès in 1877, died in Rome on 22 October 1948, was a French Jesuit, archaeologist and explorer of Cappadocia. Biography Source: Guillaume de Jerphanion was born on 3 March 1877, the third in a family of eight children. He came from a family of old nobility originating from Haute-Loire in France. Rather than a career as a naval officer, he chose to join the Jesuits when he was 16 years of age. In 1903 Guillaume was sent to Tokat in Turkey to teach science to Armenian children in one of the numerous schools founded by the Jesuits in Anatolia. He remained in Tokat until 1907. During his time in Tokat he learned Turkish, a language he came to master perfectly. Before returning to France to study theology and be ordained a priest, he traveled through Anatolia (Amasya - Ankara - Samsun - Sivas...) and discovered Cappadocia. ''About the Jesuit schools of Anatolia'' ''Between 1881 and 1924, the Jesuits opened 11 free and mixed schools as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eretnids
The Eretnids () were a dynasty that ruled a state spanning central and eastern Anatolia from 1335 to 1381. The dynasty's founder, Eretna, was an Ilkhanid officer of Uyghur origin, under Timurtash, who was appointed as the governor of Anatolia. Some time after the latter's downfall, Eretna became the governor under the suzerainty of the Jalayirid ruler Hasan Buzurg. After an unexpected victory at the Battle of Karanbük, against Mongol warlords competing to restore the Ilkhanate, Eretna claimed independence declaring himself the sultan of his domains. His reign was largely prosperous earning him the nickname (). Eretna's son Ghiyath al-Din Muhammad I, although initially preferred over his older brother Jafar, struggled to maintain his authority over the state and was quickly deposed by Jafar. Shortly after, he managed to restore his throne, although he could not prevent some portion of his territories from getting annexed by local Turkoman lords, the Dulkadirids to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeşilırmak (river)
The Yeşilırmak (, ), known as the Iris in antiquity (), is a river in northern Turkey. From its source northeast of Sivas, it flows past Tokat and Amasya, crosses the Pontic Mountains and the Çarşamba Plain, reaching the Black Sea east of Samsun after . Its tributaries include the Çekerek (ancient Scylax) and the Kelkit (ancient Lycus). It was mentioned by Menippus of Pergamon in the 1st century BC. Strabo's ''Geographica The ''Geographica'' (, ''Geōgraphiká''; or , "Strabo's 17 Books on Geographical Topics") or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Greek in the late 1st century BC, or early 1st cen ...'' describes it as flowing through Comana Pontica, the plain of Dazimonitis (Kaşova) (), and Gaziura (probably modern Turhal) before receiving the waters () of the Scylax, then flowing through Amaseia (Amasya) before reaching the valley of Phanaroea. Starting with Dionysius Periegetes, in hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danishmend Gazi
Danishmend Gazi (), Danishmend Taylu, or Dānishmend Aḥmed Gāzī (died 1085), was the Turkoman general of the Seljuks and later founder of the beylik of Danishmends. After the Turkic advance into Anatolia that followed the Battle of Manzikert, his dynasty controlled the north-central regions in Anatolia. Life The defeat of the Byzantine army at the Battle of Manzikert and the subsequent civil war allowed the Turks, including forces loyal to Danishmend Gazi, to occupy nearly all of Anatolia. Danishmend Gazi and his forces took as their lands central Anatolia, conquering the cities of Neocaesarea, Tokat, Sivas, and Euchaita from the Byzantine Empire. According to Michael the Syrian, he ruled Cappadocia in 1085, and most likely died the same year. However, Amin Maalouf claims in '' The Crusades Through Arab Eyes'' that Danishmend Gazi answered the call of Kilij Arslan to defend Asia Minor from incursions by Christian forces during the First Crusade in 1097. He was succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Kourkouas
John Kourkouas (, ), also transliterated as Kurkuas or Curcuas, was one of the most important generals of the Byzantine Empire. His success in battles against the Muslim states in the East reversed the course of the centuries-long Arab–Byzantine wars and set the stage for Byzantium's eastern conquests later in the century. Kourkouas belonged to a family of Armenian descent that produced several notable Byzantine generals. As commander of an imperial bodyguard regiment, Kourkouas was among the chief supporters of Emperor Romanos I Lekapenos () and facilitated the latter's rise to the throne. In 923, Kourkouas was appointed commander-in-chief of the Byzantine armies along the eastern frontier, facing the Abbasid Caliphate and the semi-autonomous Arab Muslim border emirates. He kept this post for more than twenty years, overseeing decisive Byzantine military successes that altered the strategic balance in the region. During the 9th century, Byzantium had gradually recovered its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilij Arslan II
Kilij Arslan II () or ʿIzz ad-Dīn Kilij Arslān ibn Masʿūd () ( Modern Turkish ''Kılıç Arslan'', meaning "Sword Lion") was a Seljuk Sultan of Rûm from 1156 until his death in 1192. Reign In 1159, Kilij Arslan attacked Byzantine emperor Manuel I Comnenus as he marched past Iconium (Konya, capital of Rüm), as Manuel returned from negotiating with Nur ad-Din Zengi in Syria. In 1161, Manuel's nephew John Contostephanus defeated Kilij Arslan, and the sultan travelled to Constantinople in a show of submission. As Arnold of Lübeck reports in his '' Chronica Slavorum'', he was present at the meeting of Henry the Lion with Kilij-Arslan during the former's pilgrimage to Jerusalem in 1172. When they met near Tarsus, the sultan embraced and kissed the German duke, reminding him that they were blood cousins ('amplexans et deosculans eum, dicens, eum consanguineum suum esse'). When the duke asked for details of this relationship, Kilij Arslan informed him that 'a noble lady from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean Sea to the west, the Turkish Straits to the northwest, and the Black Sea to the north. The eastern and southeastern limits have been expanded either to the entirety of Asiatic Turkey or to an imprecise line from the Black Sea to the Gulf of Alexandretta. Topographically, the Sea of Marmara connects the Black Sea with the Aegean Sea through the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, and separates Anatolia from Thrace in Southeast Europe. During the Neolithic, Anatolia was an early centre for the development of farming after it originated in the adjacent Fertile Crescent. Beginning around 9,000 years ago, there was a major migration of Anatolian Neolithic Farmers into Neolithic Europe, Europe, with their descendants coming to dominate the continent a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |