|
The Holocaust In France
The Holocaust in France was the persecution, deportation, and annihilation of Jews between 1940 and 1944 in occupied France, metropolitan Vichy France, and in Vichy-controlled French North Africa, during World War II. The persecution began in 1940, and culminated in deportations of Jews from France to Nazi concentration camps in Nazi Germany and Nazi-occupied Poland. The deportation started in 1942 and lasted until July 1944. In 1940, 340,000 Jews, about one half French citizens and one-half refugees from Nazi Germany, were living in continental France. More than 75,000 Jews, mostly foreign Jews, were deported to death camps, where about 72,500 were killed. Antisemitism was prevalent throughout Europe at the time. As in other German-occupied and aligned states, the Nazis in France relied to a considerable extent on the co-operation of local authorities to carry out what they called the Final Solution. The government of Vichy France and the French police organized and implemente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 101I-027-1477-07, Marseille, Gare D'Arenc
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior (Germany), Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest docum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moselle
The Moselle ( , ; ; ) is a river that rises in the Vosges mountains and flows through north-eastern France and Luxembourg to western Germany. It is a bank (geography), left bank tributary of the Rhine, which it joins at Koblenz. A small part of Belgium is in its drainage basin, basin as it includes the Sauer and the Our River, Our. Its lower course "twists and turns its way between Trier and Koblenz along one of Germany's most beautiful river valleys."''Moselle: Holidays in one of Germany's most beautiful river valleys'' at www.romantic-germany.info. Retrieved 23 Jan 2016. In this section the land to the north is the Eifel which stretches into Belgium; to the south lies the Hunsrück. The river flows through a region that was cultivated by the Romans. Today, its hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphaël Alibert
Henri Albert François Joseph Raphaël Alibert (; 17 February 1887 – 5 June 1963) was a French politician known for his association with the collaborationist regime of Vichy France during World War II. A royalist, traditionalist, and member of '' Action Française'', Alibert was one of the chief ideologues of the constitutional law that transformed the French Third Republic into an authoritarian state under the rule of Marshal Philippe Pétain. Politics Raphael Alibert was an ardent Roman Catholic convert and someone with strong royalist ideas. One of the most intense followers of Charles Maurras, Alibert was elected to the Chamber of Deputies for the Action Française party. In October 1939 he and Henry Lémery had visited Maréchal Petain to discuss in private the make-up of a possible ministry with him. Enters government In the French government's new Cabinet formed on 16 June 1940 he was appointed Under- Secretary of State to the Prime Minister, now Pétain. He was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law On The Status Of Jews
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the art of justice. State-enforced laws can be made by a legislature, resulting in statutes; by the executive through decrees and regulations; or by judges' decisions, which form precedent in common law jurisdictions. An autocrat may exercise those functions within their realm. The creation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history and society in various ways and also serves as a mediator of relations between people. Legal systems vary between jurisdictions, with their differences analysed in comparative law. In civil law jurisdictions, a legislature or other central body codifies and consolidates the law. In common law systems, judge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vichy Anti-Jewish Legislation
Anti-Jewish laws were enacted by the Vichy France government in 1940 and 1941 affecting metropolitan France and its overseas territories during World War II. These laws were, in fact, decrees of head of state Marshal Philippe Pétain, since Parliament was no longer in office as of 11 July 1940. The motivation for the legislation was spontaneous and was not mandated by Germany. These laws were declared null and void on 9 August 1944 after liberation and on the restoration of republican legality. The statutes were aimed at depriving Jews of the right to hold public office, designating them as a lower class, and depriving them of citizenship. Many Jews were subsequently rounded up at Drancy internment camp before being deported for extermination in Nazi concentration camps. History The denaturalization law was enacted on 16 July 1940, barely a month after the announcement of the Vichy regime of Petain. On 22 July 1940, the Deputy Secretary of State Raphaël Alibert created a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expropriation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization contrasts with privatization and with demutualization. When previously nationalized assets are privatized and subsequently returned to public ownership at a later stage, they are said to have undergone renationalization (or deprivatization). Industries often subject to nationalization include telecommunications, electric power, fossil fuels, railways, airlines, iron ore, media, postal services, banks, and water (sometimes called the commanding heights of the economy), and in many jurisdictions such entities have no history of private ownership. Nationalization may occur with or without financial compensation to the former owners. Nationalization is distinguished from property redistribution in that the government retains control of nationalized prope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Abetz
Otto Friedrich Abetz (26 March 1903 – 5 May 1958) was a German diplomat, a Nazi official and a convicted war criminal during World War II. Abetz joined the Nazi Party and the SA in the early 1930s later becoming a member of the SS. Abetz played a significant role in strengthening ties between Nazi Germany and Vichy France during World War II. In 1940, after the German occupation of France, he was appointed German ambassador to France. Abetz played a significant role in strengthening ties between Nazi Germany and the collaborationist Vichy government. Abetz played a significant role in facilitating the persecution and deportation of Jews by the Nazi regime from France during the Holocaust. After Germany's defeat in 1945, Abetz was captured and later stood trial at the Nuremberg Trials. He was found guilty of war crimes and crimes against humanity, and was sentenced to 20 years in prison. He was released in 1954 for health reasons and died in a car crash in 1958. Early years A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juif
Juif may refer to: *Jews *Juif, Saône-et-Loire, a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne in eastern France *Île aux Juifs (), Seine River, Paris, France; a former island that was landfilled in and became part of Île de la Cité with the construction of Pont Neuf * Jamiat Ulema-e-Islam (F) or JUIF, a political party in Pakistan See also * * Juive (other), Juive (other) () * Jew (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Bild 183-N0619-506, Paris, Jüdische Frauen Mit Stern
The German Federal Archives or Bundesarchiv (BArch) (, lit. "Federal Archive") are the national archives of Germany. They were established at the current location in Koblenz in 1952. They are subordinated to the Federal Commissioner for Culture and the Media (Claudia Roth since 2021) under the German Chancellery, and before 1998, to the Federal Ministry of the Interior. On 6 December 2008, the Archives donated 100,000 photos to the public, by making them accessible via Wikimedia Commons. History The federal archive for institutions and authorities in Germany, the first precursor to the present-day Federal Archives, was established in Potsdam, Brandenburg in 1919, a later date than in other European countries. This national archive documented German government dating from the founding of the North German Confederation in 1867. It also included material from the older German Confederation and the Imperial Chamber Court. The oldest documents in this collection dated back to the y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Algeria
French Algeria ( until 1839, then afterwards; unofficially ; ), also known as Colonial Algeria, was the period of History of Algeria, Algerian history when the country was a colony and later an integral part of France. French rule lasted until the end of the Algerian War which resulted in Algeria's Independence Day (Algeria), gaining independence on 5 July 1962. The French conquest of Algeria began in 1830 with the Invasion of Algiers (1830), invasion of Algiers which toppled the Regency of Algiers, though Algeria was not fully conquered and Pacification of Algeria, pacified until 1903. It is estimated that by 1875, approximately 825,000 indigenous Algerians were killed. Various scholars describe the French conquest as genocide. Algeria was ruled as a French colony, colony from 1830 to 1848, and then as multiple Departments of France#Departments of Algeria (Départements d'Algérie), departments, an integral part of France, with the implementing of the French Constitution of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
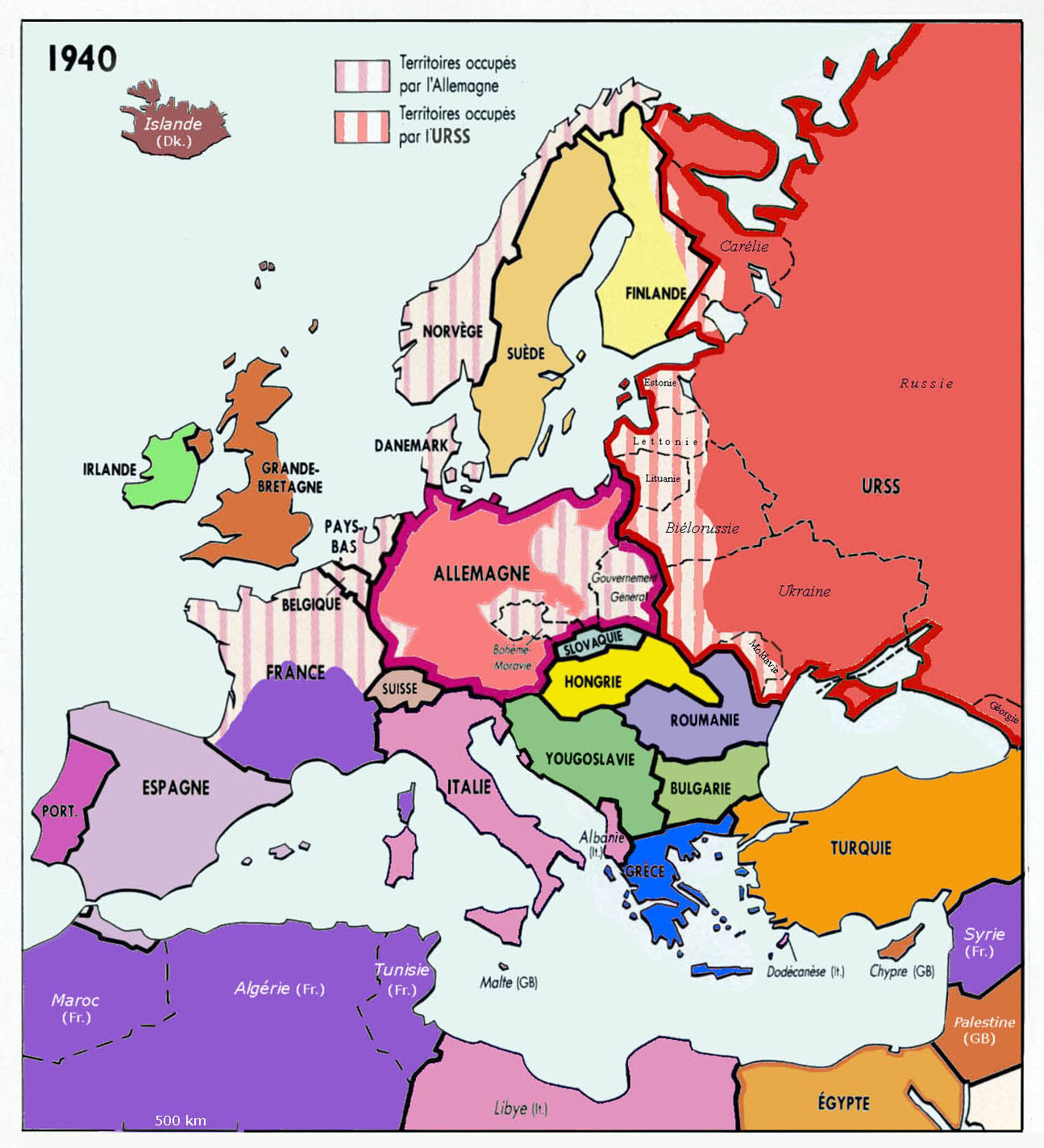
French State
Vichy France (; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was a French rump state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II, established as a result of the French capitulation after the defeat against Germany. It was named after its seat of government, the city of Vichy. Officially independent, but with half of its territory occupied under the harsh terms of the 1940 armistice with Nazi Germany, it adopted a policy of collaboration. Though Paris was nominally its capital, the government established itself in Vichy in the unoccupied "free zone" (). The occupation of France by Germany at first affected only the northern and western portions of the country. In November 1942, the Allies occupied French North Africa, and in response the Germans and Italians occupied the entirety of Metropolitan France, ending any pretence of independence by the Vichy government. On 10 May 1940, France was invaded by Nazi Germany. Paul Reynaud resign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |